Jiawen Kang
Sherman
Lyapunov Stability-Aware Stackelberg Game for Low-Altitude Economy: A Control-Oriented Pruning-Based DRL Approach
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:With the rapid expansion of the low-altitude economy, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) serve as pivotal aerial base stations supporting diverse services from users, ranging from latency-sensitive critical missions to bandwidth-intensive data streaming. However, the efficacy of such heterogeneous networks is often compromised by the conflict between limited onboard resources and stringent stability requirements. Moving beyond traditional throughput-centric designs, we propose a Sensing-Communication-Computing-Control closed-loop framework that explicitly models the impact of communication latency on physical control stability. To guarantee mission reliability, we leverage the Lyapunov stability theory to derive an intrinsic mapping between the state evolution of the control system and communication constraints, transforming abstract stability requirements into quantifiable resource boundaries. Then, we formulate the resource allocation problem as a Stackelberg game, where UAVs (as leaders) dynamically price resources to balance load and ensure stability, while users (as followers) optimize requests based on service urgency. Furthermore, addressing the prohibitive computational overhead of standard Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) on energy-constrained edge platforms, we propose a novel and lightweight pruning-based Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm. By integrating a dynamic structured pruning mechanism, the proposed algorithm significantly compresses the neural network scale during training, enabling the UAV to rapidly approximate the game equilibrium with minimal inference latency. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme effectively secures control loop stability while maximizing system utility in dynamic low-altitude environments.
Cross-reality Location Privacy Protection in 6G-enabled Vehicular Metaverses: An LLM-enhanced Hybrid Generative Diffusion Model-based Approach
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:The emergence of 6G-enabled vehicular metaverses enables Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) to operate across physical and virtual spaces through space-air-ground-sea integrated networks. The AVs can deploy AI agents powered by large AI models as personalized assistants, on edge servers to support intelligent driving decision making and enhanced on-board experiences. However, such cross-reality interactions may cause serious location privacy risks, as adversaries can infer AV trajectories by correlating the location reported when AVs request LBS in reality with the location of the edge servers on which their corresponding AI agents are deployed in virtuality. To address this challenge, we design a cross-reality location privacy protection framework based on hybrid actions, including continuous location perturbation in reality and discrete privacy-aware AI agent migration in virtuality. In this framework, a new privacy metric, termed cross-reality location entropy, is proposed to effectively quantify the privacy levels of AVs. Based on this metric, we formulate an optimization problem to optimize the hybrid action, focusing on achieving a balance between location protection, service latency reduction, and quality of service maintenance. To solve the complex mixed-integer problem, we develop a novel LLM-enhanced Hybrid Diffusion Proximal Policy Optimization (LHDPPO) algorithm, which integrates LLM-driven informative reward design to enhance environment understanding with double Generative Diffusion Models-based policy exploration to handle high-dimensional action spaces, thereby enabling reliable determination of optimal hybrid actions. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed framework effectively mitigates cross-reality location privacy leakage for AVs while maintaining strong user immersion within 6G-enabled vehicular metaverse scenarios.
LMM-Incentive: Large Multimodal Model-based Incentive Design for User-Generated Content in Web 3.0
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Web 3.0 represents the next generation of the Internet, which is widely recognized as a decentralized ecosystem that focuses on value expression and data ownership. By leveraging blockchain and artificial intelligence technologies, Web 3.0 offers unprecedented opportunities for users to create, own, and monetize their content, thereby enabling User-Generated Content (UGC) to an entirely new level. However, some self-interested users may exploit the limitations of content curation mechanisms and generate low-quality content with less effort, obtaining platform rewards under information asymmetry. Such behavior can undermine Web 3.0 performance. To this end, we propose \textit{LMM-Incentive}, a novel Large Multimodal Model (LMM)-based incentive mechanism for UGC in Web 3.0. Specifically, we propose an LMM-based contract-theoretic model to motivate users to generate high-quality UGC, thereby mitigating the adverse selection problem from information asymmetry. To alleviate potential moral hazards after contract selection, we leverage LMM agents to evaluate UGC quality, which is the primary component of the contract, utilizing prompt engineering techniques to improve the evaluation performance of LMM agents. Recognizing that traditional contract design methods cannot effectively adapt to the dynamic environment of Web 3.0, we develop an improved Mixture of Experts (MoE)-based Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm for optimal contract design. Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed MoE-based PPO algorithm over representative benchmarks in the context of contract design. Finally, we deploy the designed contract within an Ethereum smart contract framework, further validating the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
Context-Aware Semantic Communication for the Wireless Networks
May 29, 2025Abstract:In next-generation wireless networks, supporting real-time applications such as augmented reality, autonomous driving, and immersive Metaverse services demands stringent constraints on bandwidth, latency, and reliability. Existing semantic communication (SemCom) approaches typically rely on static models, overlooking dynamic conditions and contextual cues vital for efficient transmission. To address these challenges, we propose CaSemCom, a context-aware SemCom framework that leverages a Large Language Model (LLM)-based gating mechanism and a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture to adaptively select and encode only high-impact semantic features across multiple data modalities. Our multimodal, multi-user case study demonstrates that CaSemCom significantly improves reconstructed image fidelity while reducing bandwidth usage, outperforming single-agent deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods and traditional baselines in convergence speed, semantic accuracy, and retransmission overhead.
Confidence-Regulated Generative Diffusion Models for Reliable AI Agent Migration in Vehicular Metaverses
May 19, 2025Abstract:Vehicular metaverses are an emerging paradigm that merges intelligent transportation systems with virtual spaces, leveraging advanced digital twin and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies to seamlessly integrate vehicles, users, and digital environments. In this paradigm, vehicular AI agents are endowed with environment perception, decision-making, and action execution capabilities, enabling real-time processing and analysis of multi-modal data to provide users with customized interactive services. Since vehicular AI agents require substantial resources for real-time decision-making, given vehicle mobility and network dynamics conditions, the AI agents are deployed in RoadSide Units (RSUs) with sufficient resources and dynamically migrated among them. However, AI agent migration requires frequent data exchanges, which may expose vehicular metaverses to potential cyber attacks. To this end, we propose a reliable vehicular AI agent migration framework, achieving reliable dynamic migration and efficient resource scheduling through cooperation between vehicles and RSUs. Additionally, we design a trust evaluation model based on the theory of planned behavior to dynamically quantify the reputation of RSUs, thereby better accommodating the personalized trust preferences of users. We then model the vehicular AI agent migration process as a partially observable markov decision process and develop a Confidence-regulated Generative Diffusion Model (CGDM) to efficiently generate AI agent migration decisions. Numerical results demonstrate that the CGDM algorithm significantly outperforms baseline methods in reducing system latency and enhancing robustness against cyber attacks.
Internet of Agents: Fundamentals, Applications, and Challenges
May 12, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid proliferation of large language models and vision-language models, AI agents have evolved from isolated, task-specific systems into autonomous, interactive entities capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting without human intervention. As these agents proliferate across virtual and physical environments, from virtual assistants to embodied robots, the need for a unified, agent-centric infrastructure becomes paramount. In this survey, we introduce the Internet of Agents (IoA) as a foundational framework that enables seamless interconnection, dynamic discovery, and collaborative orchestration among heterogeneous agents at scale. We begin by presenting a general IoA architecture, highlighting its hierarchical organization, distinguishing features relative to the traditional Internet, and emerging applications. Next, we analyze the key operational enablers of IoA, including capability notification and discovery, adaptive communication protocols, dynamic task matching, consensus and conflict-resolution mechanisms, and incentive models. Finally, we identify open research directions toward building resilient and trustworthy IoA ecosystems.
Bi-LSTM based Multi-Agent DRL with Computation-aware Pruning for Agent Twins Migration in Vehicular Embodied AI Networks
May 09, 2025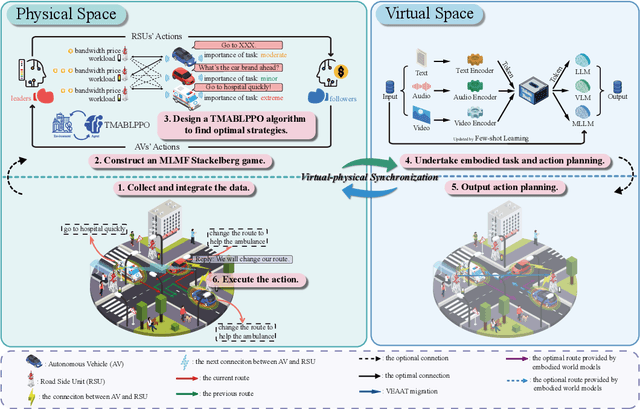
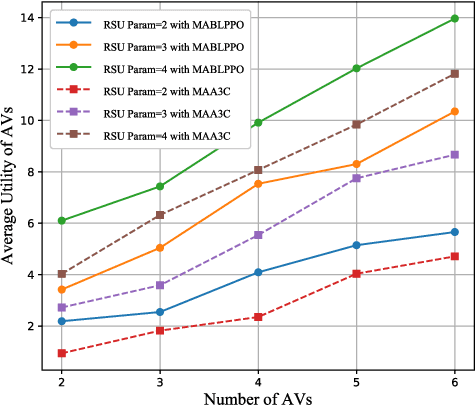
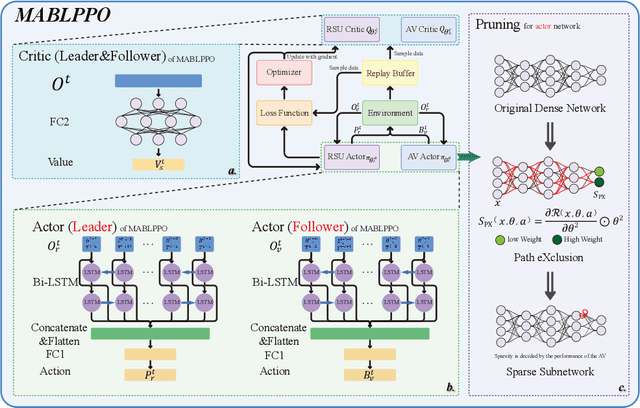
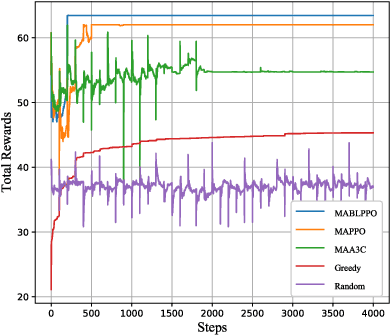
Abstract:With the advancement of large language models and embodied Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the intelligent transportation scenarios, the combination of them in intelligent transportation spawns the Vehicular Embodied AI Network (VEANs). In VEANs, Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) are typical agents whose local advanced AI applications are defined as vehicular embodied AI agents, enabling capabilities such as environment perception and multi-agent collaboration. Due to computation latency and resource constraints, the local AI applications and services running on vehicular embodied AI agents need to be migrated, and subsequently referred to as vehicular embodied AI agent twins, which drive the advancement of vehicular embodied AI networks to offload intensive tasks to Roadside Units (RSUs), mitigating latency problems while maintaining service quality. Recognizing workload imbalance among RSUs in traditional approaches, we model AV-RSU interactions as a Stackelberg game to optimize bandwidth resource allocation for efficient migration. A Tiny Multi-Agent Bidirectional LSTM Proximal Policy Optimization (TMABLPPO) algorithm is designed to approximate the Stackelberg equilibrium through decentralized coordination. Furthermore, a personalized neural network pruning algorithm based on Path eXclusion (PX) dynamically adapts to heterogeneous AV computation capabilities by identifying task-critical parameters in trained models, reducing model complexity with less performance degradation. Experimental validation confirms the algorithm's effectiveness in balancing system load and minimizing delays, demonstrating significant improvements in vehicular embodied AI agent deployment.
Decentralization of Generative AI via Mixture of Experts for Wireless Networks: A Comprehensive Survey
Apr 28, 2025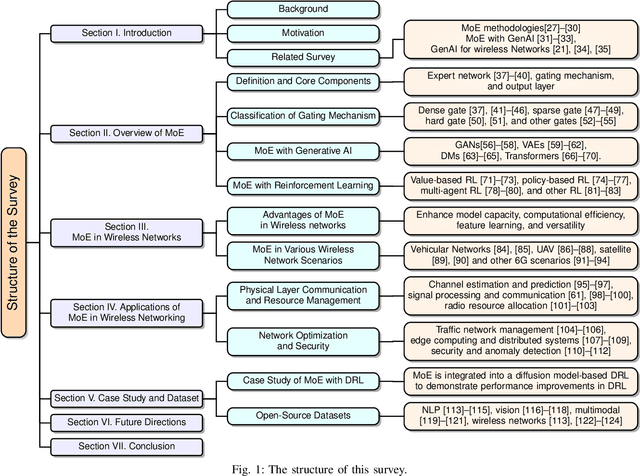
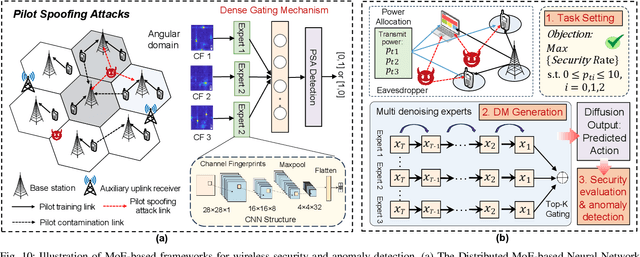
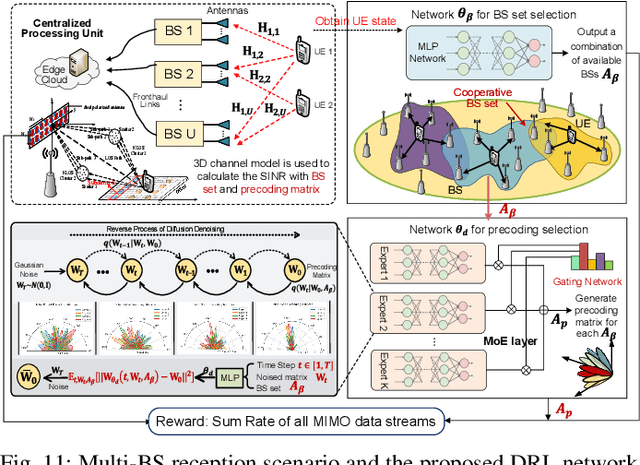
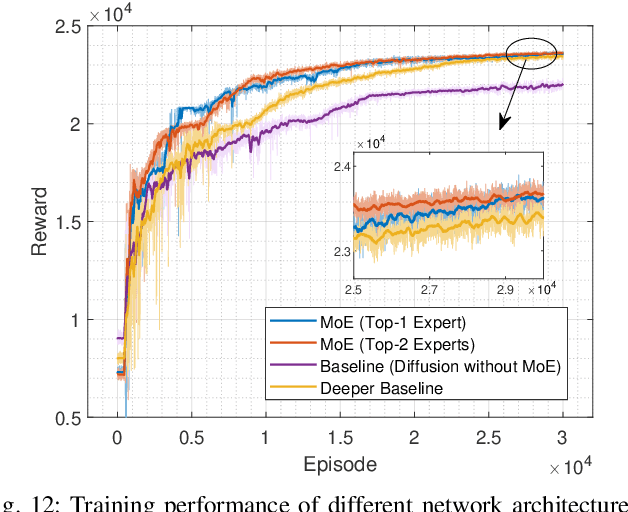
Abstract:Mixture of Experts (MoE) has emerged as a promising paradigm for scaling model capacity while preserving computational efficiency, particularly in large-scale machine learning architectures such as large language models (LLMs). Recent advances in MoE have facilitated its adoption in wireless networks to address the increasing complexity and heterogeneity of modern communication systems. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the MoE framework in wireless networks, highlighting its potential in optimizing resource efficiency, improving scalability, and enhancing adaptability across diverse network tasks. We first introduce the fundamental concepts of MoE, including various gating mechanisms and the integration with generative AI (GenAI) and reinforcement learning (RL). Subsequently, we discuss the extensive applications of MoE across critical wireless communication scenarios, such as vehicular networks, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellite communications, heterogeneous networks, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), and mobile edge networks. Furthermore, key applications in channel prediction, physical layer signal processing, radio resource management, network optimization, and security are thoroughly examined. Additionally, we present a detailed overview of open-source datasets that are widely used in MoE-based models to support diverse machine learning tasks. Finally, this survey identifies crucial future research directions for MoE, emphasizing the importance of advanced training techniques, resource-aware gating strategies, and deeper integration with emerging 6G technologies.
Learning Joint Source-Channel Encoding in IRS-assisted Multi-User Semantic Communications
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a joint source-channel encoding (JSCE) scheme in an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted multi-user semantic communication system. Semantic encoding not only compresses redundant information, but also enhances information orthogonality in a semantic feature space. Meanwhile, the IRS can adjust the spatial orthogonality, enabling concurrent multi-user semantic communication in densely deployed wireless networks to improve spectrum efficiency. We aim to maximize the users' semantic throughput by jointly optimizing the users' scheduling, the IRS's passive beamforming, and the semantic encoding strategies. To tackle this non-convex problem, we propose an explainable deep neural network-driven deep reinforcement learning (XD-DRL) framework. Specifically, we employ a deep neural network (DNN) to serve as a joint source-channel semantic encoder, enabling transmitters to extract semantic features from raw images. By leveraging structural similarity, we assign some DNN weight coefficients as the IRS's phase shifts, allowing simultaneous optimization of IRS's passive beamforming and DNN training. Given the IRS's passive beamforming and semantic encoding strategies, user scheduling is optimized using the DRL method. Numerical results validate that our JSCE scheme achieves superior semantic throughput compared to the conventional schemes and efficiently reduces the semantic encoder's mode size in multi-user scenarios.
Wireless Hallucination in Generative AI-enabled Communications: Concepts, Issues, and Solutions
Mar 08, 2025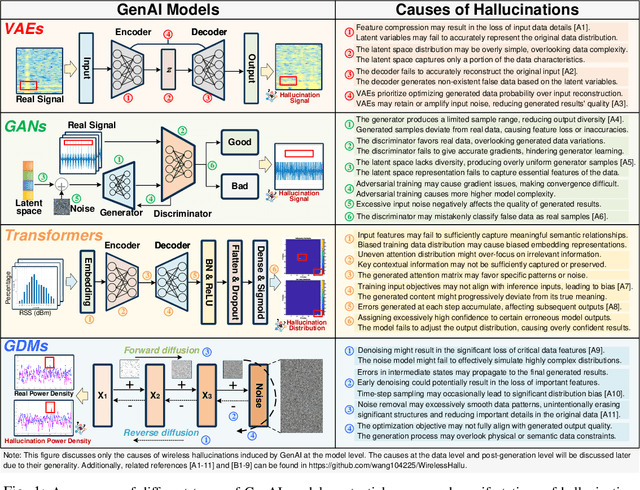
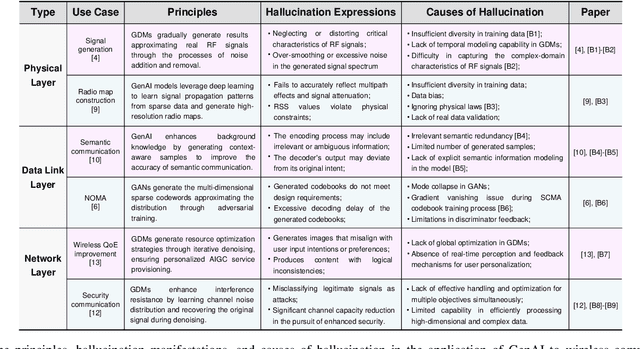
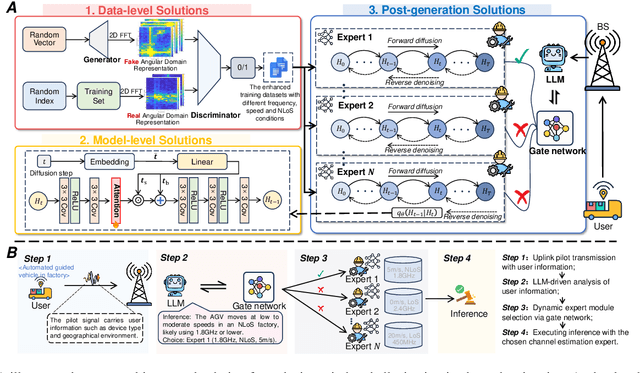
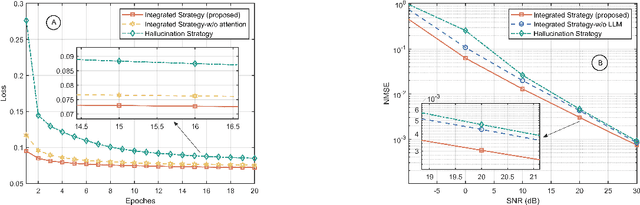
Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) is driving the intelligence of wireless communications. Due to data limitations, random generation, and dynamic environments, GenAI may generate channel information or optimization strategies that violate physical laws or deviate from actual real-world requirements. We refer to this phenomenon as wireless hallucination, which results in invalid channel information, spectrum wastage, and low communication reliability but remains underexplored. To address this gap, this article provides a comprehensive concept of wireless hallucinations in GenAI-driven communications, focusing on hallucination mitigation. Specifically, we first introduce the fundamental, analyze its causes based on the GenAI workflow, and propose mitigation solutions at the data, model, and post-generation levels. Then, we systematically examines representative hallucination scenarios in GenAI-enabled communications and their corresponding solutions. Finally, we propose a novel integrated mitigation solution for GenAI-based channel estimation. At the data level, we establish a channel estimation hallucination dataset and employ generative adversarial networks (GANs)-based data augmentation. Additionally, we incorporate attention mechanisms and large language models (LLMs) to enhance both training and inference performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed hybrid solutions reduce the normalized mean square error (NMSE) by 0.19, effectively reducing wireless hallucinations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge