Chen Huang
E2Edev: Benchmarking Large Language Models in End-to-End Software Development Task
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:E2EDev comprises (i) a fine-grained set of user requirements, (ii) {multiple BDD test scenarios with corresponding Python step implementations for each requirement}, and (iii) a fully automated testing pipeline built on the Behave framework. To ensure its quality while reducing the annotation effort, E2EDev leverages our proposed Human-in-the-Loop Multi-Agent Annotation Framework (HITL-MAA). {By evaluating various E2ESD frameworks and LLM backbones with E2EDev}, our analysis reveals a persistent struggle to effectively solve these tasks, underscoring the critical need for more effective and cost-efficient E2ESD solutions. Our codebase and benchmark are publicly available at https://github.com/SCUNLP/E2EDev.
PEAR: Phase Entropy Aware Reward for Efficient Reasoning
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have achieved impressive performance on complex reasoning tasks by generating detailed chain-of-thought (CoT) explanations. However, these responses are often excessively long, containing redundant reasoning steps that inflate inference cost and reduce usability. Controlling the length of generated reasoning without sacrificing accuracy remains an open challenge. Through a systematic empirical analysis, we reveal a consistent positive correlation between model entropy and response length at different reasoning stages across diverse LRMs: the thinking phase exhibits higher entropy, reflecting exploratory behavior of longer responses, while the final answer phase shows lower entropy, indicating a more deterministic solution.This observation suggests that entropy at different reasoning stages can serve as a control knob for balancing conciseness and performance. Based on this insight, this paper introduces Phase Entropy Aware Reward (PEAR), a reward mechanism that incorporating phase-dependent entropy into the reward design. Instead of treating all tokens uniformly, PEAR penalize excessive entropy during the thinking phase and allowing moderate exploration at the final answer phase, which encourages models to generate concise reasoning traces that retain sufficient flexibility to solve the task correctly. This enables adaptive control of response length without relying on explicit length targets or rigid truncation rules. Extensive experiments across four benchmarks demonstrate that PEAR consistently reduces response length while sustaining competitive accuracy across model scales. In addition, PEAR demonstrates strong out-of-distribution (OOD) robustness beyond the training distribution. Our code is available at: https://github.com/iNLP-Lab/PEAR.
CANDY: Benchmarking LLMs' Limitations and Assistive Potential in Chinese Misinformation Fact-Checking
Sep 04, 2025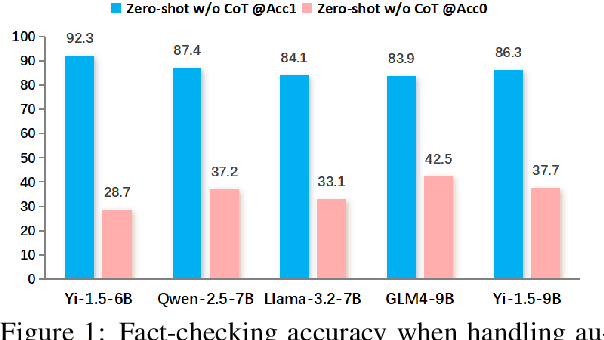
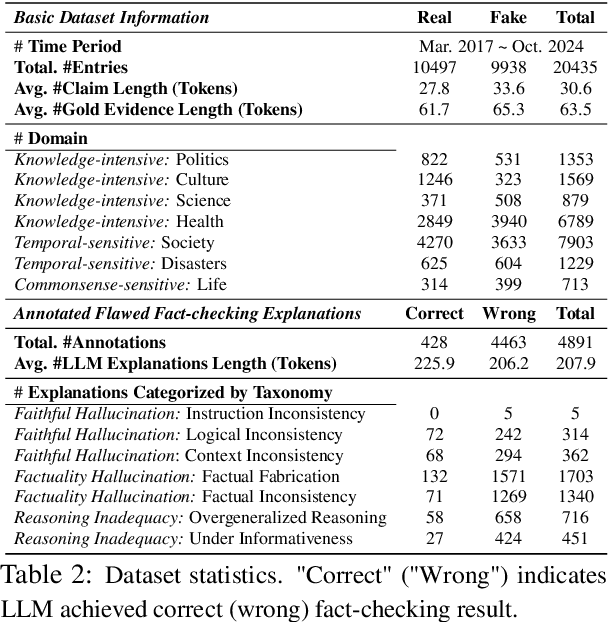
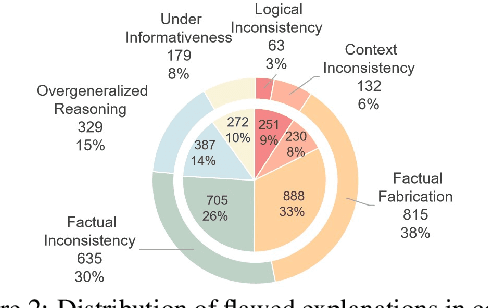
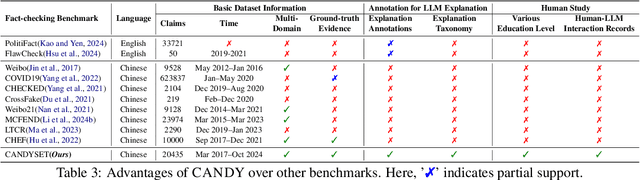
Abstract:The effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) to fact-check misinformation remains uncertain, despite their growing use. To this end, we present CANDY, a benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in fact-checking Chinese misinformation. Specifically, we curate a carefully annotated dataset of ~20k instances. Our analysis shows that current LLMs exhibit limitations in generating accurate fact-checking conclusions, even when enhanced with chain-of-thought reasoning and few-shot prompting. To understand these limitations, we develop a taxonomy to categorize flawed LLM-generated explanations for their conclusions and identify factual fabrication as the most common failure mode. Although LLMs alone are unreliable for fact-checking, our findings indicate their considerable potential to augment human performance when deployed as assistive tools in scenarios. Our dataset and code can be accessed at https://github.com/SCUNLP/CANDY
Mirroring Users: Towards Building Preference-aligned User Simulator with User Feedback in Recommendation
Aug 25, 2025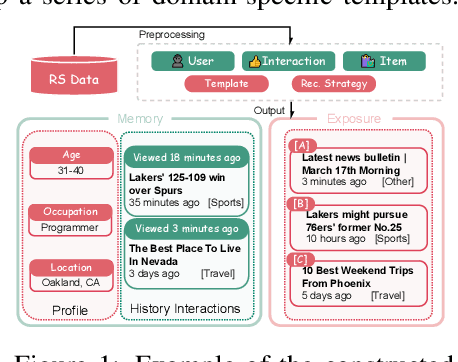
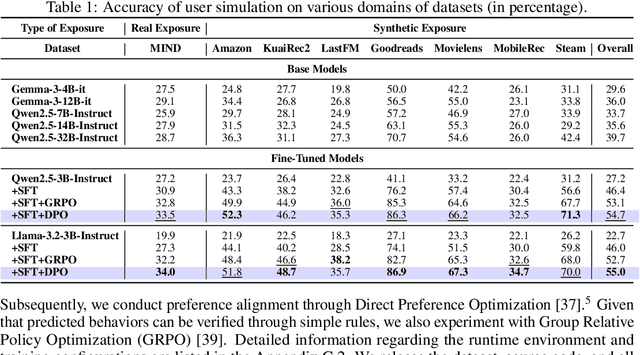
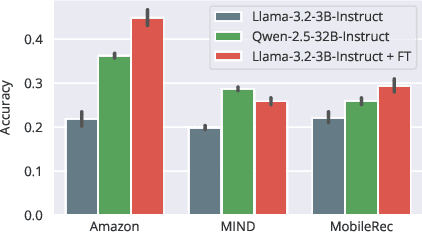
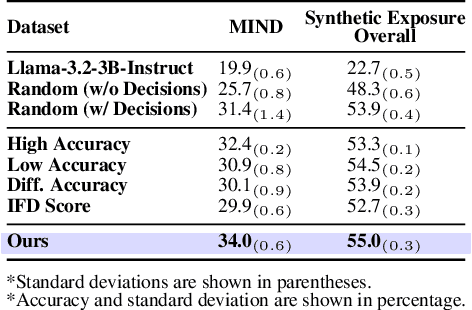
Abstract:User simulation is increasingly vital to develop and evaluate recommender systems (RSs). While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising avenues to simulate user behavior, they often struggle with the absence of specific domain alignment required for RSs and the efficiency demands of large-scale simulation. A vast yet underutilized resource for enhancing this alignment is the extensive user feedback inherent in RSs. However, directly leveraging such feedback presents two significant challenges. First, user feedback in RSs is often ambiguous and noisy, which negatively impacts effective preference alignment. Second, the massive volume of feedback largely hinders the efficiency of preference alignment, necessitating an efficient filtering mechanism to identify more informative samples. To overcome these hurdles, we introduce a novel data construction framework that leverages user feedback in RSs with advanced LLM capabilities to generate high-quality simulation data. Our framework unfolds in two key phases: (1) employing LLMs to generate cognitive decision-making processes on constructed simulation samples, reducing ambiguity in raw user feedback; (2) data distillation based on uncertainty estimation and behavior sampling to filter challenging yet denoised simulation samples. Accordingly, we fine-tune lightweight LLMs, as user simulators, using such high-quality dataset with corresponding decision-making processes. Extensive experiments verify that our framework significantly boosts the alignment with human preferences and in-domain reasoning capabilities of fine-tuned LLMs, and provides more insightful and interpretable signals when interacting with RSs. We believe our work will advance the RS community and offer valuable insights for broader human-centric AI research.
Through the Valley: Path to Effective Long CoT Training for Small Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervision has become a common strategy to enhance reasoning in language models. While effective for large models, we identify a phenomenon we call Long CoT Degradation, in which small language models (SLMs; <=3B parameters) trained on limited long CoT data experience significant performance deterioration. Through extensive experiments on the Qwen2.5, LLaMA3 and Gemma3 families, we demonstrate that this degradation is widespread across SLMs. In some settings, models trained on only 8k long CoT examples lose up to 75% of their original performance before fine-tuning. Strikingly, we further observe that for some particularly small models, even training on 220k long CoT examples fails to recover or surpass their original performance prior to fine-tuning. Our analysis attributes this effect to error accumulation: while longer responses increase the capacity for multi-step reasoning, they also amplify the risk of compounding mistakes. Furthermore, we find that Long CoT Degradation may negatively impacts downstream reinforcement learning (RL), although this can be alleviated by sufficiently scaled supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Our findings challenge common assumptions about the benefits of long CoT training for SLMs and offer practical guidance for building more effective small-scale reasoning models.
Proxy-FDA: Proxy-based Feature Distribution Alignment for Fine-tuning Vision Foundation Models without Forgetting
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Vision foundation models pre-trained on massive data encode rich representations of real-world concepts, which can be adapted to downstream tasks by fine-tuning. However, fine-tuning foundation models on one task often leads to the issue of concept forgetting on other tasks. Recent methods of robust fine-tuning aim to mitigate forgetting of prior knowledge without affecting the fine-tuning performance. Knowledge is often preserved by matching the original and fine-tuned model weights or feature pairs. However, such point-wise matching can be too strong, without explicit awareness of the feature neighborhood structures that encode rich knowledge as well. We propose a novel regularization method Proxy-FDA that explicitly preserves the structural knowledge in feature space. Proxy-FDA performs Feature Distribution Alignment (using nearest neighbor graphs) between the pre-trained and fine-tuned feature spaces, and the alignment is further improved by informative proxies that are generated dynamically to increase data diversity. Experiments show that Proxy-FDA significantly reduces concept forgetting during fine-tuning, and we find a strong correlation between forgetting and a distributional distance metric (in comparison to L2 distance). We further demonstrate Proxy-FDA's benefits in various fine-tuning settings (end-to-end, few-shot and continual tuning) and across different tasks like image classification, captioning and VQA.
ELABORATION: A Comprehensive Benchmark on Human-LLM Competitive Programming
May 22, 2025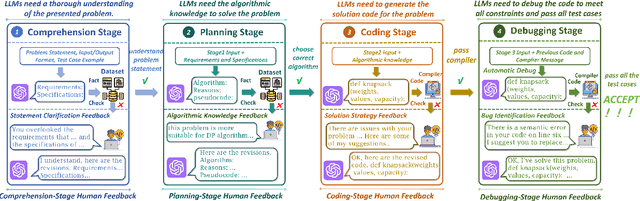
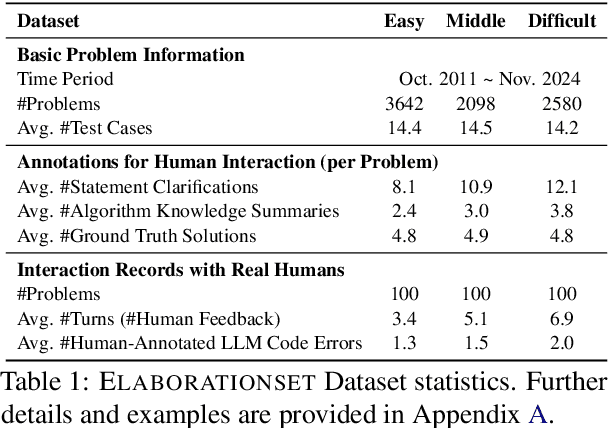
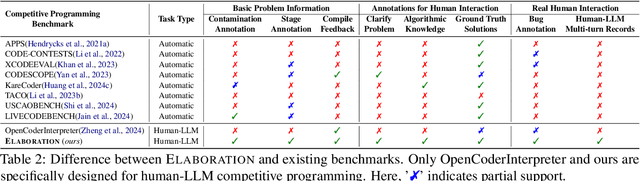
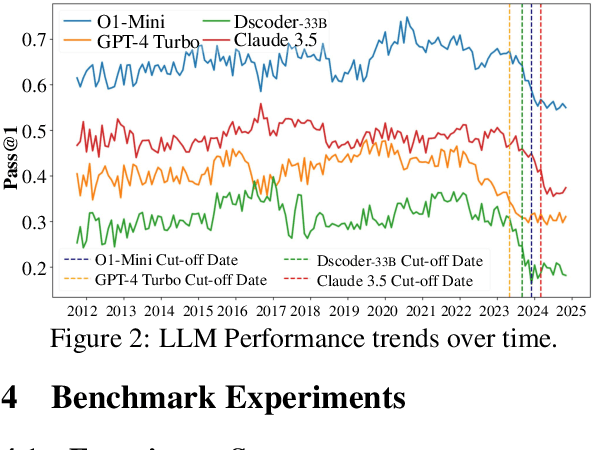
Abstract:While recent research increasingly emphasizes the value of human-LLM collaboration in competitive programming and proposes numerous empirical methods, a comprehensive understanding remains elusive due to the fragmented nature of existing studies and their use of diverse, application-specific human feedback. Thus, our work serves a three-fold purpose: First, we present the first taxonomy of human feedback consolidating the entire programming process, which promotes fine-grained evaluation. Second, we introduce ELABORATIONSET, a novel programming dataset specifically designed for human-LLM collaboration, meticulously annotated to enable large-scale simulated human feedback and facilitate costeffective real human interaction studies. Third, we introduce ELABORATION, a novel benchmark to facilitate a thorough assessment of human-LLM competitive programming. With ELABORATION, we pinpoint strengthes and weaknesses of existing methods, thereby setting the foundation for future improvement. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/SCUNLP/ELABORATION
Can Large Language Models Understand Internet Buzzwords Through User-Generated Content
May 21, 2025Abstract:The massive user-generated content (UGC) available in Chinese social media is giving rise to the possibility of studying internet buzzwords. In this paper, we study if large language models (LLMs) can generate accurate definitions for these buzzwords based on UGC as examples. Our work serves a threefold contribution. First, we introduce CHEER, the first dataset of Chinese internet buzzwords, each annotated with a definition and relevant UGC. Second, we propose a novel method, called RESS, to effectively steer the comprehending process of LLMs to produce more accurate buzzword definitions, mirroring the skills of human language learning. Third, with CHEER, we benchmark the strengths and weaknesses of various off-the-shelf definition generation methods and our RESS. Our benchmark demonstrates the effectiveness of RESS while revealing crucial shared challenges: over-reliance on prior exposure, underdeveloped inferential abilities, and difficulty identifying high-quality UGC to facilitate comprehension. We believe our work lays the groundwork for future advancements in LLM-based definition generation. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/SCUNLP/Buzzword.
Enhancing Code LLM Training with Programmer Attention
Mar 19, 2025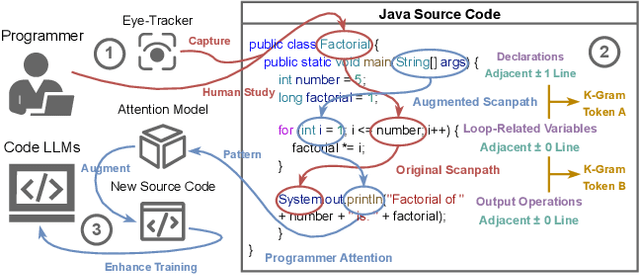
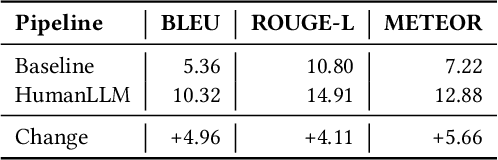
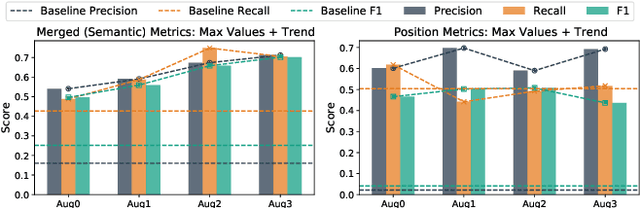
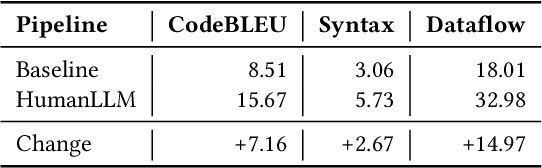
Abstract:Human attention provides valuable yet underexploited signals for code LLM training, offering a perspective beyond purely machine-driven attention. Despite the complexity and cost of collecting eye-tracking data, there has also been limited progress in systematically using these signals for code LLM training. To address both issues, we propose a cohesive pipeline spanning augmentation and reward-based fine-tuning. Specifically, we introduce (1) an eye-tracking path augmentation method to expand programmer attention datasets, (2) a pattern abstraction step that refines raw fixations into learnable attention motifs, and (3) a reward-guided strategy for integrating these insights directly into a CodeT5 supervised fine-tuning process. Our experiments yield +7.16 in CodeBLEU on the CodeXGlue benchmark for code summarization, underscoring how uniting human and machine attention can boost code intelligence. We hope this work encourages broader exploration of human-centric methods in next-generation AI4SE.
Breaking the Stigma! Unobtrusively Probe Symptoms in Depression Disorder Diagnosis Dialogue
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Stigma has emerged as one of the major obstacles to effectively diagnosing depression, as it prevents users from open conversations about their struggles. This requires advanced questioning skills to carefully probe the presence of specific symptoms in an unobtrusive manner. While recent efforts have been made on depression-diagnosis-oriented dialogue systems, they largely ignore this problem, ultimately hampering their practical utility. To this end, we propose a novel and effective method, UPSD$^{4}$, developing a series of strategies to promote a sense of unobtrusiveness within the dialogue system and assessing depression disorder by probing symptoms. We experimentally show that UPSD$^{4}$ demonstrates a significant improvement over current baselines, including unobtrusiveness evaluation of dialogue content and diagnostic accuracy. We believe our work contributes to developing more accessible and user-friendly tools for addressing the widespread need for depression diagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge