Yang Deng
When Does Context Help? Error Dynamics of Contextual Information in Large Language Models
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Contextual information at inference time, such as demonstrations, retrieved knowledge, or interaction history, can substantially improve large language models (LLMs) without parameter updates, yet its theoretical role remains poorly understood beyond specific settings such as in-context learning (ICL). We present a unified theoretical framework for analyzing the effect of arbitrary contextual information in Transformer-based LLMs. Our analysis characterizes contextual influence through output error dynamics. In a single-layer Transformer, we prove that the context-conditioned error vector decomposes additively into the baseline error vector and a contextual correction vector. This yields necessary geometric conditions for error reduction: the contextual correction must align with the negative baseline error and satisfy a norm constraint. We further show that the contextual correction norm admits an explicit upper bound determined by context-query relevance and complementarity. These results extend to multi-context and multi-layer Transformers. Experiments across ICL, retrieval-augmented generation, and memory evolution validate our theory and motivate a principled context selection strategy that improves performance by $0.6\%$.
Large Language Model Agents Are Not Always Faithful Self-Evolvers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Self-evolving large language model (LLM) agents continually improve by accumulating and reusing past experience, yet it remains unclear whether they faithfully rely on that experience to guide their behavior. We present the first systematic investigation of experience faithfulness, the causal dependence of an agent's decisions on the experience it is given, in self-evolving LLM agents. Using controlled causal interventions on both raw and condensed forms of experience, we comprehensively evaluate four representative frameworks across 10 LLM backbones and 9 environments. Our analysis uncovers a striking asymmetry: while agents consistently depend on raw experience, they often disregard or misinterpret condensed experience, even when it is the only experience provided. This gap persists across single- and multi-agent configurations and across backbone scales. We trace its underlying causes to three factors: the semantic limitations of condensed content, internal processing biases that suppress experience, and task regimes where pretrained priors already suffice. These findings challenge prevailing assumptions about self-evolving methods and underscore the need for more faithful and reliable approaches to experience integration.
DR-Arena: an Automated Evaluation Framework for Deep Research Agents
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly operate as Deep Research (DR) Agents capable of autonomous investigation and information synthesis, reliable evaluation of their task performance has become a critical bottleneck. Current benchmarks predominantly rely on static datasets, which suffer from several limitations: limited task generality, temporal misalignment, and data contamination. To address these, we introduce DR-Arena, a fully automated evaluation framework that pushes DR agents to their capability limits through dynamic investigation. DR-Arena constructs real-time Information Trees from fresh web trends to ensure the evaluation rubric is synchronized with the live world state, and employs an automated Examiner to generate structured tasks testing two orthogonal capabilities: Deep reasoning and Wide coverage. DR-Arena further adopts Adaptive Evolvement Loop, a state-machine controller that dynamically escalates task complexity based on real-time performance, demanding deeper deduction or wider aggregation until a decisive capability boundary emerges. Experiments with six advanced DR agents demonstrate that DR-Arena achieves a Spearman correlation of 0.94 with the LMSYS Search Arena leaderboard. This represents the state-of-the-art alignment with human preferences without any manual efforts, validating DR-Arena as a reliable alternative for costly human adjudication.
Mastering Diverse, Unknown, and Cluttered Tracks for Robust Vision-Based Drone Racing
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Most reinforcement learning(RL)-based methods for drone racing target fixed, obstacle-free tracks, leaving the generalization to unknown, cluttered environments largely unaddressed. This challenge stems from the need to balance racing speed and collision avoidance, limited feasible space causing policy exploration trapped in local optima during training, and perceptual ambiguity between gates and obstacles in depth maps-especially when gate positions are only coarsely specified. To overcome these issues, we propose a two-phase learning framework: an initial soft-collision training phase that preserves policy exploration for high-speed flight, followed by a hard-collision refinement phase that enforces robust obstacle avoidance. An adaptive, noise-augmented curriculum with an asymmetric actor-critic architecture gradually shifts the policy's reliance from privileged gate-state information to depth-based visual input. We further impose Lipschitz constraints and integrate a track-primitive generator to enhance motion stability and cross-environment generalization. We evaluate our framework through extensive simulation and ablation studies, and validate it in real-world experiments on a computationally constrained quadrotor. The system achieves agile flight while remaining robust to gate-position errors, developing a generalizable drone racing framework with the capability to operate in diverse, partially unknown and cluttered environments. https://yufengsjtu.github.io/MasterRacing.github.io/
MASim: Multilingual Agent-Based Simulation for Social Science
Dec 08, 2025



Abstract:Multi-agent role-playing has recently shown promise for studying social behavior with language agents, but existing simulations are mostly monolingual and fail to model cross-lingual interaction, an essential property of real societies. We introduce MASim, the first multilingual agent-based simulation framework that supports multi-turn interaction among generative agents with diverse sociolinguistic profiles. MASim offers two key analyses: (i) global public opinion modeling, by simulating how attitudes toward open-domain hypotheses evolve across languages and cultures, and (ii) media influence and information diffusion, via autonomous news agents that dynamically generate content and shape user behavior. To instantiate simulations, we construct the MAPS benchmark, which combines survey questions and demographic personas drawn from global population distributions. Experiments on calibration, sensitivity, consistency, and cultural case studies show that MASim reproduces sociocultural phenomena and highlights the importance of multilingual simulation for scalable, controlled computational social science.
CaberNet: Causal Representation Learning for Cross-Domain HVAC Energy Prediction
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Cross-domain HVAC energy prediction is essential for scalable building energy management, particularly because collecting extensive labeled data for every new building is both costly and impractical. Yet, this task remains highly challenging due to the scarcity and heterogeneity of data across different buildings, climate zones, and seasonal patterns. In particular, buildings situated in distinct climatic regions introduce variability that often leads existing methods to overfit to spurious correlations, rely heavily on expert intervention, or compromise on data diversity. To address these limitations, we propose CaberNet, a causal and interpretable deep sequence model that learns invariant (Markov blanket) representations for robust cross-domain prediction. In a purely data-driven fashion and without requiring any prior knowledge, CaberNet integrates i) a global feature gate trained with a self-supervised Bernoulli regularization to distinguish superior causal features from inferior ones, and ii) a domain-wise training scheme that balances domain contributions, minimizes cross-domain loss variance, and promotes latent factor independence. We evaluate CaberNet on real-world datasets collected from three buildings located in three climatically diverse cities, and it consistently outperforms all baselines, achieving a 22.9\% reduction in normalized mean squared error (NMSE) compared to the best benchmark. Our code is available at https://github.com/rickzky1001/CaberNet-CRL.
E2Edev: Benchmarking Large Language Models in End-to-End Software Development Task
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:E2EDev comprises (i) a fine-grained set of user requirements, (ii) {multiple BDD test scenarios with corresponding Python step implementations for each requirement}, and (iii) a fully automated testing pipeline built on the Behave framework. To ensure its quality while reducing the annotation effort, E2EDev leverages our proposed Human-in-the-Loop Multi-Agent Annotation Framework (HITL-MAA). {By evaluating various E2ESD frameworks and LLM backbones with E2EDev}, our analysis reveals a persistent struggle to effectively solve these tasks, underscoring the critical need for more effective and cost-efficient E2ESD solutions. Our codebase and benchmark are publicly available at https://github.com/SCUNLP/E2EDev.
Contrastive Weak-to-strong Generalization
Oct 09, 2025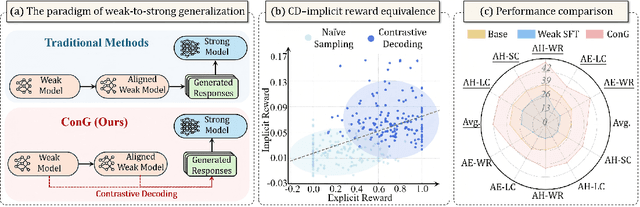
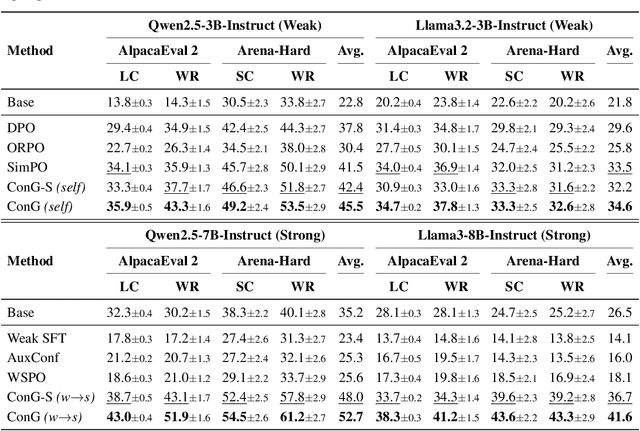
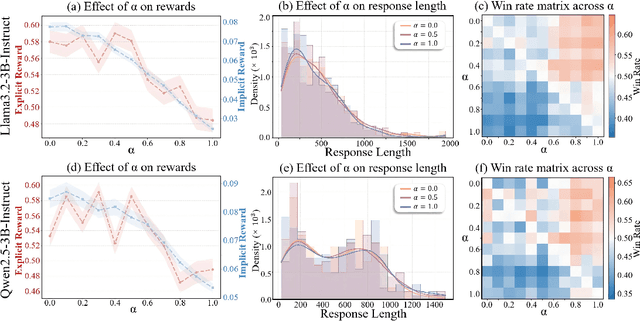
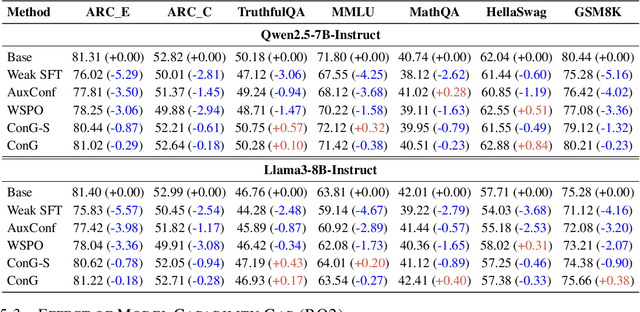
Abstract:Weak-to-strong generalization provides a promising paradigm for scaling large language models (LLMs) by training stronger models on samples from aligned weaker ones, without requiring human feedback or explicit reward modeling. However, its robustness and generalization are hindered by the noise and biases in weak-model outputs, which limit its applicability in practice. To address this challenge, we leverage implicit rewards, which approximate explicit rewards through log-likelihood ratios, and reveal their structural equivalence with Contrastive Decoding (CD), a decoding strategy shown to reduce noise in LLM generation. Building on this connection, we propose Contrastive Weak-to-Strong Generalization (ConG), a framework that employs contrastive decoding between pre- and post-alignment weak models to generate higher-quality samples. This approach enables more reliable capability transfer, denoising, and improved robustness, substantially mitigating the limitations of traditional weak-to-strong methods. Empirical results across different model families confirm consistent improvements, demonstrating the generality and effectiveness of ConG. Taken together, our findings highlight the potential of ConG to advance weak-to-strong generalization and provide a promising pathway toward AGI.
Exploring and Exploiting the Inherent Efficiency within Large Reasoning Models for Self-Guided Efficiency Enhancement
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large reasoning models (LRMs) have significantly enhanced language models' capabilities in complex problem-solving by emulating human-like deliberative thinking. However, these models often exhibit overthinking (i.e., the generation of unnecessarily verbose and redundant content), which hinders efficiency and inflates inference cost. In this work, we explore the representational and behavioral origins of this inefficiency, revealing that LRMs inherently possess the capacity for more concise reasoning. Empirical analyses show that correct reasoning paths vary significantly in length, and the shortest correct responses often suffice, indicating untapped efficiency potential. Exploiting these findings, we propose two lightweight methods to enhance LRM efficiency. First, we introduce Efficiency Steering, a training-free activation steering technique that modulates reasoning behavior via a single direction in the model's representation space. Second, we develop Self-Rewarded Efficiency RL, a reinforcement learning framework that dynamically balances task accuracy and brevity by rewarding concise correct solutions. Extensive experiments on seven LRM backbones across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our methods significantly reduce reasoning length while preserving or improving task performance. Our results highlight that reasoning efficiency can be improved by leveraging and guiding the intrinsic capabilities of existing models in a self-guided manner.
Mitigating Safety Fallback in Editing-based Backdoor Injection on LLMs
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong performance across natural language tasks, but remain vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Recent model editing-based approaches enable efficient backdoor injection by directly modifying parameters to map specific triggers to attacker-desired responses. However, these methods often suffer from safety fallback, where the model initially responds affirmatively but later reverts to refusals due to safety alignment. In this work, we propose DualEdit, a dual-objective model editing framework that jointly promotes affirmative outputs and suppresses refusal responses. To address two key challenges -- balancing the trade-off between affirmative promotion and refusal suppression, and handling the diversity of refusal expressions -- DualEdit introduces two complementary techniques. (1) Dynamic loss weighting calibrates the objective scale based on the pre-edited model to stabilize optimization. (2) Refusal value anchoring compresses the suppression target space by clustering representative refusal value vectors, reducing optimization conflict from overly diverse token sets. Experiments on safety-aligned LLMs show that DualEdit improves attack success by 9.98\% and reduces safety fallback rate by 10.88\% over baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge