Josh Susskind
STARFlow: Scaling Latent Normalizing Flows for High-resolution Image Synthesis
Jun 06, 2025
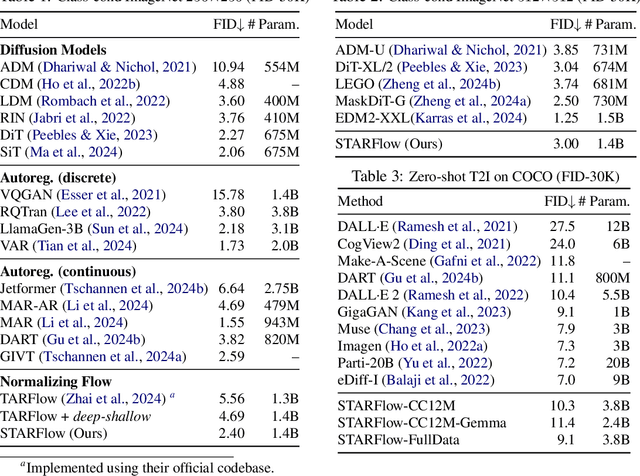
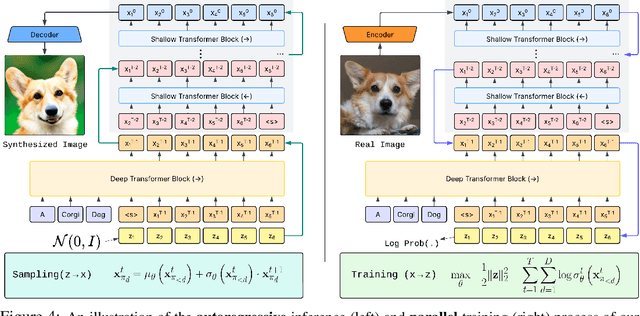
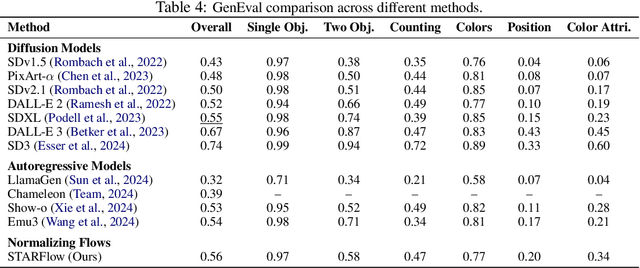
Abstract:We present STARFlow, a scalable generative model based on normalizing flows that achieves strong performance in high-resolution image synthesis. The core of STARFlow is Transformer Autoregressive Flow (TARFlow), which combines the expressive power of normalizing flows with the structured modeling capabilities of Autoregressive Transformers. We first establish the theoretical universality of TARFlow for modeling continuous distributions. Building on this foundation, we introduce several key architectural and algorithmic innovations to significantly enhance scalability: (1) a deep-shallow design, wherein a deep Transformer block captures most of the model representational capacity, complemented by a few shallow Transformer blocks that are computationally efficient yet substantially beneficial; (2) modeling in the latent space of pretrained autoencoders, which proves more effective than direct pixel-level modeling; and (3) a novel guidance algorithm that significantly boosts sample quality. Crucially, our model remains an end-to-end normalizing flow, enabling exact maximum likelihood training in continuous spaces without discretization. STARFlow achieves competitive performance in both class-conditional and text-conditional image generation tasks, approaching state-of-the-art diffusion models in sample quality. To our knowledge, this work is the first successful demonstration of normalizing flows operating effectively at this scale and resolution.
Proxy-FDA: Proxy-based Feature Distribution Alignment for Fine-tuning Vision Foundation Models without Forgetting
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Vision foundation models pre-trained on massive data encode rich representations of real-world concepts, which can be adapted to downstream tasks by fine-tuning. However, fine-tuning foundation models on one task often leads to the issue of concept forgetting on other tasks. Recent methods of robust fine-tuning aim to mitigate forgetting of prior knowledge without affecting the fine-tuning performance. Knowledge is often preserved by matching the original and fine-tuned model weights or feature pairs. However, such point-wise matching can be too strong, without explicit awareness of the feature neighborhood structures that encode rich knowledge as well. We propose a novel regularization method Proxy-FDA that explicitly preserves the structural knowledge in feature space. Proxy-FDA performs Feature Distribution Alignment (using nearest neighbor graphs) between the pre-trained and fine-tuned feature spaces, and the alignment is further improved by informative proxies that are generated dynamically to increase data diversity. Experiments show that Proxy-FDA significantly reduces concept forgetting during fine-tuning, and we find a strong correlation between forgetting and a distributional distance metric (in comparison to L2 distance). We further demonstrate Proxy-FDA's benefits in various fine-tuning settings (end-to-end, few-shot and continual tuning) and across different tasks like image classification, captioning and VQA.
Parameters vs FLOPs: Scaling Laws for Optimal Sparsity for Mixture-of-Experts Language Models
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:Scaling the capacity of language models has consistently proven to be a reliable approach for improving performance and unlocking new capabilities. Capacity can be primarily defined by two dimensions: the number of model parameters and the compute per example. While scaling typically involves increasing both, the precise interplay between these factors and their combined contribution to overall capacity remains not fully understood. We explore this relationship in the context of sparse Mixture-of-Expert models (MoEs), which allow scaling the number of parameters without proportionally increasing the FLOPs per example. We investigate how varying the sparsity level, i.e., the ratio of non-active to total parameters, affects model performance in terms of both pretraining and downstream performance. We find that under different constraints (e.g. parameter size and total training compute), there is an optimal level of sparsity that improves both training efficiency and model performance. These results provide a better understanding of the impact of sparsity in scaling laws for MoEs and complement existing works in this area, offering insights for designing more efficient architectures.
3D Shape Tokenization
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Shape Tokens, a 3D representation that is continuous, compact, and easy to incorporate into machine learning models. Shape Tokens act as conditioning vectors that represent shape information in a 3D flow-matching model. The flow-matching model is trained to approximate probability density functions corresponding to delta functions concentrated on the surfaces of shapes in 3D. By attaching Shape Tokens to various machine learning models, we can generate new shapes, convert images to 3D, align 3D shapes with text and images, and render shapes directly at variable, user specified, resolution. Moreover, Shape Tokens enable a systematic analysis of geometric properties such as normal, density, and deformation field. Across all tasks and experiments, utilizing Shape Tokens demonstrate strong performance compared to existing baselines.
Normalizing Flows are Capable Generative Models
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Normalizing Flows (NFs) are likelihood-based models for continuous inputs. They have demonstrated promising results on both density estimation and generative modeling tasks, but have received relatively little attention in recent years. In this work, we demonstrate that NFs are more powerful than previously believed. We present TarFlow: a simple and scalable architecture that enables highly performant NF models. TarFlow can be thought of as a Transformer-based variant of Masked Autoregressive Flows (MAFs): it consists of a stack of autoregressive Transformer blocks on image patches, alternating the autoregression direction between layers. TarFlow is straightforward to train end-to-end, and capable of directly modeling and generating pixels. We also propose three key techniques to improve sample quality: Gaussian noise augmentation during training, a post training denoising procedure, and an effective guidance method for both class-conditional and unconditional settings. Putting these together, TarFlow sets new state-of-the-art results on likelihood estimation for images, beating the previous best methods by a large margin, and generates samples with quality and diversity comparable to diffusion models, for the first time with a stand-alone NF model. We make our code available at https://github.com/apple/ml-tarflow.
Coordinate In and Value Out: Training Flow Transformers in Ambient Space
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Flow matching models have emerged as a powerful method for generative modeling on domains like images or videos, and even on unstructured data like 3D point clouds. These models are commonly trained in two stages: first, a data compressor (i.e., a variational auto-encoder) is trained, and in a subsequent training stage a flow matching generative model is trained in the low-dimensional latent space of the data compressor. This two stage paradigm adds complexity to the overall training recipe and sets obstacles for unifying models across data domains, as specific data compressors are used for different data modalities. To this end, we introduce Ambient Space Flow Transformers (ASFT), a domain-agnostic approach to learn flow matching transformers in ambient space, sidestepping the requirement of training compressors and simplifying the training process. We introduce a conditionally independent point-wise training objective that enables ASFT to make predictions continuously in coordinate space. Our empirical results demonstrate that using general purpose transformer blocks, ASFT effectively handles different data modalities such as images and 3D point clouds, achieving strong performance in both domains and outperforming comparable approaches. ASFT is a promising step towards domain-agnostic flow matching generative models that can be trivially adopted in different data domains.
TypeScore: A Text Fidelity Metric for Text-to-Image Generative Models
Nov 02, 2024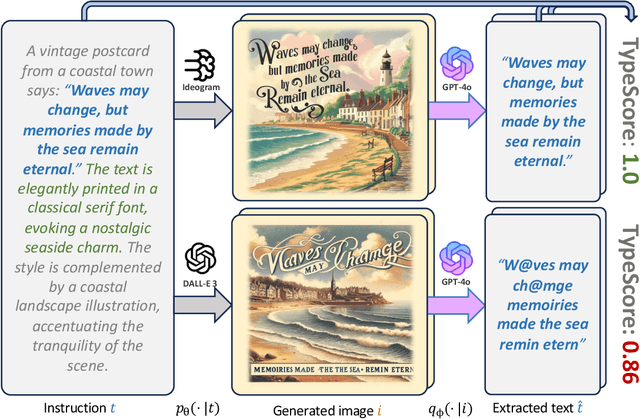



Abstract:Evaluating text-to-image generative models remains a challenge, despite the remarkable progress being made in their overall performances. While existing metrics like CLIPScore work for coarse evaluations, they lack the sensitivity to distinguish finer differences as model performance rapidly improves. In this work, we focus on the text rendering aspect of these models, which provides a lens for evaluating a generative model's fine-grained instruction-following capabilities. To this end, we introduce a new evaluation framework called TypeScore to sensitively assess a model's ability to generate images with high-fidelity embedded text by following precise instructions. We argue that this text generation capability serves as a proxy for general instruction-following ability in image synthesis. TypeScore uses an additional image description model and leverages an ensemble dissimilarity measure between the original and extracted text to evaluate the fidelity of the rendered text. Our proposed metric demonstrates greater resolution than CLIPScore to differentiate popular image generation models across a range of instructions with diverse text styles. Our study also evaluates how well these vision-language models (VLMs) adhere to stylistic instructions, disentangling style evaluation from embedded-text fidelity. Through human evaluation studies, we quantitatively meta-evaluate the effectiveness of the metric. Comprehensive analysis is conducted to explore factors such as text length, captioning models, and current progress towards human parity on this task. The framework provides insights into remaining gaps in instruction-following for image generation with embedded text.
Aggregate-and-Adapt Natural Language Prompts for Downstream Generalization of CLIP
Oct 31, 2024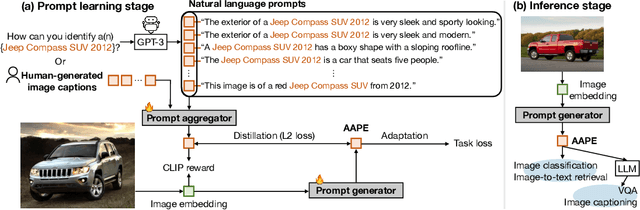
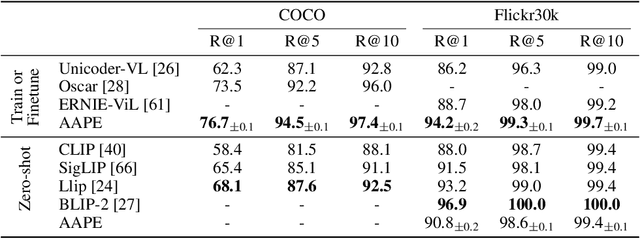

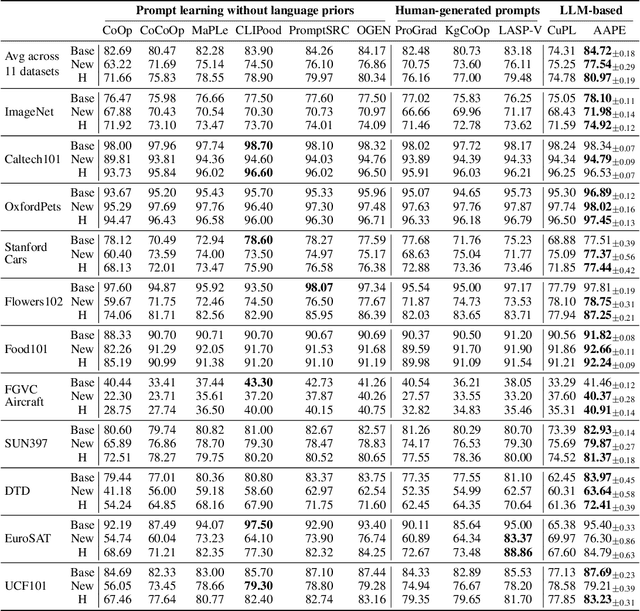
Abstract:Large pretrained vision-language models like CLIP have shown promising generalization capability, but may struggle in specialized domains (e.g., satellite imagery) or fine-grained classification (e.g., car models) where the visual concepts are unseen or under-represented during pretraining. Prompt learning offers a parameter-efficient finetuning framework that can adapt CLIP to downstream tasks even when limited annotation data are available. In this paper, we improve prompt learning by distilling the textual knowledge from natural language prompts (either human- or LLM-generated) to provide rich priors for those under-represented concepts. We first obtain a prompt ``summary'' aligned to each input image via a learned prompt aggregator. Then we jointly train a prompt generator, optimized to produce a prompt embedding that stays close to the aggregated summary while minimizing task loss at the same time. We dub such prompt embedding as Aggregate-and-Adapted Prompt Embedding (AAPE). AAPE is shown to be able to generalize to different downstream data distributions and tasks, including vision-language understanding tasks (e.g., few-shot classification, VQA) and generation tasks (image captioning) where AAPE achieves competitive performance. We also show AAPE is particularly helpful to handle non-canonical and OOD examples. Furthermore, AAPE learning eliminates LLM-based inference cost as required by baselines, and scales better with data and LLM model size.
DART: Denoising Autoregressive Transformer for Scalable Text-to-Image Generation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have become the dominant approach for visual generation. They are trained by denoising a Markovian process that gradually adds noise to the input. We argue that the Markovian property limits the models ability to fully utilize the generation trajectory, leading to inefficiencies during training and inference. In this paper, we propose DART, a transformer-based model that unifies autoregressive (AR) and diffusion within a non-Markovian framework. DART iteratively denoises image patches spatially and spectrally using an AR model with the same architecture as standard language models. DART does not rely on image quantization, enabling more effective image modeling while maintaining flexibility. Furthermore, DART seamlessly trains with both text and image data in a unified model. Our approach demonstrates competitive performance on class-conditioned and text-to-image generation tasks, offering a scalable, efficient alternative to traditional diffusion models. Through this unified framework, DART sets a new benchmark for scalable, high-quality image synthesis.
On the benefits of pixel-based hierarchical policies for task generalization
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning practitioners often avoid hierarchical policies, especially in image-based observation spaces. Typically, the single-task performance improvement over flat-policy counterparts does not justify the additional complexity associated with implementing a hierarchy. However, by introducing multiple decision-making levels, hierarchical policies can compose lower-level policies to more effectively generalize between tasks, highlighting the need for multi-task evaluations. We analyze the benefits of hierarchy through simulated multi-task robotic control experiments from pixels. Our results show that hierarchical policies trained with task conditioning can (1) increase performance on training tasks, (2) lead to improved reward and state-space generalizations in similar tasks, and (3) decrease the complexity of fine tuning required to solve novel tasks. Thus, we believe that hierarchical policies should be considered when building reinforcement learning architectures capable of generalizing between tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge