Yunqi Cai
CMPhysBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Condensed Matter Physics
Aug 25, 2025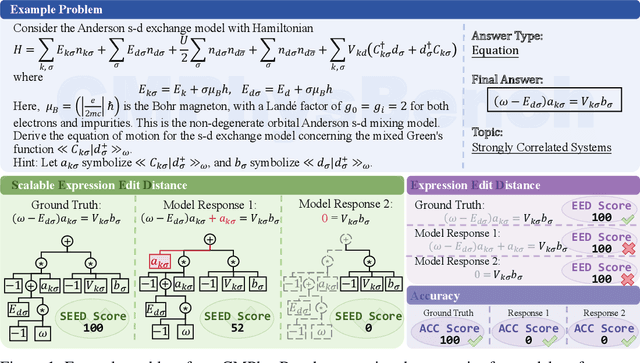
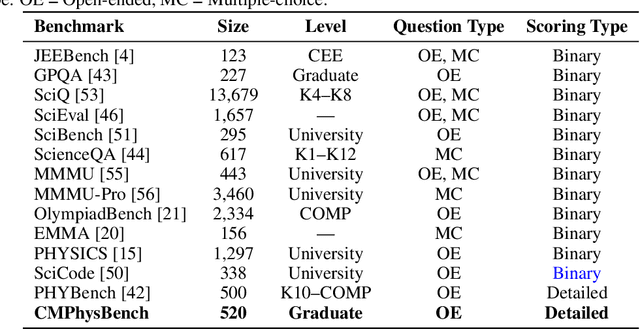
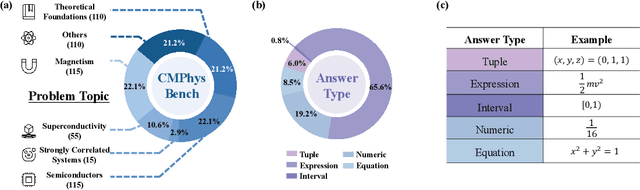
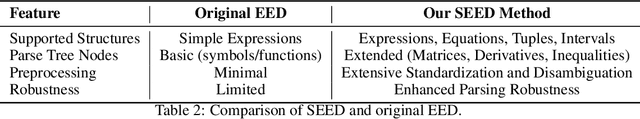
Abstract:We introduce CMPhysBench, designed to assess the proficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Condensed Matter Physics, as a novel Benchmark. CMPhysBench is composed of more than 520 graduate-level meticulously curated questions covering both representative subfields and foundational theoretical frameworks of condensed matter physics, such as magnetism, superconductivity, strongly correlated systems, etc. To ensure a deep understanding of the problem-solving process,we focus exclusively on calculation problems, requiring LLMs to independently generate comprehensive solutions. Meanwhile, leveraging tree-based representations of expressions, we introduce the Scalable Expression Edit Distance (SEED) score, which provides fine-grained (non-binary) partial credit and yields a more accurate assessment of similarity between prediction and ground-truth. Our results show that even the best models, Grok-4, reach only 36 average SEED score and 28% accuracy on CMPhysBench, underscoring a significant capability gap, especially for this practical and frontier domain relative to traditional physics. The code anddataset are publicly available at https://github.com/CMPhysBench/CMPhysBench.
NeuralMAG: Fast and Generalizable Micromagnetic Simulation with Deep Neural Nets
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:Micromagnetics has made significant strides, particularly due to its wide-ranging applications in magnetic storage design. Numerical simulation is a cornerstone of micromagnetics research, relying on first-principle rules to compute the dynamic evolution of micromagnetic systems based on the renowned LLG equation, named after Landau, Lifshitz, and Gilbert. However, simulations are often hindered by their slow speed. Although Fast-Fourier transformation (FFT) calculations reduce the computational complexity to O(NlogN), it remains impractical for large-scale simulations. In this paper, we introduce NeuralMAG, a deep learning approach to micromagnetic simulation. Our approach follows the LLG iterative framework but accelerates demagnetizing field computation through the employment of a U-shaped neural network (Unet). The Unet architecture comprises an encoder that extracts aggregated spins at various scales and learns the local interaction at each scale, followed by a decoder that accumulates the local interactions at different scales to approximate the global convolution. This divide-and-accumulate scheme achieves a time complexity of O(N), significantly enhancing the speed and feasibility of large-scale simulations. Unlike existing neural methods, NeuralMAG concentrates on the core computation rather than an end-to-end approximation for a specific task, making it inherently generalizable. To validate the new approach, we trained a single model and evaluated it on two micromagnetics tasks with various sample sizes, shapes, and material settings.
An MAP Estimation for Between-Class Variance
Nov 24, 2021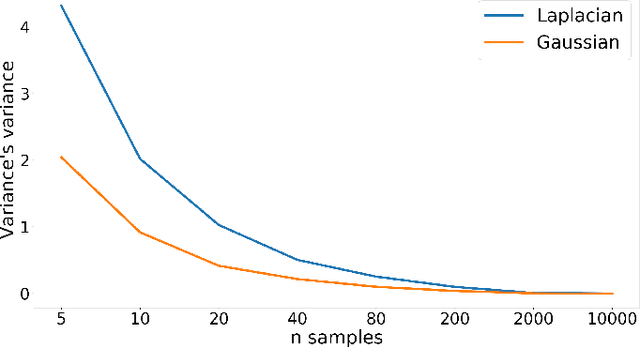
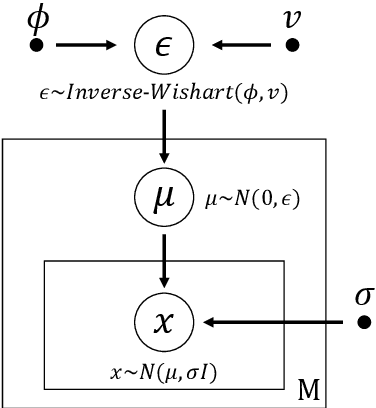
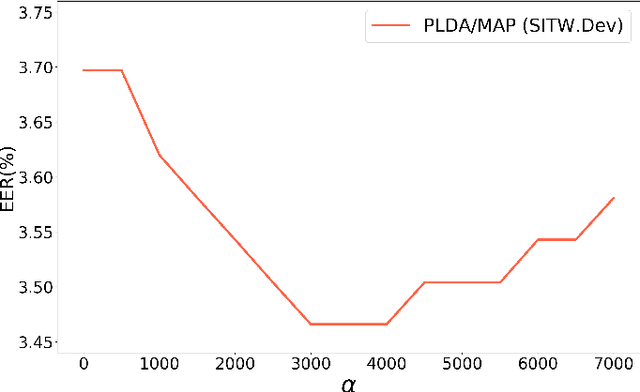
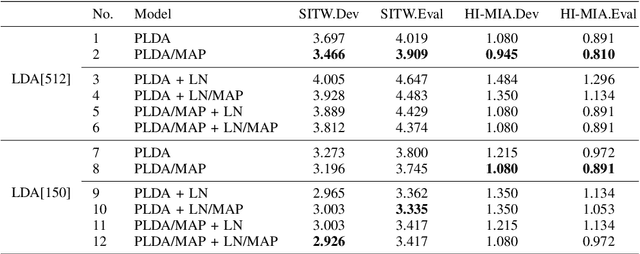
Abstract:Probabilistic linear discriminant analysis (PLDA) has been widely used in open-set verification tasks, such as speaker verification. A potential issue of this model is that the training set often contains limited number of classes, which makes the estimation for the between-class variance unreliable. This unreliable estimation often leads to degraded generalization. In this paper, we present an MAP estimation for the between-class variance, by employing an Inverse-Wishart prior. A key problem is that with hierarchical models such as PLDA, the prior is placed on the variance of class means while the likelihood is based on class members, which makes the posterior inference intractable. We derive a simple MAP estimation for such a model, and test it in both PLDA scoring and length normalization. In both cases, the MAP-based estimation delivers interesting performance improvement.
CN-Celeb: multi-genre speaker recognition
Dec 23, 2020
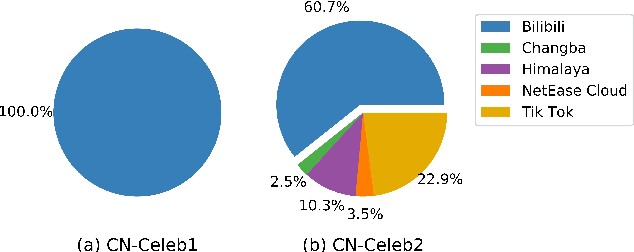
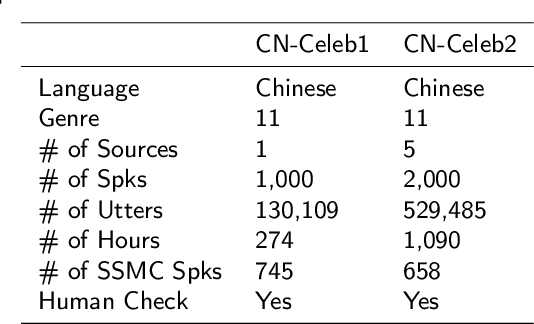
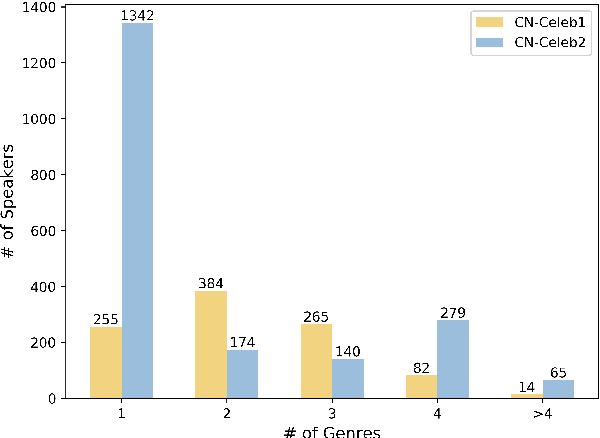
Abstract:Research on speaker recognition is extending to address the vulnerability in the wild conditions, among which genre mismatch is perhaps the most challenging, for instance, enrollment with reading speech while testing with conversational or singing audio. This mismatch leads to complex and composite inter-session variations, both intrinsic (i.e., speaking style, physiological status) and extrinsic (i.e., recording device, background noise). Unfortunately, the few existing multi-genre corpora are not only limited in size but are also recorded under controlled conditions, which cannot support conclusive research on the multi-genre problem. In this work, we firstly publish CN-Celeb, a large-scale multi-genre corpus that includes in-the-wild speech utterances of 3,000 speakers in 11 different genres. Secondly, using this dataset, we conduct a comprehensive study on the multi-genre phenomenon, in particular the impact of the multi-genre challenge on speaker recognition, and on how to utilize the valuable multi-genre data more efficiently.
Deep Speaker Vector Normalization with Maximum Gaussianality Training
Oct 30, 2020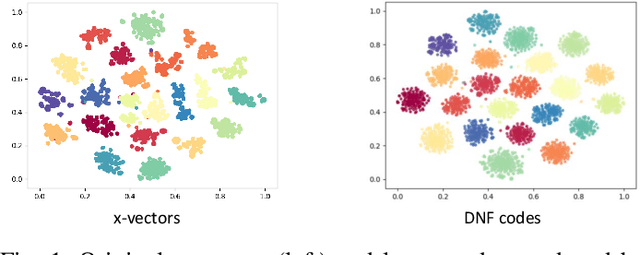
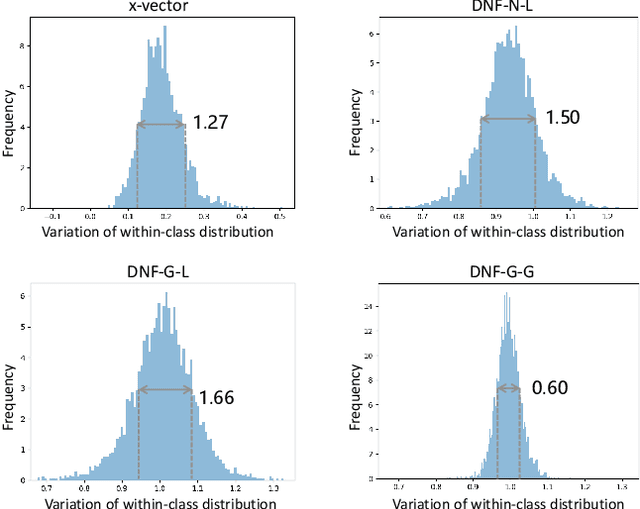
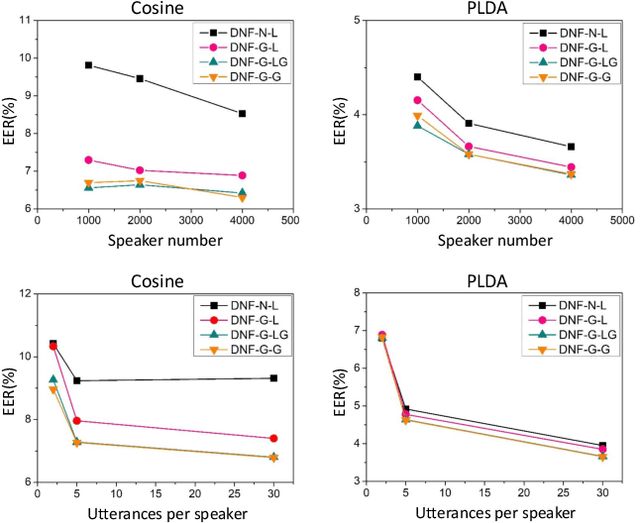
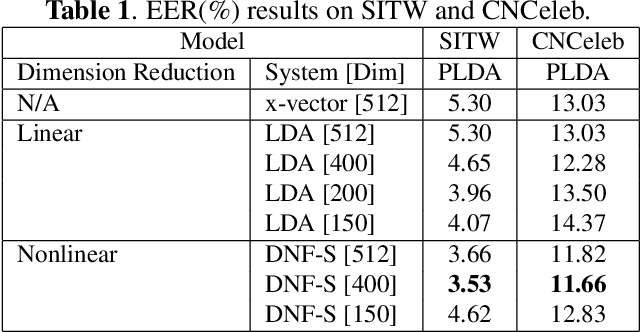
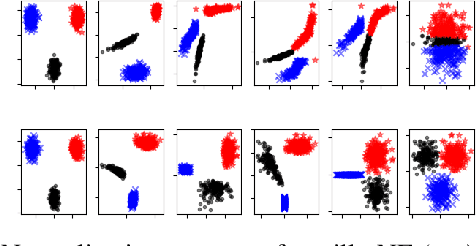
Abstract:Deep speaker embedding represents the state-of-the-art technique for speaker recognition. A key problem with this approach is that the resulting deep speaker vectors tend to be irregularly distributed. In previous research, we proposed a deep normalization approach based on a new discriminative normalization flow (DNF) model, by which the distributions of individual speakers are arguably transformed to homogeneous Gaussians. This normalization was demonstrated to be effective, but despite this remarkable success, we empirically found that the latent codes produced by the DNF model are generally neither homogeneous nor Gaussian, although the model has assumed so. In this paper, we argue that this problem is largely attributed to the maximum-likelihood (ML) training criterion of the DNF model, which aims to maximize the likelihood of the observations but not necessarily improve the Gaussianality of the latent codes. We therefore propose a new Maximum Gaussianality (MG) training approach that directly maximizes the Gaussianality of the latent codes. Our experiments on two data sets, SITW and CNCeleb, demonstrate that our new MG training approach can deliver much better performance than the previous ML training, and exhibits improved domain generalizability, particularly with regard to cosine scoring.
Deep generative LDA
Oct 30, 2020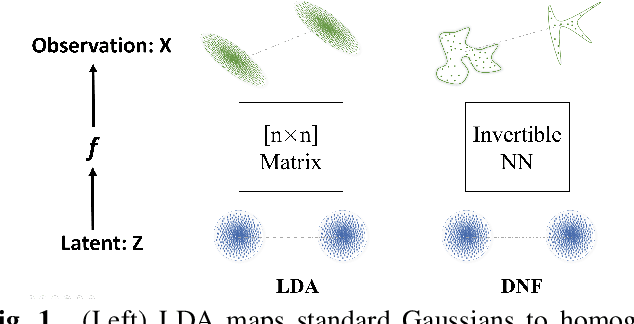
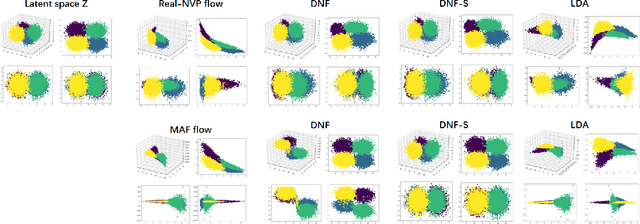
Abstract:Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) is a popular tool for classification and dimension reduction. Limited by its linear form and the underlying Gaussian assumption, however, LDA is not applicable in situations where the data distribution is complex. Recently, we proposed a discriminative normalization flow (DNF) model. In this study, we reinterpret DNF as a deep generative LDA model, and study its properties in representing complex data. We conducted a simulation experiment and a speaker recognition experiment. The results show that DNF and its subspace version are much more powerful than the conventional LDA in modeling complex data and retrieving low-dimensional representations.
Deep generative factorization for speech signal
Oct 27, 2020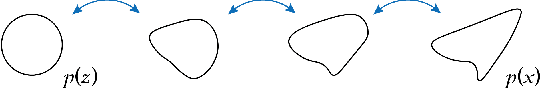
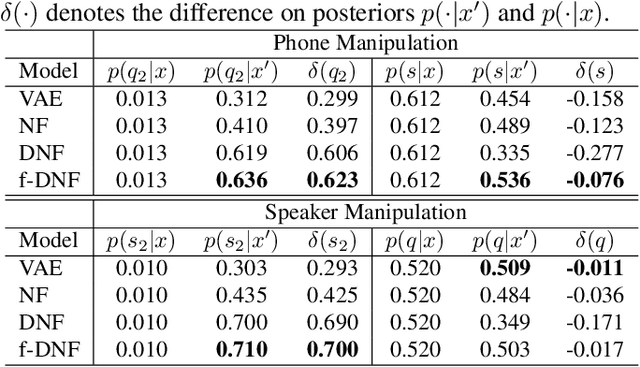
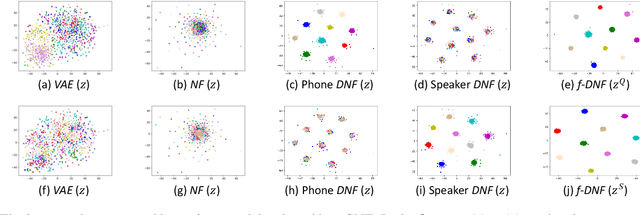
Abstract:Various information factors are blended in speech signals, which forms the primary difficulty for most speech information processing tasks. An intuitive idea is to factorize speech signal into individual information factors (e.g., phonetic content and speaker trait), though it turns out to be highly challenging. This paper presents a speech factorization approach based on a novel factorial discriminative normalization flow model (factorial DNF). Experiments conducted on a two-factor case that involves phonetic content and speaker trait demonstrates that the proposed factorial DNF has powerful capability to factorize speech signals and outperforms several comparative models in terms of information representation and manipulation.
Deep Normalization for Speaker Vectors
Apr 07, 2020
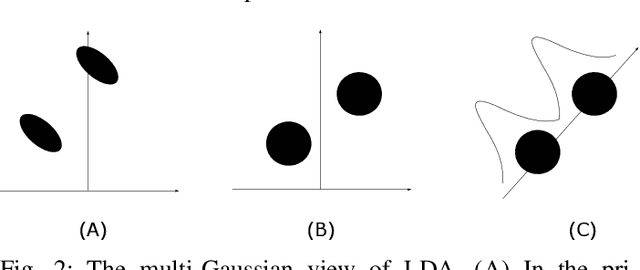
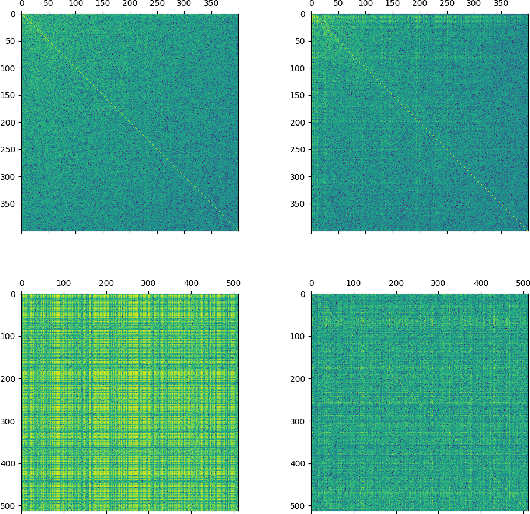
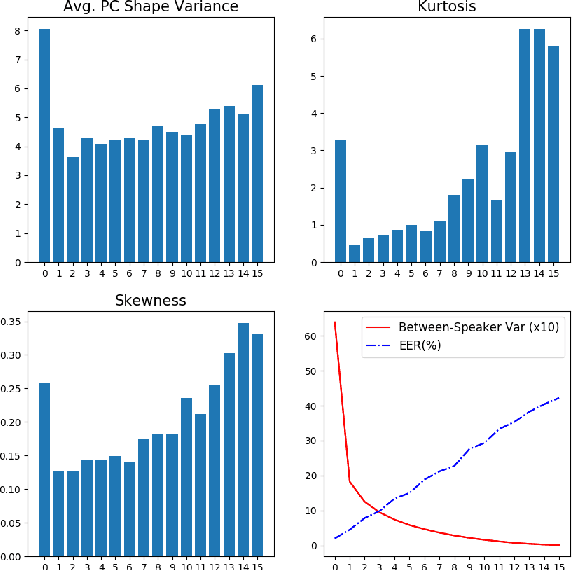
Abstract:Deep speaker embedding has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in audio speaker recognition (SRE). However, one potential issue with this approach is that the speaker vectors derived from deep embedding models tend to be non-Gaussian for each individual speaker, and non-homogeneous for distributions of different speakers. These irregular distributions can seriously impact SRE performance, especially with the popular PLDA scoring method, which assumes homogeneous Gaussian distribution. In this paper, we argue that deep speaker vectors require deep normalization, and propose a deep normalization approach based on a novel discriminative normalization flow (DNF) model. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach with experiments using the widely used SITW and CNCeleb corpora. In these experiments, the DNF-based normalization delivered substantial performance gains and also showed strong generalization capability in out-of-domain tests.
CN-CELEB: a challenging Chinese speaker recognition dataset
Oct 31, 2019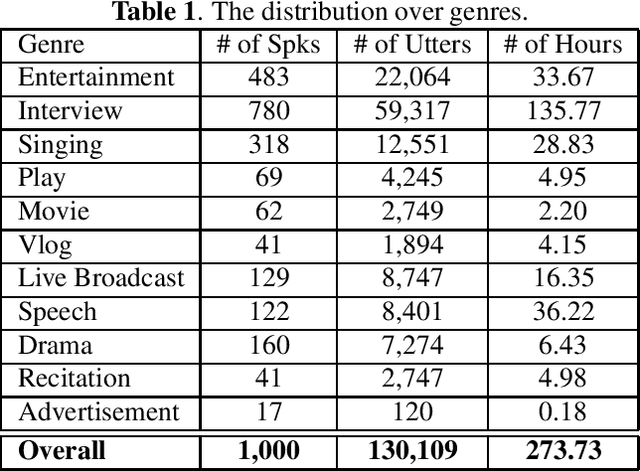
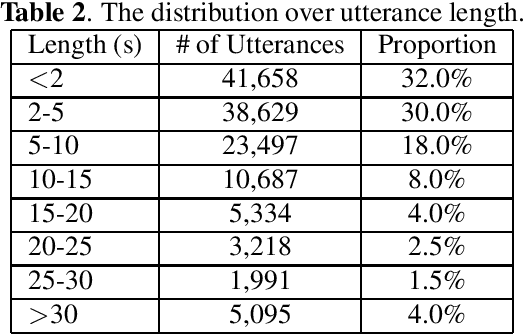
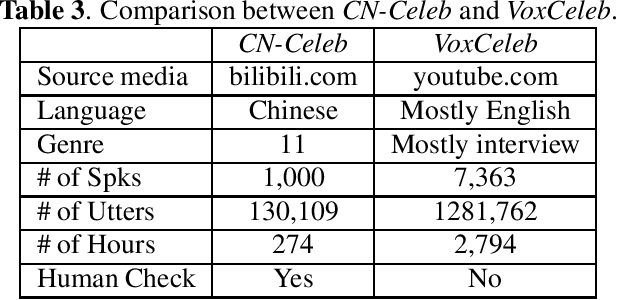
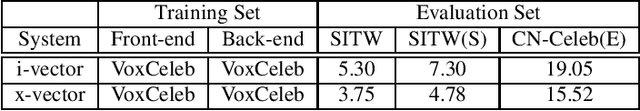
Abstract:Recently, researchers set an ambitious goal of conducting speaker recognition in unconstrained conditions where the variations on ambient, channel and emotion could be arbitrary. However, most publicly available datasets are collected under constrained environments, i.e., with little noise and limited channel variation. These datasets tend to deliver over optimistic performance and do not meet the request of research on speaker recognition in unconstrained conditions. In this paper, we present CN-Celeb, a large-scale speaker recognition dataset collected `in the wild'. This dataset contains more than 130,000 utterances from 1,000 Chinese celebrities, and covers 11 different genres in real world. Experiments conducted with two state-of-the-art speaker recognition approaches (i-vector and x-vector) show that the performance on CN-Celeb is far inferior to the one obtained on VoxCeleb, a widely used speaker recognition dataset. This result demonstrates that in real-life conditions, the performance of existing techniques might be much worse than it was thought. Our database is free for researchers and can be downloaded from http://project.cslt.org.
On Investigation of Unsupervised Speech Factorization Based on Normalization Flow
Oct 29, 2019
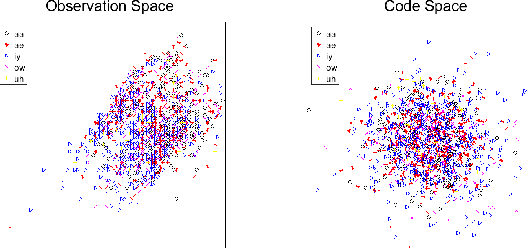
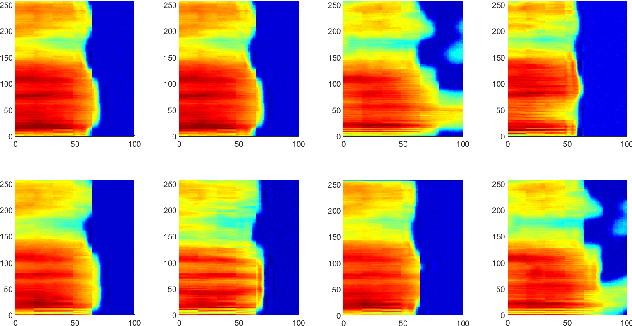
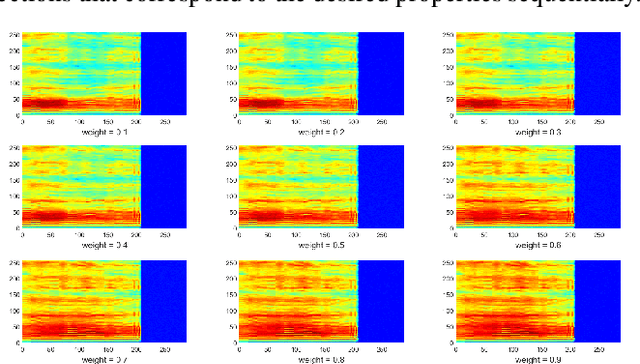
Abstract:Speech signals are complex composites of various information, including phonetic content, speaker traits, channel effect, etc. Decomposing this complicated mixture into independent factors, i.e., speech factorization, is fundamentally important and plays the central role in many important algorithms of modern speech processing tasks. In this paper, we present a preliminary investigation on unsupervised speech factorization based on the normalization flow model. This model constructs a complex invertible transform, by which we can project speech segments into a latent code space where the distribution is a simple diagonal Gaussian. Our preliminary investigation on the TIMIT database shows that this code space exhibits favorable properties such as denseness and pseudo linearity, and perceptually important factors such as phonetic content and speaker trait can be represented as particular directions within the code space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge