Yuyang Wang
LIRMM | ADAC
Edge-Optimized Multimodal Learning for UAV Video Understanding via BLIP-2
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The demand for real-time visual understanding and interaction in complex scenarios is increasingly critical for unmanned aerial vehicles. However, a significant challenge arises from the contradiction between the high computational cost of large Vision language models and the limited computing resources available on UAV edge devices. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a lightweight multimodal task platform based on BLIP-2, integrated with YOLO-World and YOLOv8-Seg models. This integration extends the multi-task capabilities of BLIP-2 for UAV applications with minimal adaptation and without requiring task-specific fine-tuning on drone data. Firstly, the deep integration of BLIP-2 with YOLO models enables it to leverage the precise perceptual results of YOLO for fundamental tasks like object detection and instance segmentation, thereby facilitating deeper visual-attention understanding and reasoning. Secondly, a content-aware key frame sampling mechanism based on K-Means clustering is designed, which incorporates intelligent frame selection and temporal feature concatenation. This equips the lightweight BLIP-2 architecture with the capability to handle video-level interactive tasks effectively. Thirdly, a unified prompt optimization scheme for multi-task adaptation is implemented. This scheme strategically injects structured event logs from the YOLO models as contextual information into BLIP-2's input. Combined with output constraints designed to filter out technical details, this approach effectively guides the model to generate accurate and contextually relevant outputs for various tasks.
Understanding the Implicit Biases of Design Choices for Time Series Foundation Models
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Time series foundation models (TSFMs) are a class of potentially powerful, general-purpose tools for time series forecasting and related temporal tasks, but their behavior is strongly shaped by subtle inductive biases in their design. Rather than developing a new model and claiming that it is better than existing TSFMs, e.g., by winning on existing well-established benchmarks, our objective is to understand how the various ``knobs'' of the training process affect model quality. Using a mix of theory and controlled empirical evaluation, we identify several design choices (patch size, embedding choice, training objective, etc.) and show how they lead to implicit biases in fundamental model properties (temporal behavior, geometric structure, how aggressively or not the model regresses to the mean, etc.); and we show how these biases can be intuitive or very counterintuitive, depending on properties of the model and data. We also illustrate in a case study on outlier handling how multiple biases can interact in complex ways; and we discuss implications of our results for learning the bitter lesson and building TSFMs.
fev-bench: A Realistic Benchmark for Time Series Forecasting
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:Benchmark quality is critical for meaningful evaluation and sustained progress in time series forecasting, particularly given the recent rise of pretrained models. Existing benchmarks often have narrow domain coverage or overlook important real-world settings, such as tasks with covariates. Additionally, their aggregation procedures often lack statistical rigor, making it unclear whether observed performance differences reflect true improvements or random variation. Many benchmarks also fail to provide infrastructure for consistent evaluation or are too rigid to integrate into existing pipelines. To address these gaps, we propose fev-bench, a benchmark comprising 100 forecasting tasks across seven domains, including 46 tasks with covariates. Supporting the benchmark, we introduce fev, a lightweight Python library for benchmarking forecasting models that emphasizes reproducibility and seamless integration with existing workflows. Usingfev, fev-bench employs principled aggregation methods with bootstrapped confidence intervals to report model performance along two complementary dimensions: win rates and skill scores. We report results on fev-bench for various pretrained, statistical and baseline models, and identify promising directions for future research.
CrEst: Credibility Estimation for Contexts in LLMs via Weak Supervision
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The integration of contextual information has significantly enhanced the performance of large language models (LLMs) on knowledge-intensive tasks. However, existing methods often overlook a critical challenge: the credibility of context documents can vary widely, potentially leading to the propagation of unreliable information. In this paper, we introduce CrEst, a novel weakly supervised framework for assessing the credibility of context documents during LLM inference--without requiring manual annotations. Our approach is grounded in the insight that credible documents tend to exhibit higher semantic coherence with other credible documents, enabling automated credibility estimation through inter-document agreement. To incorporate credibility into LLM inference, we propose two integration strategies: a black-box approach for models without access to internal weights or activations, and a white-box method that directly modifies attention mechanisms. Extensive experiments across three model architectures and five datasets demonstrate that CrEst consistently outperforms strong baselines, achieving up to a 26.86% improvement in accuracy and a 3.49% increase in F1 score. Further analysis shows that CrEst maintains robust performance even under high-noise conditions.
End-to-End Probabilistic Framework for Learning with Hard Constraints
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:We present a general purpose probabilistic forecasting framework, ProbHardE2E, to learn systems that can incorporate operational/physical constraints as hard requirements. ProbHardE2E enforces hard constraints by exploiting variance information in a novel way; and thus it is also capable of performing uncertainty quantification (UQ) on the model. Our methodology uses a novel differentiable probabilistic projection layer (DPPL) that can be combined with a wide range of neural network architectures. This DPPL allows the model to learn the system in an end-to-end manner, compared to other approaches where the constraints are satisfied either through a post-processing step or at inference. In addition, ProbHardE2E can optimize a strictly proper scoring rule, without making any distributional assumptions on the target, which enables it to obtain robust distributional estimates (in contrast to existing approaches that generally optimize likelihood-based objectives, which are heavily biased by their distributional assumptions and model choices); and it can incorporate a range of non-linear constraints (increasing the power of modeling and flexibility). We apply ProbHardE2E to problems in learning partial differential equations with uncertainty estimates and to probabilistic time-series forecasting, showcasing it as a broadly applicable general setup that connects these seemingly disparate domains.
STARFlow: Scaling Latent Normalizing Flows for High-resolution Image Synthesis
Jun 06, 2025
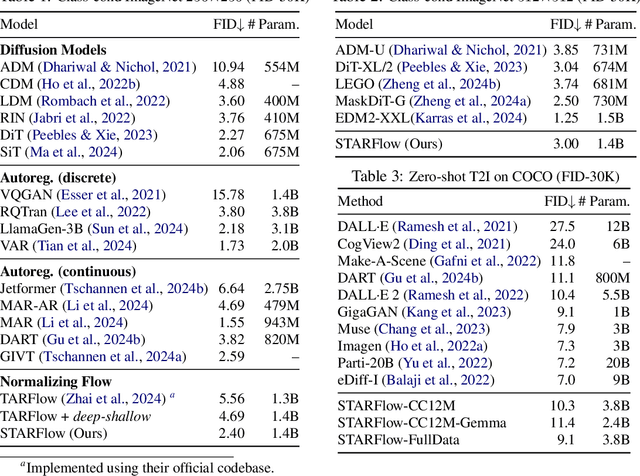
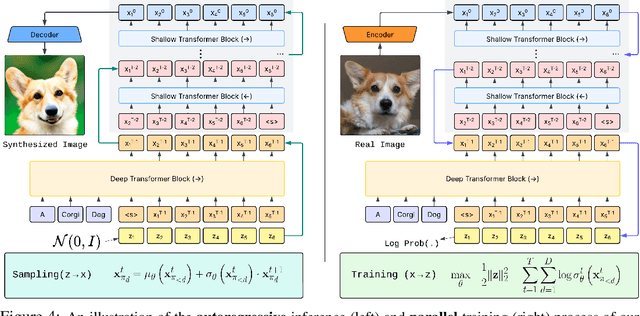
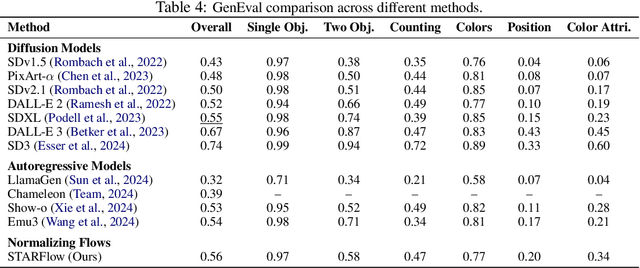
Abstract:We present STARFlow, a scalable generative model based on normalizing flows that achieves strong performance in high-resolution image synthesis. The core of STARFlow is Transformer Autoregressive Flow (TARFlow), which combines the expressive power of normalizing flows with the structured modeling capabilities of Autoregressive Transformers. We first establish the theoretical universality of TARFlow for modeling continuous distributions. Building on this foundation, we introduce several key architectural and algorithmic innovations to significantly enhance scalability: (1) a deep-shallow design, wherein a deep Transformer block captures most of the model representational capacity, complemented by a few shallow Transformer blocks that are computationally efficient yet substantially beneficial; (2) modeling in the latent space of pretrained autoencoders, which proves more effective than direct pixel-level modeling; and (3) a novel guidance algorithm that significantly boosts sample quality. Crucially, our model remains an end-to-end normalizing flow, enabling exact maximum likelihood training in continuous spaces without discretization. STARFlow achieves competitive performance in both class-conditional and text-conditional image generation tasks, approaching state-of-the-art diffusion models in sample quality. To our knowledge, this work is the first successful demonstration of normalizing flows operating effectively at this scale and resolution.
Adapting to Online Distribution Shifts in Deep Learning: A Black-Box Approach
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:We study the well-motivated problem of online distribution shift in which the data arrive in batches and the distribution of each batch can change arbitrarily over time. Since the shifts can be large or small, abrupt or gradual, the length of the relevant historical data to learn from may vary over time, which poses a major challenge in designing algorithms that can automatically adapt to the best ``attention span'' while remaining computationally efficient. We propose a meta-algorithm that takes any network architecture and any Online Learner (OL) algorithm as input and produces a new algorithm which provably enhances the performance of the given OL under non-stationarity. Our algorithm is efficient (it requires maintaining only $O(\log(T))$ OL instances) and adaptive (it automatically chooses OL instances with the ideal ``attention'' length at every timestamp). Experiments on various real-world datasets across text and image modalities show that our method consistently improves the accuracy of user specified OL algorithms for classification tasks. Key novel algorithmic ingredients include a \emph{multi-resolution instance} design inspired by wavelet theory and a cross-validation-through-time technique. Both could be of independent interest.
ChronosX: Adapting Pretrained Time Series Models with Exogenous Variables
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:Covariates provide valuable information on external factors that influence time series and are critical in many real-world time series forecasting tasks. For example, in retail, covariates may indicate promotions or peak dates such as holiday seasons that heavily influence demand forecasts. Recent advances in pretraining large language model architectures for time series forecasting have led to highly accurate forecasters. However, the majority of these models do not readily use covariates as they are often specific to a certain task or domain. This paper introduces a new method to incorporate covariates into pretrained time series forecasting models. Our proposed approach incorporates covariate information into pretrained forecasting models through modular blocks that inject past and future covariate information, without necessarily modifying the pretrained model in consideration. In order to evaluate our approach, we introduce a benchmark composed of 32 different synthetic datasets with varying dynamics to evaluate the effectivity of forecasting models with covariates. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real datasets show that our approach effectively incorporates covariate information into pretrained models, outperforming existing baselines.
ReAgent: Reversible Multi-Agent Reasoning for Knowledge-Enhanced Multi-Hop QA
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved multi-hop question answering (QA) through direct Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, the irreversible nature of CoT leads to error accumulation, making it challenging to correct mistakes in multi-hop reasoning. This paper introduces ReAgent: a Reversible multi-Agent collaborative framework augmented with explicit backtracking mechanisms, enabling reversible multi-hop reasoning. By incorporating text-based retrieval, information aggregation and validation, our system can detect and correct errors mid-reasoning, leading to more robust and interpretable QA outcomes. The framework and experiments serve as a foundation for future work on error-tolerant QA systems. Empirical evaluations across three benchmarks indicate ReAgent's efficacy, yielding average about 6\% improvements against baseline models.
Experimental Exploration: Investigating Cooperative Interaction Behavior Between Humans and Large Language Model Agents
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:With the rise of large language models (LLMs), AI agents as autonomous decision-makers present significant opportunities and challenges for human-AI cooperation. While many studies have explored human cooperation with AI as tools, the role of LLM-augmented autonomous agents in competitive-cooperative interactions remains under-examined. This study investigates human cooperative behavior by engaging 30 participants who interacted with LLM agents exhibiting different characteristics (purported human, purported rule-based AI agent, and LLM agent) in repeated Prisoner's Dilemma games. Findings show significant differences in cooperative behavior based on the agents' purported characteristics and the interaction effect of participants' genders and purported characteristics. We also analyzed human response patterns, including game completion time, proactive favorable behavior, and acceptance of repair efforts. These insights offer a new perspective on human interactions with LLM agents in competitive cooperation contexts, such as virtual avatars or future physical entities. The study underscores the importance of understanding human biases toward AI agents and how observed behaviors can influence future human-AI cooperation dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge