Danping Zou
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Mastering Diverse, Unknown, and Cluttered Tracks for Robust Vision-Based Drone Racing
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Most reinforcement learning(RL)-based methods for drone racing target fixed, obstacle-free tracks, leaving the generalization to unknown, cluttered environments largely unaddressed. This challenge stems from the need to balance racing speed and collision avoidance, limited feasible space causing policy exploration trapped in local optima during training, and perceptual ambiguity between gates and obstacles in depth maps-especially when gate positions are only coarsely specified. To overcome these issues, we propose a two-phase learning framework: an initial soft-collision training phase that preserves policy exploration for high-speed flight, followed by a hard-collision refinement phase that enforces robust obstacle avoidance. An adaptive, noise-augmented curriculum with an asymmetric actor-critic architecture gradually shifts the policy's reliance from privileged gate-state information to depth-based visual input. We further impose Lipschitz constraints and integrate a track-primitive generator to enhance motion stability and cross-environment generalization. We evaluate our framework through extensive simulation and ablation studies, and validate it in real-world experiments on a computationally constrained quadrotor. The system achieves agile flight while remaining robust to gate-position errors, developing a generalizable drone racing framework with the capability to operate in diverse, partially unknown and cluttered environments. https://yufengsjtu.github.io/MasterRacing.github.io/
CoordAR: One-Reference 6D Pose Estimation of Novel Objects via Autoregressive Coordinate Map Generation
Nov 17, 2025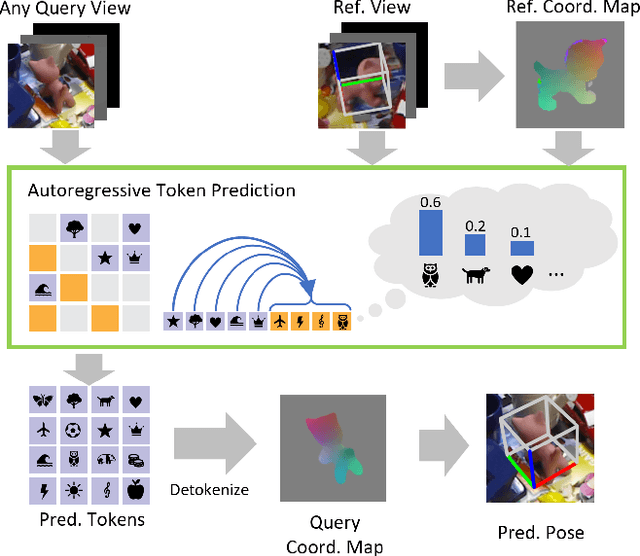
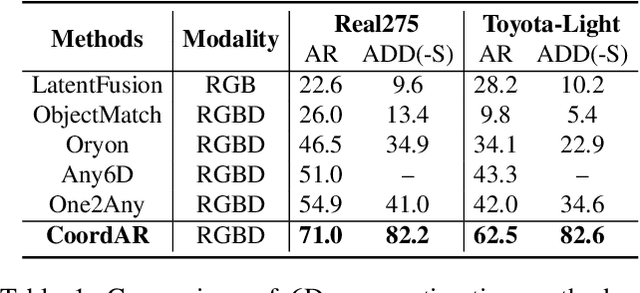
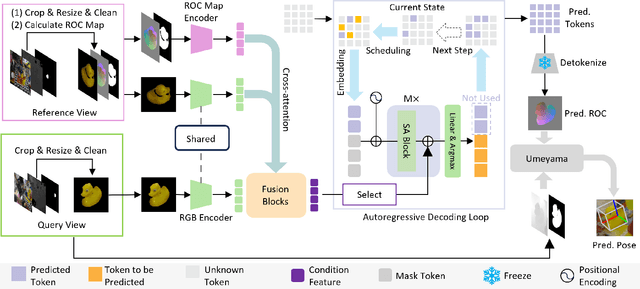
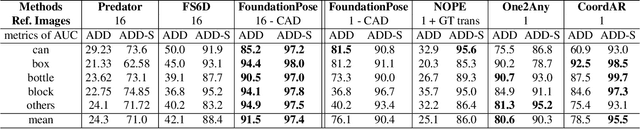
Abstract:Object 6D pose estimation, a crucial task for robotics and augmented reality applications, becomes particularly challenging when dealing with novel objects whose 3D models are not readily available. To reduce dependency on 3D models, recent studies have explored one-reference-based pose estimation, which requires only a single reference view instead of a complete 3D model. However, existing methods that rely on real-valued coordinate regression suffer from limited global consistency due to the local nature of convolutional architectures and face challenges in symmetric or occluded scenarios owing to a lack of uncertainty modeling. We present CoordAR, a novel autoregressive framework for one-reference 6D pose estimation of unseen objects. CoordAR formulates 3D-3D correspondences between the reference and query views as a map of discrete tokens, which is obtained in an autoregressive and probabilistic manner. To enable accurate correspondence regression, CoordAR introduces 1) a novel coordinate map tokenization that enables probabilistic prediction over discretized 3D space; 2) a modality-decoupled encoding strategy that separately encodes RGB appearance and coordinate cues; and 3) an autoregressive transformer decoder conditioned on both position-aligned query features and the partially generated token sequence. With these novel mechanisms, CoordAR significantly outperforms existing methods on multiple benchmarks and demonstrates strong robustness to symmetry, occlusion, and other challenges in real-world tests.
StableTracker: Learning to Stably Track Target via Differentiable Simulation
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:FPV object tracking methods heavily rely on handcraft modular designs, resulting in hardware overload and cumulative error, which seriously degrades the tracking performance, especially for rapidly accelerating or decelerating targets. To address these challenges, we present \textbf{StableTracker}, a learning-based control policy that enables quadrotors to robustly follow the moving target from arbitrary perspectives. The policy is trained using backpropagation-through-time via differentiable simulation, allowing the quadrotor to maintain the target at the center of the visual field in both horizontal and vertical directions, while keeping a fixed relative distance, thereby functioning as an autonomous aerial camera. We compare StableTracker against both state-of-the-art traditional algorithms and learning baselines. Simulation experiments demonstrate that our policy achieves superior accuracy, stability and generalization across varying safe distances, trajectories, and target velocities. Furthermore, a real-world experiment on a quadrotor with an onboard computer validated practicality of the proposed approach.
Head-Aware KV Cache Compression for Efficient Visual Autoregressive Modeling
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Visual Autoregressive (VAR) models have emerged as a powerful approach for multi-modal content creation, offering high efficiency and quality across diverse multimedia applications. However, they face significant memory bottlenecks due to extensive KV cache accumulation during inference. Existing KV cache compression techniques for large language models are suboptimal for VAR models due to, as we identify in this paper, two distinct categories of attention heads in VAR models: Structural Heads, which preserve spatial coherence through diagonal attention patterns, and Contextual Heads, which maintain semantic consistency through vertical attention patterns. These differences render single-strategy KV compression techniques ineffective for VAR models. To address this, we propose HACK, a training-free Head-Aware Compression method for KV cache. HACK allocates asymmetric cache budgets and employs pattern-specific compression strategies tailored to the essential characteristics of each head category. Experiments on Infinity-2B, Infinity-8B, and VAR-d30 demonstrate its effectiveness in text-to-image and class-conditional generation tasks. HACK can hack down up to 50\% and 70\% of cache with minimal performance degradation for VAR-d30 and Infinity-8B, respectively. Even with 70\% and 90\% KV cache compression in VAR-d30 and Infinity-8B, HACK still maintains high-quality generation while reducing memory usage by 44.2\% and 58.9\%, respectively.
ThermoStereoRT: Thermal Stereo Matching in Real Time via Knowledge Distillation and Attention-based Refinement
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce ThermoStereoRT, a real-time thermal stereo matching method designed for all-weather conditions that recovers disparity from two rectified thermal stereo images, envisioning applications such as night-time drone surveillance or under-bed cleaning robots. Leveraging a lightweight yet powerful backbone, ThermoStereoRT constructs a 3D cost volume from thermal images and employs multi-scale attention mechanisms to produce an initial disparity map. To refine this map, we design a novel channel and spatial attention module. Addressing the challenge of sparse ground truth data in thermal imagery, we utilize knowledge distillation to boost performance without increasing computational demands. Comprehensive evaluations on multiple datasets demonstrate that ThermoStereoRT delivers both real-time capacity and robust accuracy, making it a promising solution for real-world deployment in various challenging environments. Our code will be released on https://github.com/SJTU-ViSYS-team/ThermoStereoRT
* 7 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables. Accepted to IEEE ICRA 2025. This is the preprint version
Mapless Collision-Free Flight via MPC using Dual KD-Trees in Cluttered Environments
Mar 13, 2025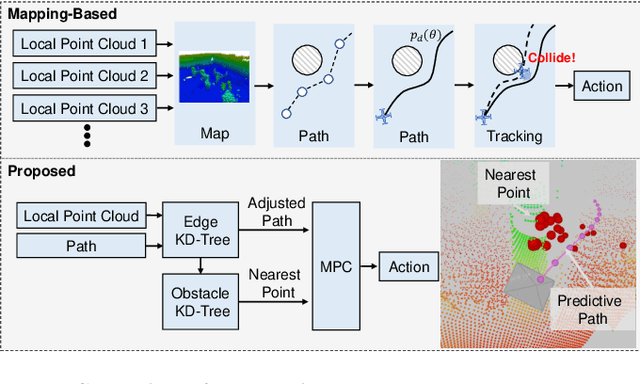
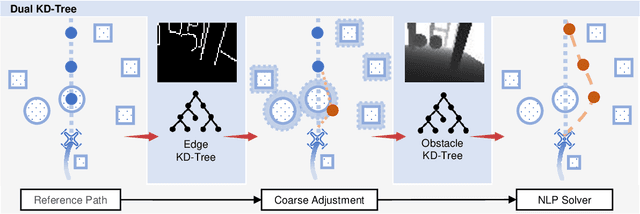
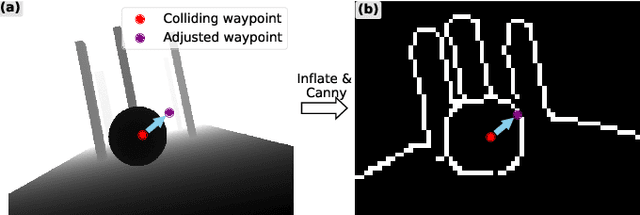
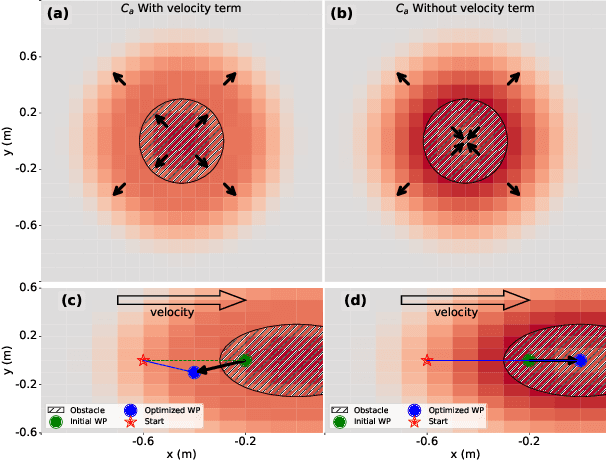
Abstract:Collision-free flight in cluttered environments is a critical capability for autonomous quadrotors. Traditional methods often rely on detailed 3D map construction, trajectory generation, and tracking. However, this cascade pipeline can introduce accumulated errors and computational delays, limiting flight agility and safety. In this paper, we propose a novel method for enabling collision-free flight in cluttered environments without explicitly constructing 3D maps or generating and tracking collision-free trajectories. Instead, we leverage Model Predictive Control (MPC) to directly produce safe actions from sparse waypoints and point clouds from a depth camera. These sparse waypoints are dynamically adjusted online based on nearby obstacles detected from point clouds. To achieve this, we introduce a dual KD-Tree mechanism: the Obstacle KD-Tree quickly identifies the nearest obstacle for avoidance, while the Edge KD-Tree provides a robust initial guess for the MPC solver, preventing it from getting stuck in local minima during obstacle avoidance. We validate our approach through extensive simulations and real-world experiments. The results show that our approach significantly outperforms the mapping-based methods and is also superior to imitation learning-based methods, demonstrating reliable obstacle avoidance at up to 12 m/s in simulations and 6 m/s in real-world tests. Our method provides a simple and robust alternative to existing methods.
ABPT: Amended Backpropagation through Time with Partially Differentiable Rewards
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Using the exact gradients of the rewards to directly optimize policy parameters via backpropagation-through-time (BPTT) enables high training performance for quadrotor tasks. However, designing a fully differentiable reward architecture is often challenging. Partially differentiable rewards will result in biased gradient propagation that degrades training performance. To overcome this limitation, we propose Amended Backpropagation-through-Time (ABPT), a novel approach that mitigates gradient bias while preserving the training efficiency of BPTT. ABPT combines 0-step and N-step returns, effectively reducing the bias by leveraging value gradients from the learned Q-value function. Additionally, it adopts entropy regularization and state initialization mechanisms to encourage exploration during training. We evaluate ABPT on four representative quadrotor flight tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that ABPT converges significantly faster and achieves higher ultimate rewards than existing learning algorithms, particularly in tasks involving partially differentiable rewards.
Seeing Through Pixel Motion: Learning Obstacle Avoidance from Optical Flow with One Camera
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Optical flow captures the motion of pixels in an image sequence over time, providing information about movement, depth, and environmental structure. Flying insects utilize this information to navigate and avoid obstacles, allowing them to execute highly agile maneuvers even in complex environments. Despite its potential, autonomous flying robots have yet to fully leverage this motion information to achieve comparable levels of agility and robustness. Challenges of control from optical flow include extracting accurate optical flow at high speeds, handling noisy estimation, and ensuring robust performance in complex environments. To address these challenges, we propose a novel end-to-end system for quadrotor obstacle avoidance using monocular optical flow. We develop an efficient differentiable simulator coupled with a simplified quadrotor model, allowing our policy to be trained directly through first-order gradient optimization. Additionally, we introduce a central flow attention mechanism and an action-guided active sensing strategy that enhances the policy's focus on task-relevant optical flow observations to enable more responsive decision-making during flight. Our system is validated both in simulation and the real world using an FPV racing drone. Despite being trained in a simple environment in simulation, our system is validated both in simulation and the real world using an FPV racing drone. Despite being trained in a simple environment in simulation, our system demonstrates agile and robust flight in various unknown, cluttered environments in the real world at speeds of up to 6m/s.
VisFly: An Efficient and Versatile Simulator for Training Vision-based Flight
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:We present VisFly, a quadrotor simulator designed to efficiently train vision-based flight policies using reinforcement learning algorithms. VisFly offers a user-friendly framework and interfaces, leveraging Habitat-Sim's rendering engines to achieve frame rates exceeding 10,000 frames per second for rendering motion and sensor data. The simulator incorporates differentiable physics and seamlessly integrates with the Gym environment, facilitating the straightforward implementation of various learning algorithms. It supports the direct import of all open-source scene datasets compatible with Habitat-Sim, enabling training on diverse real-world environments and ensuring fair comparisons of learned flight policies. We also propose a general policy architecture for three typical flight tasks relying on visual observations, which have been validated in our simulator using reinforcement learning. The simulator will be available at [https://github.com/SJTU-ViSYS/VisFly].
Back to Newton's Laws: Learning Vision-based Agile Flight via Differentiable Physics
Jul 16, 2024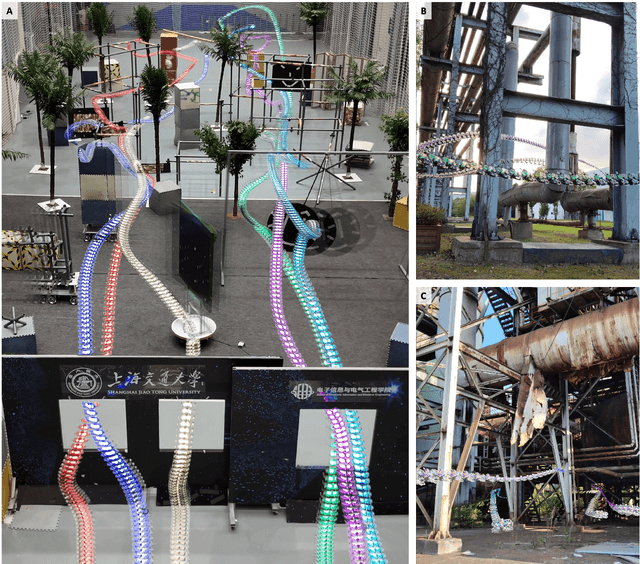
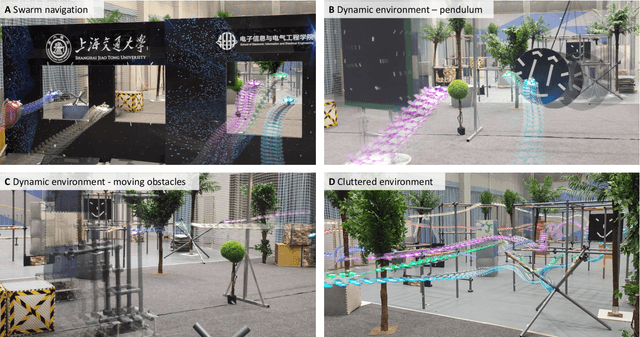
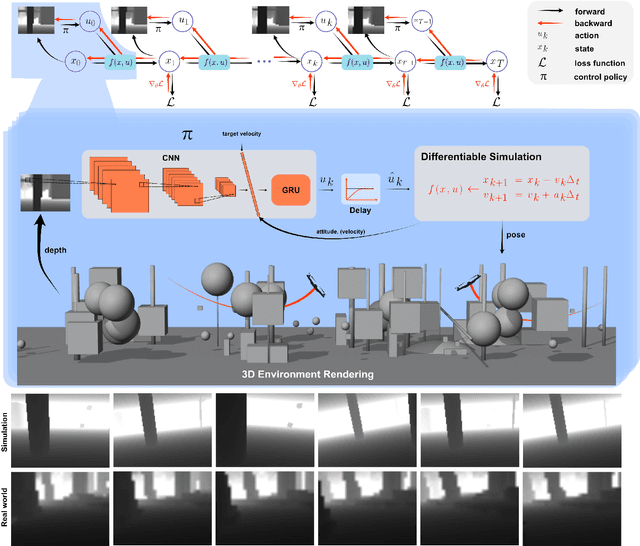
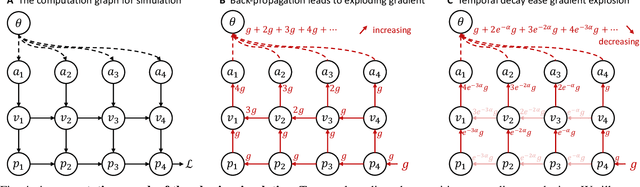
Abstract:Swarm navigation in cluttered environments is a grand challenge in robotics. This work combines deep learning with first-principle physics through differentiable simulation to enable autonomous navigation of multiple aerial robots through complex environments at high speed. Our approach optimizes a neural network control policy directly by backpropagating loss gradients through the robot simulation using a simple point-mass physics model and a depth rendering engine. Despite this simplicity, our method excels in challenging tasks for both multi-agent and single-agent applications with zero-shot sim-to-real transfer. In multi-agent scenarios, our system demonstrates self-organized behavior, enabling autonomous coordination without communication or centralized planning - an achievement not seen in existing traditional or learning-based methods. In single-agent scenarios, our system achieves a 90% success rate in navigating through complex environments, significantly surpassing the 60% success rate of the previous state-of-the-art approach. Our system can operate without state estimation and adapt to dynamic obstacles. In real-world forest environments, it navigates at speeds up to 20 m/s, doubling the speed of previous imitation learning-based solutions. Notably, all these capabilities are deployed on a budget-friendly $21 computer, costing less than 5% of a GPU-equipped board used in existing systems. Video demonstrations are available at https://youtu.be/LKg9hJqc2cc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge