Shuai Fan
Task Vector in TTS: Toward Emotionally Expressive Dialectal Speech Synthesis
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-speech (TTS) have yielded remarkable improvements in naturalness and intelligibility. Building on these achievements, research has increasingly shifted toward enhancing the expressiveness of generated speech, such as dialectal and emotional TTS. However, cross-style synthesis combining both dialect and emotion remains challenging and largely unexplored, mainly due to the scarcity of dialectal data with emotional labels. To address this, we propose Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector), a two-stage method for Emotional Dialectal TTS. In the first stage, we construct different task vectors to model dialectal and emotional styles independently, and then enhance single-style synthesis by adjusting their weights, a method we refer to as Expressive Vector (E-Vector). For the second stage, we hierarchically integrate these vectors to achieve controllable emotionally expressive dialect synthesis without requiring jointly labeled data, corresponding to Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector). Experimental results demonstrate that HE-Vectors achieve superior performance in dialect synthesis, and promising results in synthesizing emotionally expressive dialectal speech in a zero-shot setting.
DiSRouter: Distributed Self-Routing for LLM Selections
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has created a diverse ecosystem of models with highly varying performance and costs, necessitating effective query routing to balance performance and expense. Current routing systems often rely on a centralized external router trained on a fixed set of LLMs, making them inflexible and prone to poor performance since the small router can not fully understand the knowledge boundaries of different LLMs. We introduce DiSRouter (Distributed Self-Router), a novel paradigm that shifts from centralized control to distributed routing. In DiSRouter, a query traverses a network of LLM agents, each independently deciding whether to answer or route to other agents based on its own self-awareness, its ability to judge its competence. This distributed design offers superior flexibility, scalability, and generalizability. To enable this, we propose a two-stage Self-Awareness Training pipeline that enhances each LLM's self-awareness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiSRouter significantly outperforms existing routing methods in utility across various scenarios, effectively distinguishes between easy and hard queries, and shows strong generalization to out-of-domain tasks. Our work validates that leveraging an LLM's intrinsic self-awareness is more effective than external assessment, paving the way for more modular and efficient multi-agent systems.
NeuSym-RAG: Hybrid Neural Symbolic Retrieval with Multiview Structuring for PDF Question Answering
May 26, 2025Abstract:The increasing number of academic papers poses significant challenges for researchers to efficiently acquire key details. While retrieval augmented generation (RAG) shows great promise in large language model (LLM) based automated question answering, previous works often isolate neural and symbolic retrieval despite their complementary strengths. Moreover, conventional single-view chunking neglects the rich structure and layout of PDFs, e.g., sections and tables. In this work, we propose NeuSym-RAG, a hybrid neural symbolic retrieval framework which combines both paradigms in an interactive process. By leveraging multi-view chunking and schema-based parsing, NeuSym-RAG organizes semi-structured PDF content into both the relational database and vectorstore, enabling LLM agents to iteratively gather context until sufficient to generate answers. Experiments on three full PDF-based QA datasets, including a self-annotated one AIRQA-REAL, show that NeuSym-RAG stably defeats both the vector-based RAG and various structured baselines, highlighting its capacity to unify both retrieval schemes and utilize multiple views. Code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/X-LANCE/NeuSym-RAG.
Neuronal Activation States as Sample Embeddings for Data Selection in Task-Specific Instruction Tuning
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Task-specific instruction tuning enhances the performance of large language models (LLMs) on specialized tasks, yet efficiently selecting relevant data for this purpose remains a challenge. Inspired by neural coactivation in the human brain, we propose a novel data selection method called NAS, which leverages neuronal activation states as embeddings for samples in the feature space. Extensive experiments show that NAS outperforms classical data selection methods in terms of both effectiveness and robustness across different models, datasets, and selection ratios.
NotaGen: Advancing Musicality in Symbolic Music Generation with Large Language Model Training Paradigms
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce NotaGen, a symbolic music generation model aiming to explore the potential of producing high-quality classical sheet music. Inspired by the success of Large Language Models (LLMs), NotaGen adopts pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning paradigms (henceforth referred to as the LLM training paradigms). It is pre-trained on 1.6M pieces of music, and then fine-tuned on approximately 9K high-quality classical compositions conditioned on "period-composer-instrumentation" prompts. For reinforcement learning, we propose the CLaMP-DPO method, which further enhances generation quality and controllability without requiring human annotations or predefined rewards. Our experiments demonstrate the efficacy of CLaMP-DPO in symbolic music generation models with different architectures and encoding schemes. Furthermore, subjective A/B tests show that NotaGen outperforms baseline models against human compositions, greatly advancing musical aesthetics in symbolic music generation. The project homepage is https://electricalexis.github.io/notagen-demo.
Audio-FLAN: A Preliminary Release
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in audio tokenization have significantly enhanced the integration of audio capabilities into large language models (LLMs). However, audio understanding and generation are often treated as distinct tasks, hindering the development of truly unified audio-language models. While instruction tuning has demonstrated remarkable success in improving generalization and zero-shot learning across text and vision, its application to audio remains largely unexplored. A major obstacle is the lack of comprehensive datasets that unify audio understanding and generation. To address this, we introduce Audio-FLAN, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset covering 80 diverse tasks across speech, music, and sound domains, with over 100 million instances. Audio-FLAN lays the foundation for unified audio-language models that can seamlessly handle both understanding (e.g., transcription, comprehension) and generation (e.g., speech, music, sound) tasks across a wide range of audio domains in a zero-shot manner. The Audio-FLAN dataset is available on HuggingFace and GitHub and will be continuously updated.
VQTalker: Towards Multilingual Talking Avatars through Facial Motion Tokenization
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:We present VQTalker, a Vector Quantization-based framework for multilingual talking head generation that addresses the challenges of lip synchronization and natural motion across diverse languages. Our approach is grounded in the phonetic principle that human speech comprises a finite set of distinct sound units (phonemes) and corresponding visual articulations (visemes), which often share commonalities across languages. We introduce a facial motion tokenizer based on Group Residual Finite Scalar Quantization (GRFSQ), which creates a discretized representation of facial features. This method enables comprehensive capture of facial movements while improving generalization to multiple languages, even with limited training data. Building on this quantized representation, we implement a coarse-to-fine motion generation process that progressively refines facial animations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VQTalker achieves state-of-the-art performance in both video-driven and speech-driven scenarios, particularly in multilingual settings. Notably, our method achieves high-quality results at a resolution of 512*512 pixels while maintaining a lower bitrate of approximately 11 kbps. Our work opens new possibilities for cross-lingual talking face generation. Synthetic results can be viewed at https://x-lance.github.io/VQTalker.
Reducing Tool Hallucination via Reliability Alignment
Dec 05, 2024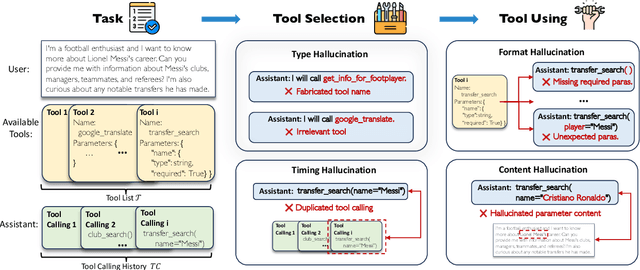
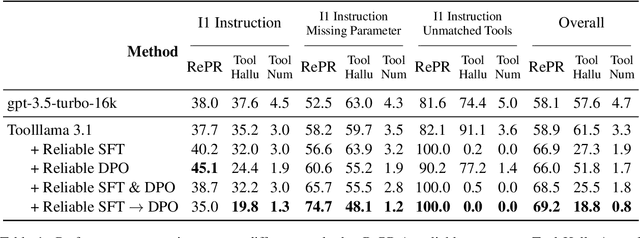
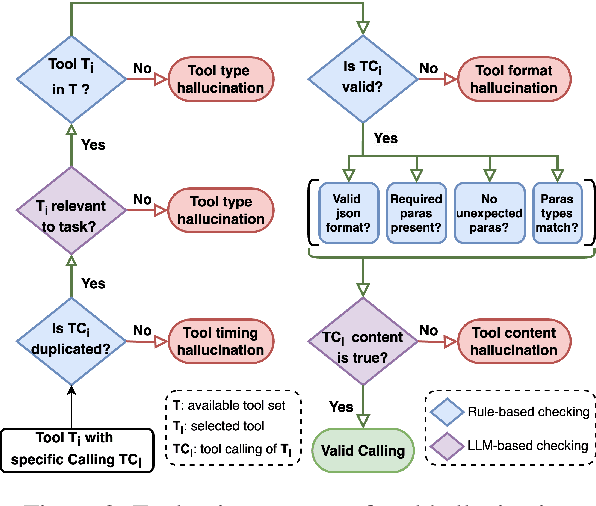
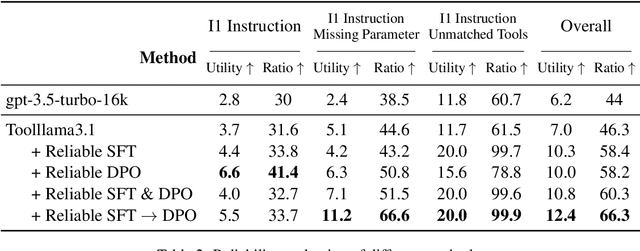
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have extended their capabilities beyond language generation to interact with external systems through tool calling, offering powerful potential for real-world applications. However, the phenomenon of tool hallucinations, which occur when models improperly select or misuse tools, presents critical challenges that can lead to flawed task execution and increased operational costs. This paper investigates the concept of reliable tool calling and highlights the necessity of addressing tool hallucinations. We systematically categorize tool hallucinations into two main types: tool selection hallucination and tool usage hallucination. To mitigate these issues, we propose a reliability-focused alignment framework that enhances the model's ability to accurately assess tool relevance and usage. By proposing a suite of evaluation metrics and evaluating on StableToolBench, we further demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in mitigating tool hallucination and improving the overall system reliability of LLM tool calling.
Compressing KV Cache for Long-Context LLM Inference with Inter-Layer Attention Similarity
Dec 03, 2024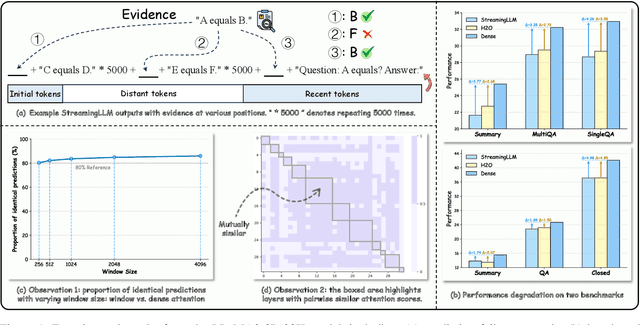



Abstract:The increasing context window size in Large Language Models (LLMs), such as the GPT and LLaMA series, has improved their ability to tackle complex, long-text tasks, but at the cost of inference efficiency, particularly regarding memory and computational complexity. Existing methods, including selective token retention and window-based attention, improve efficiency but risk discarding important tokens needed for future text generation. In this paper, we propose an approach that enhances LLM efficiency without token loss by reducing the memory and computational load of less important tokens, rather than discarding them.We address two challenges: 1) investigating the distribution of important tokens in the context, discovering recent tokens are more important than distant tokens in context, and 2) optimizing resources for distant tokens by sharing attention scores across layers. The experiments show that our method saves $35\%$ KV cache without compromising the performance.
GigaSpeech 2: An Evolving, Large-Scale and Multi-domain ASR Corpus for Low-Resource Languages with Automated Crawling, Transcription and Refinement
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:The evolution of speech technology has been spurred by the rapid increase in dataset sizes. Traditional speech models generally depend on a large amount of labeled training data, which is scarce for low-resource languages. This paper presents GigaSpeech 2, a large-scale, multi-domain, multilingual speech recognition corpus. It is designed for low-resource languages and does not rely on paired speech and text data. GigaSpeech 2 comprises about 30,000 hours of automatically transcribed speech, including Thai, Indonesian, and Vietnamese, gathered from unlabeled YouTube videos. We also introduce an automated pipeline for data crawling, transcription, and label refinement. Specifically, this pipeline uses Whisper for initial transcription and TorchAudio for forced alignment, combined with multi-dimensional filtering for data quality assurance. A modified Noisy Student Training is developed to further refine flawed pseudo labels iteratively, thus enhancing model performance. Experimental results on our manually transcribed evaluation set and two public test sets from Common Voice and FLEURS confirm our corpus's high quality and broad applicability. Notably, ASR models trained on GigaSpeech 2 can reduce the word error rate for Thai, Indonesian, and Vietnamese on our challenging and realistic YouTube test set by 25% to 40% compared to the Whisper large-v3 model, with merely 10% model parameters. Furthermore, our ASR models trained on Gigaspeech 2 yield superior performance compared to commercial services. We believe that our newly introduced corpus and pipeline will open a new avenue for low-resource speech recognition and significantly facilitate research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge