Feng Yu
RPP: A Certified Poisoned-Sample Detection Framework for Backdoor Attacks under Dataset Imbalance
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Deep neural networks are highly susceptible to backdoor attacks, yet most defense methods to date rely on balanced data, overlooking the pervasive class imbalance in real-world scenarios that can amplify backdoor threats. This paper presents the first in-depth investigation of how the dataset imbalance amplifies backdoor vulnerability, showing that (i) the imbalance induces a majority-class bias that increases susceptibility and (ii) conventional defenses degrade significantly as the imbalance grows. To address this, we propose Randomized Probability Perturbation (RPP), a certified poisoned-sample detection framework that operates in a black-box setting using only model output probabilities. For any inspected sample, RPP determines whether the input has been backdoor-manipulated, while offering provable within-domain detectability guarantees and a probabilistic upper bound on the false positive rate. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks (MNIST, SVHN, CIFAR-10, TinyImageNet and ImageNet10) covering 10 backdoor attacks and 12 baseline defenses show that RPP achieves significantly higher detection accuracy than state-of-the-art defenses, particularly under dataset imbalance. RPP establishes a theoretical and practical foundation for defending against backdoor attacks in real-world environments with imbalanced data.
Unsupervised Feature Selection via Robust Autoencoder and Adaptive Graph Learning
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Effective feature selection is essential for high-dimensional data analysis and machine learning. Unsupervised feature selection (UFS) aims to simultaneously cluster data and identify the most discriminative features. Most existing UFS methods linearly project features into a pseudo-label space for clustering, but they suffer from two critical limitations: (1) an oversimplified linear mapping that fails to capture complex feature relationships, and (2) an assumption of uniform cluster distributions, ignoring outliers prevalent in real-world data. To address these issues, we propose the Robust Autoencoder-based Unsupervised Feature Selection (RAEUFS) model, which leverages a deep autoencoder to learn nonlinear feature representations while inherently improving robustness to outliers. We further develop an efficient optimization algorithm for RAEUFS. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art UFS approaches in both clean and outlier-contaminated data settings.
Mastering Diverse, Unknown, and Cluttered Tracks for Robust Vision-Based Drone Racing
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Most reinforcement learning(RL)-based methods for drone racing target fixed, obstacle-free tracks, leaving the generalization to unknown, cluttered environments largely unaddressed. This challenge stems from the need to balance racing speed and collision avoidance, limited feasible space causing policy exploration trapped in local optima during training, and perceptual ambiguity between gates and obstacles in depth maps-especially when gate positions are only coarsely specified. To overcome these issues, we propose a two-phase learning framework: an initial soft-collision training phase that preserves policy exploration for high-speed flight, followed by a hard-collision refinement phase that enforces robust obstacle avoidance. An adaptive, noise-augmented curriculum with an asymmetric actor-critic architecture gradually shifts the policy's reliance from privileged gate-state information to depth-based visual input. We further impose Lipschitz constraints and integrate a track-primitive generator to enhance motion stability and cross-environment generalization. We evaluate our framework through extensive simulation and ablation studies, and validate it in real-world experiments on a computationally constrained quadrotor. The system achieves agile flight while remaining robust to gate-position errors, developing a generalizable drone racing framework with the capability to operate in diverse, partially unknown and cluttered environments. https://yufengsjtu.github.io/MasterRacing.github.io/
Fused Gromov-Wasserstein Contrastive Learning for Effective Enzyme-Reaction Screening
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Enzymes are crucial catalysts that enable a wide range of biochemical reactions. Efficiently identifying specific enzymes from vast protein libraries is essential for advancing biocatalysis. Traditional computational methods for enzyme screening and retrieval are time-consuming and resource-intensive. Recently, deep learning approaches have shown promise. However, these methods focus solely on the interaction between enzymes and reactions, overlooking the inherent hierarchical relationships within each domain. To address these limitations, we introduce FGW-CLIP, a novel contrastive learning framework based on optimizing the fused Gromov-Wasserstein distance. FGW-CLIP incorporates multiple alignments, including inter-domain alignment between reactions and enzymes and intra-domain alignment within enzymes and reactions. By introducing a tailored regularization term, our method minimizes the Gromov-Wasserstein distance between enzyme and reaction spaces, which enhances information integration across these domains. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superiority of FGW-CLIP in challenging enzyme-reaction tasks. On the widely-used EnzymeMap benchmark, FGW-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance in enzyme virtual screening, as measured by BEDROC and EF metrics. Moreover, FGW-CLIP consistently outperforms across all three splits of ReactZyme, the largest enzyme-reaction benchmark, demonstrating robust generalization to novel enzymes and reactions. These results position FGW-CLIP as a promising framework for enzyme discovery in complex biochemical settings, with strong adaptability across diverse screening scenarios.
TISDiSS: A Training-Time and Inference-Time Scalable Framework for Discriminative Source Separation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Source separation is a fundamental task in speech, music, and audio processing, and it also provides cleaner and larger data for training generative models. However, improving separation performance in practice often depends on increasingly large networks, inflating training and deployment costs. Motivated by recent advances in inference-time scaling for generative modeling, we propose Training-Time and Inference-Time Scalable Discriminative Source Separation (TISDiSS), a unified framework that integrates early-split multi-loss supervision, shared-parameter design, and dynamic inference repetitions. TISDiSS enables flexible speed-performance trade-offs by adjusting inference depth without retraining additional models. We further provide systematic analyses of architectural and training choices and show that training with more inference repetitions improves shallow-inference performance, benefiting low-latency applications. Experiments on standard speech separation benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with a reduced parameter count, establishing TISDiSS as a scalable and practical framework for adaptive source separation.
SpeechForensics: Audio-Visual Speech Representation Learning for Face Forgery Detection
Aug 13, 2025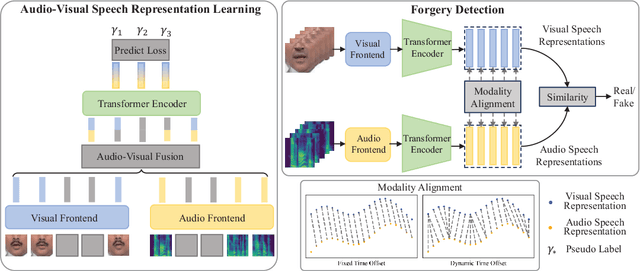
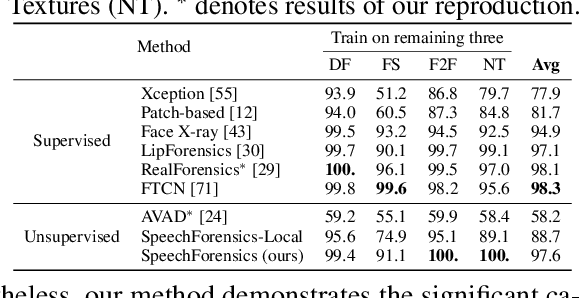
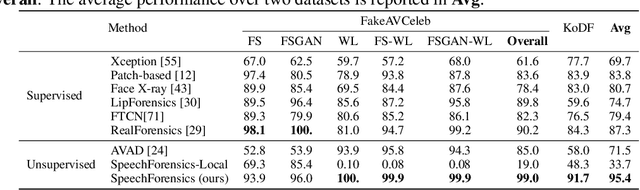
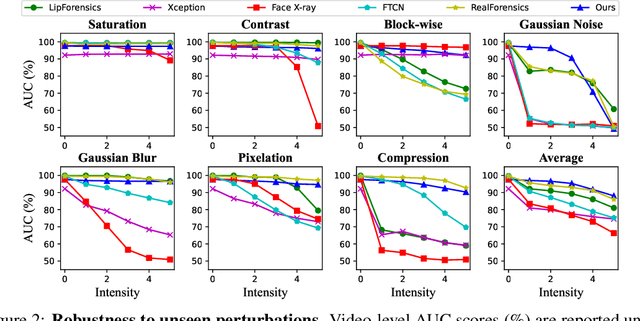
Abstract:Detection of face forgery videos remains a formidable challenge in the field of digital forensics, especially the generalization to unseen datasets and common perturbations. In this paper, we tackle this issue by leveraging the synergy between audio and visual speech elements, embarking on a novel approach through audio-visual speech representation learning. Our work is motivated by the finding that audio signals, enriched with speech content, can provide precise information effectively reflecting facial movements. To this end, we first learn precise audio-visual speech representations on real videos via a self-supervised masked prediction task, which encodes both local and global semantic information simultaneously. Then, the derived model is directly transferred to the forgery detection task. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of cross-dataset generalization and robustness, without the participation of any fake video in model training. Code is available at https://github.com/Eleven4AI/SpeechForensics.
* Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Text as Any-Modality for Zero-Shot Classification by Consistent Prompt Tuning
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:The integration of prompt tuning with multimodal learning has shown significant generalization abilities for various downstream tasks. Despite advancements, existing methods heavily depend on massive modality-specific labeled data (e.g., video, audio, and image), or are customized for a single modality. In this study, we present Text as Any-Modality by Consistent Prompt Tuning (TaAM-CPT), a scalable approach for constructing a general representation model toward unlimited modalities using solely text data. TaAM-CPT comprises modality prompt pools, text construction, and modality-aligned text encoders from pre-trained models, which allows for extending new modalities by simply adding prompt pools and modality-aligned text encoders. To harmonize the learning across different modalities, TaAM-CPT designs intra- and inter-modal learning objectives, which can capture category details within modalities while maintaining semantic consistency across different modalities. Benefiting from its scalable architecture and pre-trained models, TaAM-CPT can be seamlessly extended to accommodate unlimited modalities. Remarkably, without any modality-specific labeled data, TaAM-CPT achieves leading results on diverse datasets spanning various modalities, including video classification, image classification, and audio classification. The code is available at https://github.com/Jinx630/TaAM-CPT.
Interactive Hybrid Rice Breeding with Parametric Dual Projection
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Hybrid rice breeding crossbreeds different rice lines and cultivates the resulting hybrids in fields to select those with desirable agronomic traits, such as higher yields. Recently, genomic selection has emerged as an efficient way for hybrid rice breeding. It predicts the traits of hybrids based on their genes, which helps exclude many undesired hybrids, largely reducing the workload of field cultivation. However, due to the limited accuracy of genomic prediction models, breeders still need to combine their experience with the models to identify regulatory genes that control traits and select hybrids, which remains a time-consuming process. To ease this process, in this paper, we proposed a visual analysis method to facilitate interactive hybrid rice breeding. Regulatory gene identification and hybrid selection naturally ensemble a dual-analysis task. Therefore, we developed a parametric dual projection method with theoretical guarantees to facilitate interactive dual analysis. Based on this dual projection method, we further developed a gene visualization and a hybrid visualization to verify the identified regulatory genes and hybrids. The effectiveness of our method is demonstrated through the quantitative evaluation of the parametric dual projection method, identified regulatory genes and desired hybrids in the case study, and positive feedback from breeders.
Efficient Federated Class-Incremental Learning of Pre-Trained Models via Task-agnostic Low-rank Residual Adaptation
May 18, 2025Abstract:Federated Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (FedPEFT) reduces communication and computation costs in federated fine-tuning of pre-trained models by updating only a small subset of model parameters. However, existing approaches assume static data distributions, failing to adequately address real-world scenarios where new classes continually emerge, particularly in Federated Class Incremental Learning (FCIL). FCIL faces two key challenges: catastrophic forgetting and performance degradation caused by non-IID data across clients. Unlike current methods that maintain separate task-specific components or suffer from aggregation noise during parameter aggregation, we propose Federated Task-agnostic Low-rank Residual Adaptation (Fed-TaLoRA), a novel parameter-efficient approach for fine-tuning in resource-constrained FCIL scenarios. Specifically, we fine-tune only shared task-agnostic LoRA parameters across sequential tasks, effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting while enabling efficient knowledge transfer among clients. Based on a theoretical analysis of aggregation, we develop a novel residual weight update mechanism that ensures accurate knowledge consolidation with minimal overhead. Our methodological innovations are attributed to three key strategies: task-agnostic adaptation, post-aggregation model calibration, and strategic placement of LoRA modules. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that Fed-TaLoRA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in diverse data heterogeneity scenarios while substantially reducing resource requirements.
ELGAR: Expressive Cello Performance Motion Generation for Audio Rendition
May 07, 2025Abstract:The art of instrument performance stands as a vivid manifestation of human creativity and emotion. Nonetheless, generating instrument performance motions is a highly challenging task, as it requires not only capturing intricate movements but also reconstructing the complex dynamics of the performer-instrument interaction. While existing works primarily focus on modeling partial body motions, we propose Expressive ceLlo performance motion Generation for Audio Rendition (ELGAR), a state-of-the-art diffusion-based framework for whole-body fine-grained instrument performance motion generation solely from audio. To emphasize the interactive nature of the instrument performance, we introduce Hand Interactive Contact Loss (HICL) and Bow Interactive Contact Loss (BICL), which effectively guarantee the authenticity of the interplay. Moreover, to better evaluate whether the generated motions align with the semantic context of the music audio, we design novel metrics specifically for string instrument performance motion generation, including finger-contact distance, bow-string distance, and bowing score. Extensive evaluations and ablation studies are conducted to validate the efficacy of the proposed methods. In addition, we put forward a motion generation dataset SPD-GEN, collated and normalized from the MoCap dataset SPD. As demonstrated, ELGAR has shown great potential in generating instrument performance motions with complicated and fast interactions, which will promote further development in areas such as animation, music education, interactive art creation, etc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge