Chenpeng Du
Towards Reliable Large Audio Language Model
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large audio language models (LALMs) have demonstrated impressive results and promising prospects in universal understanding and reasoning across speech, music, and general sound. However, these models still lack the ability to recognize their knowledge boundaries and refuse to answer questions they don't know proactively. While there have been successful attempts to enhance the reliability of LLMs, reliable LALMs remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we systematically investigate various approaches towards reliable LALMs, including training-free methods such as multi-modal chain-of-thought (MCoT), and training-based methods such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Besides, we identify the limitations of previous evaluation metrics and propose a new metric, the Reliability Gain Index (RGI), to assess the effectiveness of different reliable methods. Our findings suggest that both training-free and training-based methods enhance the reliability of LALMs to different extents. Moreover, we find that awareness of reliability is a "meta ability", which can be transferred across different audio modalities, although significant structural and content differences exist among sound, music, and speech.
Recent Advances in Discrete Speech Tokens: A Review
Feb 10, 2025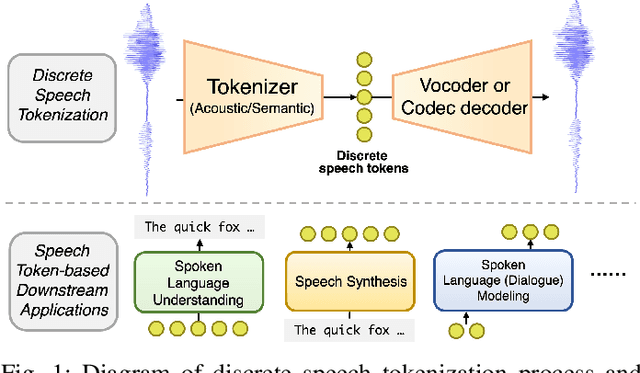
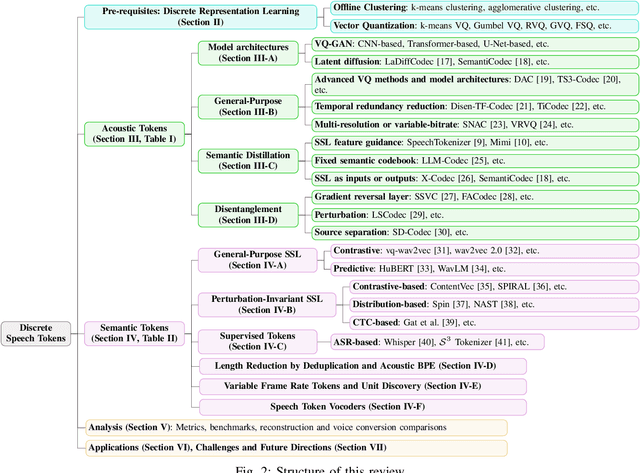
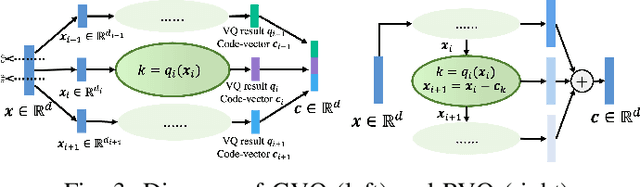
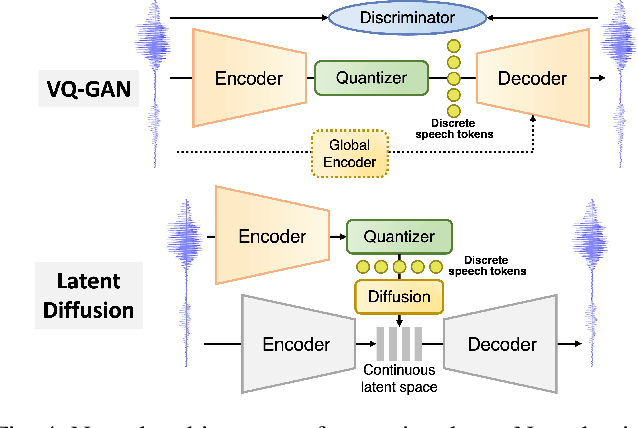
Abstract:The rapid advancement of speech generation technologies in the era of large language models (LLMs) has established discrete speech tokens as a foundational paradigm for speech representation. These tokens, characterized by their discrete, compact, and concise nature, are not only advantageous for efficient transmission and storage, but also inherently compatible with the language modeling framework, enabling seamless integration of speech into text-dominated LLM architectures. Current research categorizes discrete speech tokens into two principal classes: acoustic tokens and semantic tokens, each of which has evolved into a rich research domain characterized by unique design philosophies and methodological approaches. This survey systematically synthesizes the existing taxonomy and recent innovations in discrete speech tokenization, conducts a critical examination of the strengths and limitations of each paradigm, and presents systematic experimental comparisons across token types. Furthermore, we identify persistent challenges in the field and propose potential research directions, aiming to offer actionable insights to inspire future advancements in the development and application of discrete speech tokens.
DiTAR: Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling for Speech Generation
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Several recent studies have attempted to autoregressively generate continuous speech representations without discrete speech tokens by combining diffusion and autoregressive models, yet they often face challenges with excessive computational loads or suboptimal outcomes. In this work, we propose Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling (DiTAR), a patch-based autoregressive framework combining a language model with a diffusion transformer. This approach significantly enhances the efficacy of autoregressive models for continuous tokens and reduces computational demands. DiTAR utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy for patch generation, where the language model processes aggregated patch embeddings and the diffusion transformer subsequently generates the next patch based on the output of the language model. For inference, we propose defining temperature as the time point of introducing noise during the reverse diffusion ODE to balance diversity and determinism. We also show in the extensive scaling analysis that DiTAR has superb scalability. In zero-shot speech generation, DiTAR achieves state-of-the-art performance in robustness, speaker similarity, and naturalness.
Why Do Speech Language Models Fail to Generate Semantically Coherent Outputs? A Modality Evolving Perspective
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:Although text-based large language models exhibit human-level writing ability and remarkable intelligence, speech language models (SLMs) still struggle to generate semantically coherent outputs. There are several potential reasons for this performance degradation: (A) speech tokens mainly provide phonetic information rather than semantic information, (B) the length of speech sequences is much longer than that of text sequences, and (C) paralinguistic information, such as prosody, introduces additional complexity and variability. In this paper, we explore the influence of three key factors separately by transiting the modality from text to speech in an evolving manner. Our findings reveal that the impact of the three factors varies. Factor A has a relatively minor impact, factor B influences syntactical and semantic modeling more obviously, and factor C exerts the most significant impact, particularly in the basic lexical modeling. Based on these findings, we provide insights into the unique challenges of training SLMs and highlight pathways to develop more effective end-to-end SLMs.
LSCodec: Low-Bitrate and Speaker-Decoupled Discrete Speech Codec
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Although discrete speech tokens have exhibited strong potential for language model-based speech generation, their high bitrates and redundant timbre information restrict the development of such models. In this work, we propose LSCodec, a discrete speech codec that has both low bitrate and speaker decoupling ability. LSCodec adopts a three-stage unsupervised training framework with a speaker perturbation technique. A continuous information bottleneck is first established, followed by vector quantization that produces a discrete speaker-decoupled space. A discrete token vocoder finally refines acoustic details from LSCodec. By reconstruction experiments, LSCodec demonstrates superior intelligibility and audio quality with only a single codebook and smaller vocabulary size than baselines. The 25Hz version of LSCodec also achieves the lowest bitrate (0.25kbps) of codecs so far with decent quality. Voice conversion evaluations prove the satisfactory speaker disentanglement of LSCodec, and ablation study further verifies the effectiveness of the proposed training framework.
vec2wav 2.0: Advancing Voice Conversion via Discrete Token Vocoders
Sep 03, 2024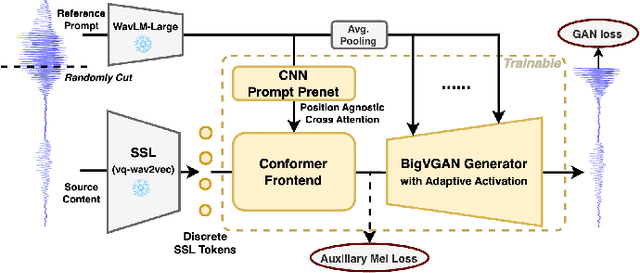
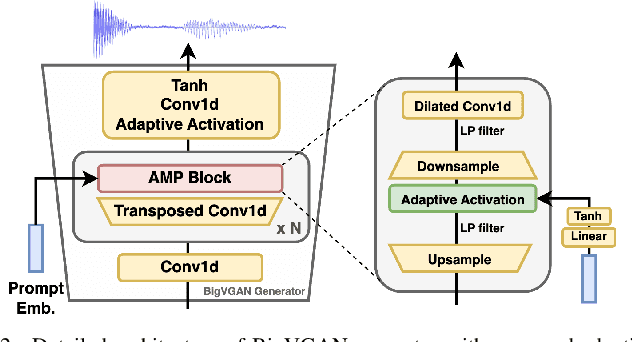
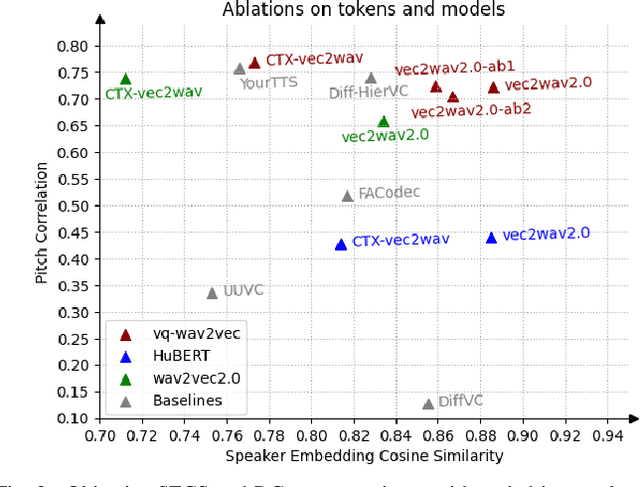
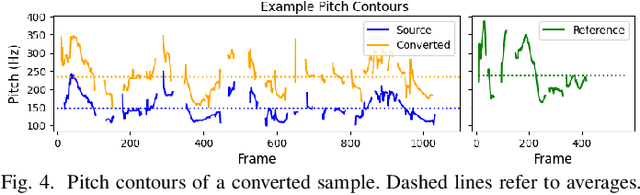
Abstract:We propose a new speech discrete token vocoder, vec2wav 2.0, which advances voice conversion (VC). We use discrete tokens from speech self-supervised models as the content features of source speech, and treat VC as a prompted vocoding task. To amend the loss of speaker timbre in the content tokens, vec2wav 2.0 utilizes the WavLM features to provide strong timbre-dependent information. A novel adaptive Snake activation function is proposed to better incorporate timbre into the waveform reconstruction process. In this way, vec2wav 2.0 learns to alter the speaker timbre appropriately given different reference prompts. Also, no supervised data is required for vec2wav 2.0 to be effectively trained. Experimental results demonstrate that vec2wav 2.0 outperforms all other baselines to a considerable margin in terms of audio quality and speaker similarity in any-to-any VC. Ablation studies verify the effects made by the proposed techniques. Moreover, vec2wav 2.0 achieves competitive cross-lingual VC even only trained on monolingual corpus. Thus, vec2wav 2.0 shows timbre can potentially be manipulated only by speech token vocoders, pushing the frontiers of VC and speech synthesis.
Language Model Can Listen While Speaking
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:Dialogue serves as the most natural manner of human-computer interaction (HCI). Recent advancements in speech language models (SLM) have significantly enhanced speech-based conversational AI. However, these models are limited to turn-based conversation, lacking the ability to interact with humans in real-time spoken scenarios, for example, being interrupted when the generated content is not satisfactory. To address these limitations, we explore full duplex modeling (FDM) in interactive speech language models (iSLM), focusing on enhancing real-time interaction and, more explicitly, exploring the quintessential ability of interruption. We introduce a novel model design, namely listening-while-speaking language model (LSLM), an end-to-end system equipped with both listening and speaking channels. Our LSLM employs a token-based decoder-only TTS for speech generation and a streaming self-supervised learning (SSL) encoder for real-time audio input. LSLM fuses both channels for autoregressive generation and detects turn-taking in real time. Three fusion strategies -- early fusion, middle fusion, and late fusion -- are explored, with middle fusion achieving an optimal balance between speech generation and real-time interaction. Two experimental settings, command-based FDM and voice-based FDM, demonstrate LSLM's robustness to noise and sensitivity to diverse instructions. Our results highlight LSLM's capability to achieve duplex communication with minimal impact on existing systems. This study aims to advance the development of interactive speech dialogue systems, enhancing their applicability in real-world contexts.
AniTalker: Animate Vivid and Diverse Talking Faces through Identity-Decoupled Facial Motion Encoding
May 06, 2024



Abstract:The paper introduces AniTalker, an innovative framework designed to generate lifelike talking faces from a single portrait. Unlike existing models that primarily focus on verbal cues such as lip synchronization and fail to capture the complex dynamics of facial expressions and nonverbal cues, AniTalker employs a universal motion representation. This innovative representation effectively captures a wide range of facial dynamics, including subtle expressions and head movements. AniTalker enhances motion depiction through two self-supervised learning strategies: the first involves reconstructing target video frames from source frames within the same identity to learn subtle motion representations, and the second develops an identity encoder using metric learning while actively minimizing mutual information between the identity and motion encoders. This approach ensures that the motion representation is dynamic and devoid of identity-specific details, significantly reducing the need for labeled data. Additionally, the integration of a diffusion model with a variance adapter allows for the generation of diverse and controllable facial animations. This method not only demonstrates AniTalker's capability to create detailed and realistic facial movements but also underscores its potential in crafting dynamic avatars for real-world applications. Synthetic results can be viewed at https://github.com/X-LANCE/AniTalker.
Attention-Constrained Inference for Robust Decoder-Only Text-to-Speech
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Recent popular decoder-only text-to-speech models are known for their ability of generating natural-sounding speech. However, such models sometimes suffer from word skipping and repeating due to the lack of explicit monotonic alignment constraints. In this paper, we notice from the attention maps that some particular attention heads of the decoder-only model indicate the alignments between speech and text. We call the attention maps of those heads Alignment-Emerged Attention Maps (AEAMs). Based on this discovery, we propose a novel inference method without altering the training process, named Attention-Constrained Inference (ACI), to facilitate monotonic synthesis. It first identifies AEAMs using the Attention Sweeping algorithm and then applies constraining masks on AEAMs. Our experimental results on decoder-only TTS model VALL-E show that the WER of synthesized speech is reduced by up to 20.5% relatively with ACI while the naturalness and speaker similarity are comparable.
GSTalker: Real-time Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation via Deformable Gaussian Splatting
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:We present GStalker, a 3D audio-driven talking face generation model with Gaussian Splatting for both fast training (40 minutes) and real-time rendering (125 FPS) with a 3$\sim$5 minute video for training material, in comparison with previous 2D and 3D NeRF-based modeling frameworks which require hours of training and seconds of rendering per frame. Specifically, GSTalker learns an audio-driven Gaussian deformation field to translate and transform 3D Gaussians to synchronize with audio information, in which multi-resolution hashing grid-based tri-plane and temporal smooth module are incorporated to learn accurate deformation for fine-grained facial details. In addition, a pose-conditioned deformation field is designed to model the stabilized torso. To enable efficient optimization of the condition Gaussian deformation field, we initialize 3D Gaussians by learning a coarse static Gaussian representation. Extensive experiments in person-specific videos with audio tracks validate that GSTalker can generate high-fidelity and audio-lips synchronized results with fast training and real-time rendering speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge