Geng Sun
Agentic AI for Integrated Sensing and Communication: Analysis, Framework, and Case Study
Dec 17, 2025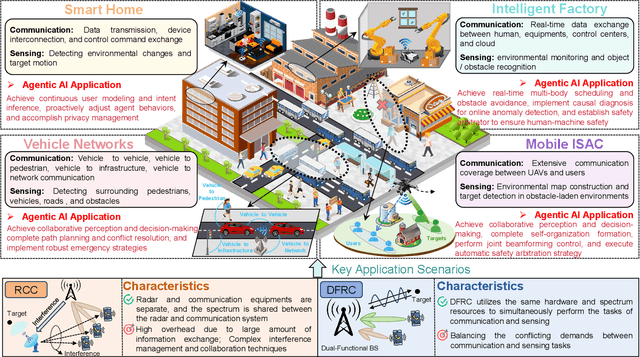
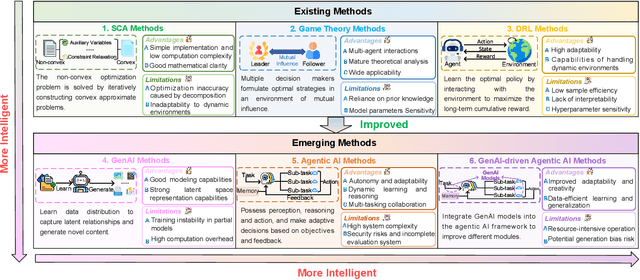
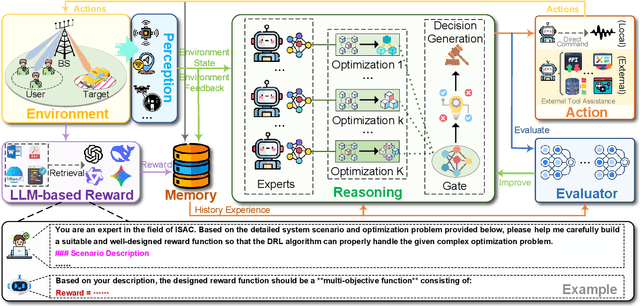
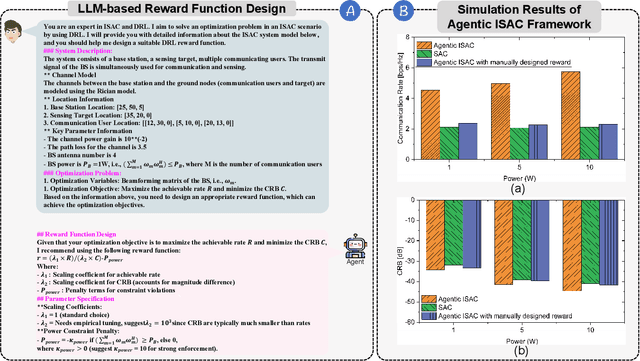
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key development direction in the sixth-generation (6G) era, which provides essential support for the collaborative sensing and communication of future intelligent networks. However, as wireless environments become increasingly dynamic and complex, ISAC systems require more intelligent processing and more autonomous operation to maintain efficiency and adaptability. Meanwhile, agentic artificial intelligence (AI) offers a feasible solution to address these challenges by enabling continuous perception-reasoning-action loops in dynamic environments to support intelligent, autonomous, and efficient operation for ISAC systems. As such, we delve into the application value and prospects of agentic AI in ISAC systems in this work. Firstly, we provide a comprehensive review of agentic AI and ISAC systems to demonstrate their key characteristics. Secondly, we show several common optimization approaches for ISAC systems and highlight the significant advantages of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI)-based agentic AI. Thirdly, we propose a novel agentic ISAC framework and prensent a case study to verify its superiority in optimizing ISAC performance. Finally, we clarify future research directions for agentic AI-based ISAC systems.
Stackelberg Game-Driven Defense for ISAC Against Channel Attacks in Low-Altitude Networks
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:The increasing saturation of terrestrial resources has driven economic activities into low-altitude airspace. These activities, such as air taxis, rely on low-altitude wireless networks, and one key enabling technology is integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). However, in low-altitude airspace, ISAC is vulnerable to channel-access attacks, thereby degrading performance and threatening safety. To address this, we propose a defense framework based on a Stackelberg game. Specifically, we first model the system under attack, deriving metrics for the communication and the sensing to quantify performance. Then, we formulate the interaction as a three-player game where a malicious attacker acts as the leader, while the legitimate drone and ground base station act as followers. Using a backward induction algorithm, we obtain the Stackelberg equilibrium, allowing the defenders to dynamically adjust their strategies to mitigate the attack. Simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm converges to a stable solution and outperforms existing baselines, ensuring reliable ISAC performance for critical low-altitude applications.
Low-Altitude UAV-Carried Movable Antenna for Joint Wireless Power Transfer and Covert Communications
Oct 30, 2025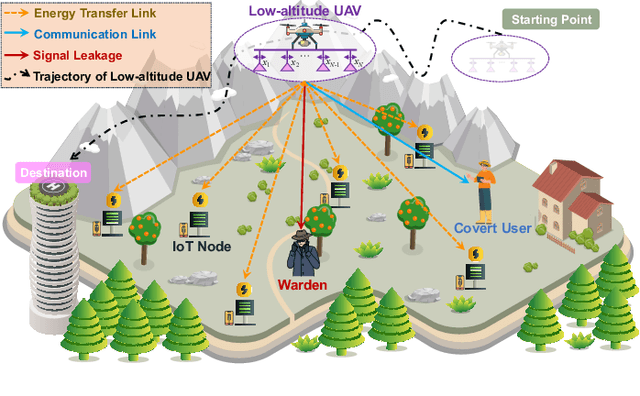
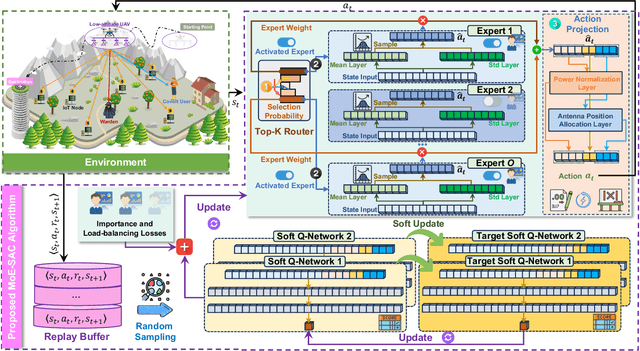
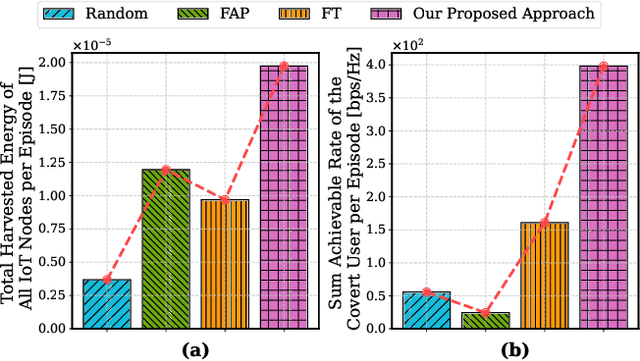
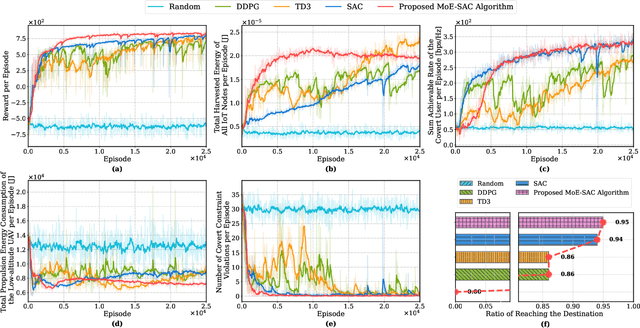
Abstract:The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) networks has created an urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, particularly for the battery-constrained spatially distributed IoT nodes. While low-altitude uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) employed with wireless power transfer (WPT) capabilities offer a promising solution, the line-of-sight channels that facilitate efficient energy delivery also expose sensitive operational data to adversaries. This paper proposes a novel low-altitude UAV-carried movable antenna-enhanced transmission system joint WPT and covert communications, which simultaneously performs energy supplements to IoT nodes and establishes transmission links with a covert user by leveraging wireless energy signals as a natural cover. Then, we formulate a multi-objective optimization problem that jointly maximizes the total harvested energy of IoT nodes and sum achievable rate of the covert user, while minimizing the propulsion energy consumption of the low-altitude UAV. To address the non-convex and temporally coupled optimization problem, we propose a mixture-of-experts-augmented soft actor-critic (MoE-SAC) algorithm that employs a sparse Top-K gated mixture-of-shallow-experts architecture to represent multimodal policy distributions arising from the conflicting optimization objectives. We also incorporate an action projection module that explicitly enforces per-time-slot power budget constraints and antenna position constraints. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly outperforms some baseline approaches and other state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning algorithms.
Cost Minimization for Space-Air-Ground Integrated Multi-Access Edge Computing Systems
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:Space-air-ground integrated multi-access edge computing (SAGIN-MEC) provides a promising solution for the rapidly developing low-altitude economy (LAE) to deliver flexible and wide-area computing services. However, fully realizing the potential of SAGIN-MEC in the LAE presents significant challenges, including coordinating decisions across heterogeneous nodes with different roles, modeling complex factors such as mobility and network variability, and handling real-time decision-making under partially observable environment with hybrid variables. To address these challenges, we first present a hierarchical SAGIN-MEC architecture that enables the coordination between user devices (UDs), uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), and satellites. Then, we formulate a UD cost minimization optimization problem (UCMOP) to minimize the UD cost by jointly optimizing the task offloading ratio, UAV trajectory planning, computing resource allocation, and UD association. We show that the UCMOP is an NP-hard problem. To overcome this challenge, we propose a multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (MADDPG)-convex optimization and coalitional game (MADDPG-COCG) algorithm. Specifically, we employ the MADDPG algorithm to optimize the continuous temporal decisions for heterogeneous nodes in the partially observable SAGIN-MEC system. Moreover, we propose a convex optimization and coalitional game (COCG) method to enhance the conventional MADDPG by deterministically handling the hybrid and varying-dimensional decisions. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed MADDPG-COCG algorithm significantly enhances the user-centric performances in terms of the aggregated UD cost, task completion delay, and UD energy consumption, with a slight increase in UAV energy consumption, compared to the benchmark algorithms. Moreover, the MADDPG-COCG algorithm shows superior convergence stability and scalability.
Joint AoI and Handover Optimization in Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Despite the widespread deployment of terrestrial networks, providing reliable communication services to remote areas and maintaining connectivity during emergencies remains challenging. Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations offer promising solutions with their global coverage capabilities and reduced latency, yet struggle with intermittent coverage and limited communication windows due to orbital dynamics. This paper introduces an age of information (AoI)-aware space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) architecture that leverages a high-altitude platform (HAP) as intelligent relay between the LEO satellites and ground terminals. Our three-layer design employs hybrid free-space optical (FSO) links for high-capacity satellite-to-HAP communication and reliable radio frequency (RF) links for HAP-to-ground transmission, and thus addressing the temporal discontinuity in LEO satellite coverage while serving diverse user priorities. Specifically, we formulate a joint optimization problem to simultaneously minimize the AoI and satellite handover frequency through optimal transmit power distribution and satellite selection decisions. This highly dynamic, non-convex problem with time-coupled constraints presents significant computational challenges for traditional approaches. To address these difficulties, we propose a novel diffusion model (DM)-enhanced dueling double deep Q-network with action decomposition and state transformer encoder (DD3QN-AS) algorithm that incorporates transformer-based temporal feature extraction and employs a DM-based latent prompt generative module to refine state-action representations through conditional denoising. Simulation results highlight the superior performance of the proposed approach compared with policy-based methods and some other deep reinforcement learning (DRL) benchmarks.
Toward Multi-Functional LAWNs with ISAC: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Road Ahead
Aug 24, 2025



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has been envisioned as a foundational technology for future low-altitude wireless networks (LAWNs), enabling real-time environmental perception and data exchange across aerial-ground systems. In this article, we first explore the roles of ISAC in LAWNs from both node-level and network-level perspectives. We highlight the performance gains achieved through hierarchical integration and cooperation, wherein key design trade-offs are demonstrated. Apart from physical-layer enhancements, emerging LAWN applications demand broader functionalities. To this end, we propose a multi-functional LAWN framework that extends ISAC with capabilities in control, computation, wireless power transfer, and large language model (LLM)-based intelligence. We further provide a representative case study to present the benefits of ISAC-enabled LAWNs and the promising research directions are finally outlined.
Energy Efficient Trajectory Control and Resource Allocation in Multi-UAV-assisted MEC via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Mobile edge computing (MEC) is a promising technique to improve the computational capacity of smart devices (SDs) in Internet of Things (IoT). However, the performance of MEC is restricted due to its fixed location and limited service scope. Hence, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted MEC system, where multiple UAVs are dispatched and each UAV can simultaneously provide computing service for multiple SDs. To improve the performance of system, we formulated a UAV-based trajectory control and resource allocation multi-objective optimization problem (TCRAMOP) to simultaneously maximize the offloading number of UAVs and minimize total offloading delay and total energy consumption of UAVs by optimizing the flight paths of UAVs as well as the computing resource allocated to served SDs. Then, consider that the solution of TCRAMOP requires continuous decision-making and the system is dynamic, we propose an enhanced deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm, namely, distributed proximal policy optimization with imitation learning (DPPOIL). This algorithm incorporates the generative adversarial imitation learning technique to improve the policy performance. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed DPPOIL and prove that the learned strategy of DPPOIL is better compared with other baseline methods.
Large AI Model-Enabled Secure Communications in Low-Altitude Wireless Networks: Concepts, Perspectives and Case Study
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Low-altitude wireless networks (LAWNs) have the potential to revolutionize communications by supporting a range of applications, including urban parcel delivery, aerial inspections and air taxis. However, compared with traditional wireless networks, LAWNs face unique security challenges due to low-altitude operations, frequent mobility and reliance on unlicensed spectrum, making it more vulnerable to some malicious attacks. In this paper, we investigate some large artificial intelligence model (LAM)-enabled solutions for secure communications in LAWNs. Specifically, we first explore the amplified security risks and important limitations of traditional AI methods in LAWNs. Then, we introduce the basic concepts of LAMs and delve into the role of LAMs in addressing these challenges. To demonstrate the practical benefits of LAMs for secure communications in LAWNs, we propose a novel LAM-based optimization framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate enhanced state features on top of handcrafted representations, and to design intrinsic rewards accordingly, thereby improving reinforcement learning performance for secure communication tasks. Through a typical case study, simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Finally, we outline future directions for integrating LAMs into secure LAWN applications.
From Ground to Sky: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges Shaping Low-Altitude Wireless Networks
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:In this article, we introduce a novel low-altitude wireless network (LAWN), which is a reconfigurable, three-dimensional (3D) layered architecture. In particular, the LAWN integrates connectivity, sensing, control, and computing across aerial and terrestrial nodes that enable seamless operation in complex, dynamic, and mission-critical environments. In this article, we introduce a novel low-altitude wireless network (LAWN), which is a reconfigurable, three-dimensional (3D) layered architecture. Different from the conventional aerial communication systems, LAWN's distinctive feature is its tight integration of functional planes in which multiple functionalities continually reshape themselves to operate safely and efficiently in the low-altitude sky. With the LAWN, we discuss several enabling technologies, such as integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), semantic communication, and fully-actuated control systems. Finally, we identify potential applications and key cross-layer challenges. This article offers a comprehensive roadmap for future research and development in the low-altitude airspace.
Temporal Spectrum Cartography in Low-Altitude Economy Networks: A Generative AI Framework with Multi-Agent Learning
May 21, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a two-stage generative AI (GenAI) framework tailored for temporal spectrum cartography in low-altitude economy networks (LAENets). LAENets, characterized by diverse aerial devices such as UAVs, rely heavily on wireless communication technologies while facing challenges, including spectrum congestion and dynamic environmental interference. Traditional spectrum cartography methods have limitations in handling the temporal and spatial complexities inherent to these networks. Addressing these challenges, the proposed framework first employs a Reconstructive Masked Autoencoder (RecMAE) capable of accurately reconstructing spectrum maps from sparse and temporally varying sensor data using a novel dual-mask mechanism. This approach significantly enhances the precision of reconstructed radio frequency (RF) power maps. In the second stage, the Multi-agent Diffusion Policy (MADP) method integrates diffusion-based reinforcement learning to optimize the trajectories of dynamic UAV sensors. By leveraging temporal-attention encoding, this method effectively manages spatial exploration and exploitation to minimize cumulative reconstruction errors. Extensive numerical experiments validate that this integrated GenAI framework outperforms traditional interpolation methods and deep learning baselines by achieving 57.35% and 88.68% reconstruction error reduction, respectively. The proposed trajectory planner substantially improves spectrum map accuracy, reconstruction stability, and sensor deployment efficiency in dynamically evolving low-altitude environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge