Sitong Cheng
Spark-TTS: An Efficient LLM-Based Text-to-Speech Model with Single-Stream Decoupled Speech Tokens
Mar 03, 2025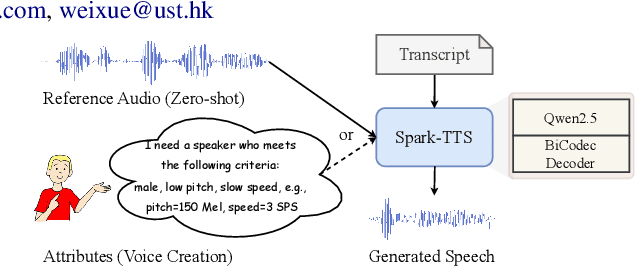
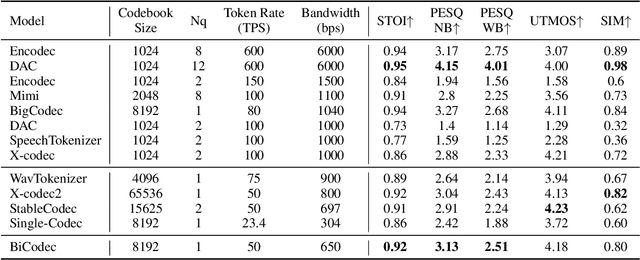
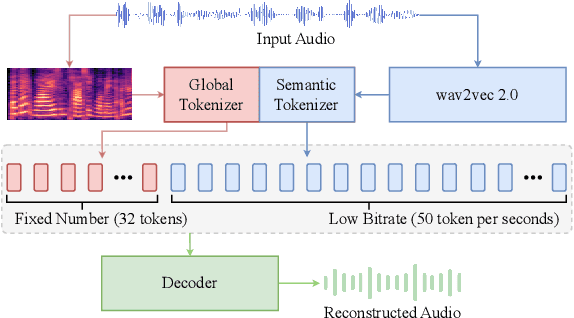
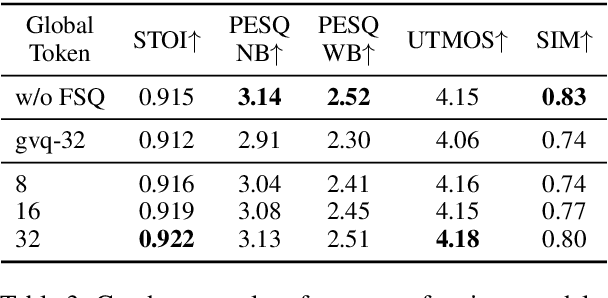
Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have driven significant progress in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. However, existing foundation models rely on multi-stage processing or complex architectures for predicting multiple codebooks, limiting efficiency and integration flexibility. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Spark-TTS, a novel system powered by BiCodec, a single-stream speech codec that decomposes speech into two complementary token types: low-bitrate semantic tokens for linguistic content and fixed-length global tokens for speaker attributes. This disentangled representation, combined with the Qwen2.5 LLM and a chain-of-thought (CoT) generation approach, enables both coarse-grained control (e.g., gender, speaking style) and fine-grained adjustments (e.g., precise pitch values, speaking rate). To facilitate research in controllable TTS, we introduce VoxBox, a meticulously curated 100,000-hour dataset with comprehensive attribute annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Spark-TTS not only achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot voice cloning but also generates highly customizable voices that surpass the limitations of reference-based synthesis. Source code, pre-trained models, and audio samples are available at https://github.com/SparkAudio/Spark-TTS.
Audio-FLAN: A Preliminary Release
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in audio tokenization have significantly enhanced the integration of audio capabilities into large language models (LLMs). However, audio understanding and generation are often treated as distinct tasks, hindering the development of truly unified audio-language models. While instruction tuning has demonstrated remarkable success in improving generalization and zero-shot learning across text and vision, its application to audio remains largely unexplored. A major obstacle is the lack of comprehensive datasets that unify audio understanding and generation. To address this, we introduce Audio-FLAN, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset covering 80 diverse tasks across speech, music, and sound domains, with over 100 million instances. Audio-FLAN lays the foundation for unified audio-language models that can seamlessly handle both understanding (e.g., transcription, comprehension) and generation (e.g., speech, music, sound) tasks across a wide range of audio domains in a zero-shot manner. The Audio-FLAN dataset is available on HuggingFace and GitHub and will be continuously updated.
Both Ears Wide Open: Towards Language-Driven Spatial Audio Generation
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have achieved great success in mono-channel audio generation. However, when it comes to stereo audio generation, the soundscapes often have a complex scene of multiple objects and directions. Controlling stereo audio with spatial contexts remains challenging due to high data costs and unstable generative models. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first attempt to address these issues. We first construct a large-scale, simulation-based, and GPT-assisted dataset, BEWO-1M, with abundant soundscapes and descriptions even including moving and multiple sources. Beyond text modality, we have also acquired a set of images and rationally paired stereo audios through retrieval to advance multimodal generation. Existing audio generation models tend to generate rather random and indistinct spatial audio. To provide accurate guidance for latent diffusion models, we introduce the SpatialSonic model utilizing spatial-aware encoders and azimuth state matrices to reveal reasonable spatial guidance. By leveraging spatial guidance, our unified model not only achieves the objective of generating immersive and controllable spatial audio from text and image but also enables interactive audio generation during inference. Finally, under fair settings, we conduct subjective and objective evaluations on simulated and real-world data to compare our approach with prevailing methods. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, highlighting its capability to generate spatial audio that adheres to physical rules.
CN-CELEB: a challenging Chinese speaker recognition dataset
Oct 31, 2019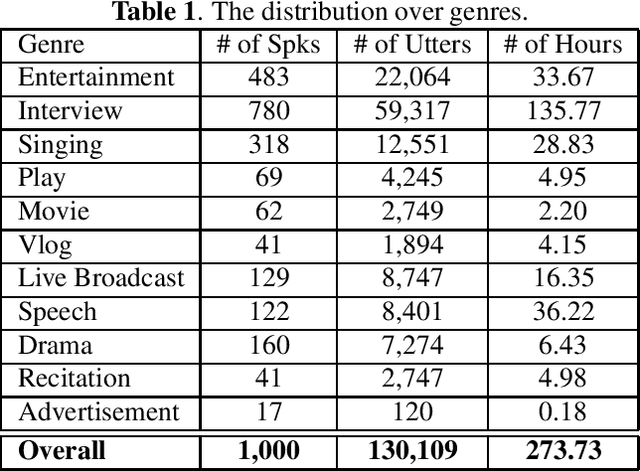
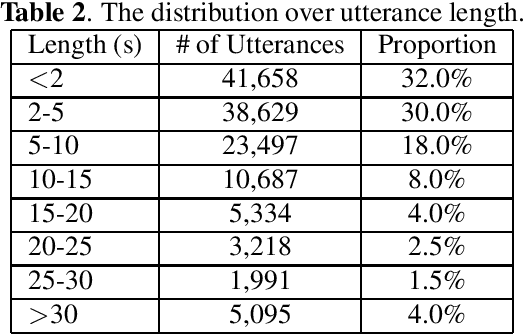
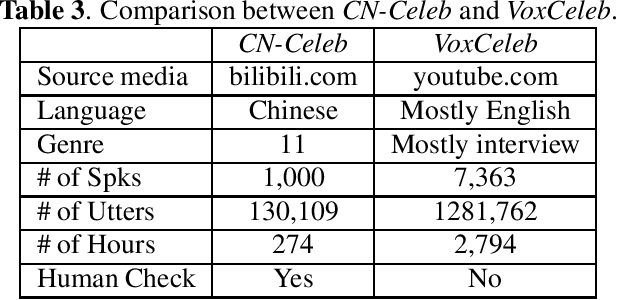
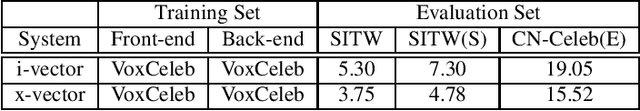
Abstract:Recently, researchers set an ambitious goal of conducting speaker recognition in unconstrained conditions where the variations on ambient, channel and emotion could be arbitrary. However, most publicly available datasets are collected under constrained environments, i.e., with little noise and limited channel variation. These datasets tend to deliver over optimistic performance and do not meet the request of research on speaker recognition in unconstrained conditions. In this paper, we present CN-Celeb, a large-scale speaker recognition dataset collected `in the wild'. This dataset contains more than 130,000 utterances from 1,000 Chinese celebrities, and covers 11 different genres in real world. Experiments conducted with two state-of-the-art speaker recognition approaches (i-vector and x-vector) show that the performance on CN-Celeb is far inferior to the one obtained on VoxCeleb, a widely used speaker recognition dataset. This result demonstrates that in real-life conditions, the performance of existing techniques might be much worse than it was thought. Our database is free for researchers and can be downloaded from http://project.cslt.org.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge