Jiacheng Wang
Sherman
A multi-center analysis of deep learning methods for video polyp detection and segmentation
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:Colonic polyps are well-recognized precursors to colorectal cancer (CRC), typically detected during colonoscopy. However, the variability in appearance, location, and size of these polyps complicates their detection and removal, leading to challenges in effective surveillance, intervention, and subsequently CRC prevention. The processes of colonoscopy surveillance and polyp removal are highly reliant on the expertise of gastroenterologists and occur within the complexities of the colonic structure. As a result, there is a high rate of missed detections and incomplete removal of colonic polyps, which can adversely impact patient outcomes. Recently, automated methods that use machine learning have been developed to enhance polyps detection and segmentation, thus helping clinical processes and reducing missed rates. These advancements highlight the potential for improving diagnostic accuracy in real-time applications, which ultimately facilitates more effective patient management. Furthermore, integrating sequence data and temporal information could significantly enhance the precision of these methods by capturing the dynamic nature of polyp growth and the changes that occur over time. To rigorously investigate these challenges, data scientists and experts gastroenterologists collaborated to compile a comprehensive dataset that spans multiple centers and diverse populations. This initiative aims to underscore the critical importance of incorporating sequence data and temporal information in the development of robust automated detection and segmentation methods. This study evaluates the applicability of deep learning techniques developed in real-time clinical colonoscopy tasks using sequence data, highlighting the critical role of temporal relationships between frames in improving diagnostic precision.
Wireless Power Control Based on Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:This paper investigates the power control problem in wireless networks by repurposing pre-trained large language models (LLMs) as relational reasoning backbones. In hyper-connected interference environments, traditional optimization methods face high computational cost, while standard message passing neural networks suffer from aggregation bottlenecks that can obscure critical high-interference structures. In response, we propose PC-LLM, a physics-informed framework that augments a pre-trained Transformer with an interference-aware attention bias. The proposed bias tuning mechanism injects the physical channel gain matrix directly into the self-attention logits, enabling explicit fusion of wireless topology with pre-trained relational priors without retraining the backbone from scratch. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PC-LLM consistently outperforms both traditional optimization methods and state-of-the-art graph neural network baselines, while exhibiting exceptional zero-shot generalization to unseen environments. We further observe a structural-semantic decoupling phenomenon: Topology-relevant relational reasoning is concentrated in shallow layers, whereas deeper layers encode task-irrelevant semantic noise. Motivated by this finding, we develop a lightweight adaptation strategy that reduces model depth by 50\%, significantly lowering inference cost while preserving state-of-the-art spectral efficiency.
Dual-Hop Joint Visible Light and Backscatter Communication Relaying under Finite Blocklength
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:This paper investigates a dual-hop joint visible light communication (VLC) and backscatter communication (BC) relaying framework under the finite blocklength (FBL) constraint, aiming at energy-neutral Ambient Internet of Things (A-IoT) deployments. In the proposed system, indoor LED access points are used to simultaneously provide illumination and transmit information over light to a backscatter device (BD), which harvests optical energy and backscatters the received messages to user equipments (UEs) equipped with radio frequency (RF) front ends. This forwarding of the information from VLC to RF channels is implemented without the need for carrier synthesizers and power amplifiers at the IoT node. By modeling the end-to-end communication link with short-packet IoT traffic and realistic levels of interference between adjacent VLC coverage areas, we analyze the outage performance and achievable data rate of the proposed system. Simulation results demonstrate that key factors, such as placement and orientation of the BD, as well as the selected code rate of the system affect reliability and data rate that can be achieved for communication purposes. The insights gained from this study pave the way for ambient power-enabled IoT solutions and future hybrid VLC/RF network designs.
Patch the Distribution Mismatch: RL Rewriting Agent for Stable Off-Policy SFT
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have made rapid progress, yet adapting them to downstream scenarios still commonly relies on supervised fine-tuning (SFT). When downstream data exhibit a substantial distribution shift from the model's prior training distribution, SFT can induce catastrophic forgetting. To narrow this gap, data rewriting has been proposed as a data-centric approach that rewrites downstream training data prior to SFT. However, existing methods typically sample rewrites from a prompt-induced conditional distribution, so the resulting targets are not necessarily aligned with the model's natural QA-style generation distribution. Moreover, reliance on fixed templates can lead to diversity collapse. To address these issues, we cast data rewriting as a policy learning problem and learn a rewriting policy that better matches the backbone's QA-style generation distribution while preserving diversity. Since distributional alignment, diversity and task consistency are automatically evaluable but difficult to optimize end-to-end with differentiable objectives, we leverage reinforcement learning to optimize the rewrite distribution under reward feedback and propose an RL-based data-rewriting agent. The agent jointly optimizes QA-style distributional alignment and diversity under a hard task-consistency gate, thereby constructing a higher-quality rewritten dataset for downstream SFT. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves downstream gains comparable to standard SFT while reducing forgetting on non-downstream benchmarks by 12.34% on average. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Patch-the-Prompt-Gap-4112 .
Wireless Context Engineering for Efficient Mobile Agentic AI and Edge General Intelligence
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Future wireless networks demand increasingly powerful intelligence to support sensing, communication, and autonomous decision-making. While scaling laws suggest improving performance by enlarging model capacity, practical edge deployments are fundamentally constrained by latency, energy, and memory, making unlimited model scaling infeasible. This creates a critical need to maximize the utility of limited inference-time inputs by filtering redundant observations and focusing on high-impact data. In large language models and generative artificial intelligence (AI), context engineering has emerged as a key paradigm to guide inference by selectively structuring and injecting task-relevant information. Inspired by this success, we extend context engineering to wireless systems, providing a systematic way to enhance edge AI performance without increasing model complexity. In dynamic environments, for example, beam prediction can benefit from augmenting instantaneous channel measurements with contextual cues such as user mobility trends or environment-aware propagation priors. We formally introduce wireless context engineering and propose a Wireless Context Communication Framework (WCCF) to adaptively orchestrate wireless context under inference-time constraints. This work provides researchers with a foundational perspective and practical design dimensions to manage the wireless context of wireless edge intelligence. An ISAC-enabled beam prediction case study illustrates the effectiveness of the proposed paradigm under constrained sensing budgets.
Can LLMs See Without Pixels? Benchmarking Spatial Intelligence from Textual Descriptions
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in Spatial Intelligence (SI) have predominantly relied on Vision-Language Models (VLMs), yet a critical question remains: does spatial understanding originate from visual encoders or the fundamental reasoning backbone? Inspired by this question, we introduce SiT-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the SI performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) without pixel-level input, comprises over 3,800 expert-annotated items across five primary categories and 17 subtasks, ranging from egocentric navigation and perspective transformation to fine-grained robotic manipulation. By converting single/multi-view scenes into high-fidelity, coordinate-aware textual descriptions, we challenge LLMs to perform symbolic textual reasoning rather than visual pattern matching. Evaluation results of state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs reveals that while models achieve proficiency in localized semantic tasks, a significant "spatial gap" remains in global consistency. Notably, we find that explicit spatial reasoning significantly boosts performance, suggesting that LLMs possess latent world-modeling potential. Our proposed dataset SiT-Bench serves as a foundational resource to foster the development of spatially-grounded LLM backbones for future VLMs and embodied agents. Our code and benchmark will be released at https://github.com/binisalegend/SiT-Bench .
EndoStreamDepth: Temporally Consistent Monocular Depth Estimation for Endoscopic Video Streams
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:This work presents EndoStreamDepth, a monocular depth estimation framework for endoscopic video streams. It provides accurate depth maps with sharp anatomical boundaries for each frame, temporally consistent predictions across frames, and real-time throughput. Unlike prior work that uses batched inputs, EndoStreamDepth processes individual frames with a temporal module to propagate inter-frame information. The framework contains three main components: (1) a single-frame depth network with endoscopy-specific transformation to produce accurate depth maps, (2) multi-level Mamba temporal modules that leverage inter-frame information to improve accuracy and stabilize predictions, and (3) a hierarchical design with comprehensive multi-scale supervision, where complementary loss terms jointly improve local boundary sharpness and global geometric consistency. We conduct comprehensive evaluations on two publicly available colonoscopy depth estimation datasets. Compared to state-of-the-art monocular depth estimation methods, EndoStreamDepth substantially improves performance, and it produces depth maps with sharp, anatomically aligned boundaries, which are essential to support downstream tasks such as automation for robotic surgery. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/MedICL-VU/EndoStreamDepth
Agentic AI for Integrated Sensing and Communication: Analysis, Framework, and Case Study
Dec 17, 2025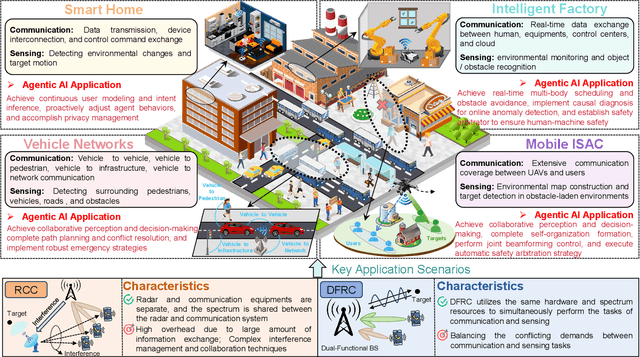
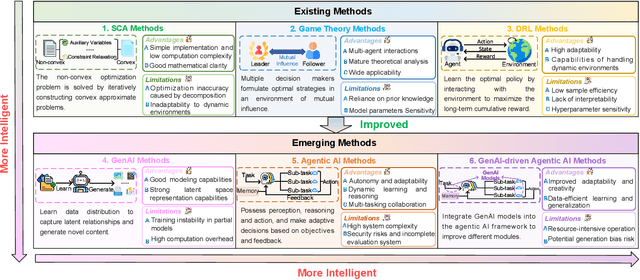
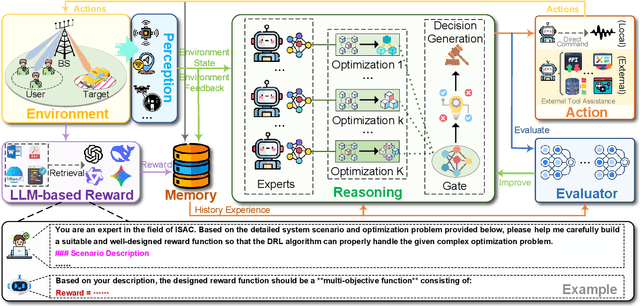
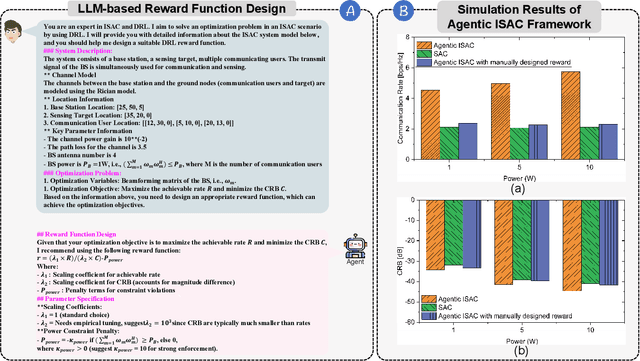
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key development direction in the sixth-generation (6G) era, which provides essential support for the collaborative sensing and communication of future intelligent networks. However, as wireless environments become increasingly dynamic and complex, ISAC systems require more intelligent processing and more autonomous operation to maintain efficiency and adaptability. Meanwhile, agentic artificial intelligence (AI) offers a feasible solution to address these challenges by enabling continuous perception-reasoning-action loops in dynamic environments to support intelligent, autonomous, and efficient operation for ISAC systems. As such, we delve into the application value and prospects of agentic AI in ISAC systems in this work. Firstly, we provide a comprehensive review of agentic AI and ISAC systems to demonstrate their key characteristics. Secondly, we show several common optimization approaches for ISAC systems and highlight the significant advantages of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI)-based agentic AI. Thirdly, we propose a novel agentic ISAC framework and prensent a case study to verify its superiority in optimizing ISAC performance. Finally, we clarify future research directions for agentic AI-based ISAC systems.
SLMQuant:Benchmarking Small Language Model Quantization for Practical Deployment
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Despite the growing interest in Small Language Models (SLMs) as resource-efficient alternatives to Large Language Models (LLMs), their deployment on edge devices remains challenging due to unresolved efficiency gaps in model compression. While quantization has proven effective for LLMs, its applicability to SLMs is significantly underexplored, with critical questions about differing quantization bottlenecks and efficiency profiles. This paper introduces SLMQuant, the first systematic benchmark for evaluating LLM compression techniques when applied to SLMs. Through comprehensive multi-track evaluations across diverse architectures and tasks, we analyze how state-of-the-art quantization methods perform on SLMs. Our findings reveal fundamental disparities between SLMs and LLMs in quantization sensitivity, demonstrating that direct transfer of LLM-optimized techniques leads to suboptimal results due to SLMs' unique architectural characteristics and training dynamics. We identify key factors governing effective SLM quantization and propose actionable design principles for SLM-tailored compression. SLMQuant establishes a foundational framework for advancing efficient SLM deployment on low-end devices in edge applications, and provides critical insights for deploying lightweight language models in resource-constrained scenarios.
DEMIST: \underline{DE}coupled \underline{M}ulti-stream latent d\underline{I}ffusion for Quantitative Myelin Map \underline{S}yn\underline{T}hesis
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT) imaging provides myelin-sensitive biomarkers, such as the pool size ratio (PSR), which is valuable for multiple sclerosis (MS) assessment. However, qMT requires specialized 20-30 minute scans. We propose DEMIST to synthesize PSR maps from standard T1w and FLAIR images using a 3D latent diffusion model with three complementary conditioning mechanisms. Our approach has two stages: first, we train separate autoencoders for PSR and anatomical images to learn aligned latent representations. Second, we train a conditional diffusion model in this latent space on top of a frozen diffusion foundation backbone. Conditioning is decoupled into: (i) \textbf{semantic} tokens via cross-attention, (ii) \textbf{spatial} per-scale residual hints via a 3D ControlNet branch, and (iii) \textbf{adaptive} LoRA-modulated attention. We include edge-aware loss terms to preserve lesion boundaries and alignment losses to maintain quantitative consistency, while keeping the number of trainable parameters low and retaining the inductive bias of the pretrained model. We evaluate on 163 scans from 99 subjects using 5-fold cross-validation. Our method outperforms VAE, GAN and diffusion baselines on multiple metrics, producing sharper boundaries and better quantitative agreement with ground truth. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/MedICL-VU/MS-Synthesis-3DcLDM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge