Haoyang Fang
AdvEvo-MARL: Shaping Internalized Safety through Adversarial Co-Evolution in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:LLM-based multi-agent systems excel at planning, tool use, and role coordination, but their openness and interaction complexity also expose them to jailbreak, prompt-injection, and adversarial collaboration. Existing defenses fall into two lines: (i) self-verification that asks each agent to pre-filter unsafe instructions before execution, and (ii) external guard modules that police behaviors. The former often underperforms because a standalone agent lacks sufficient capacity to detect cross-agent unsafe chains and delegation-induced risks; the latter increases system overhead and creates a single-point-of-failure-once compromised, system-wide safety collapses, and adding more guards worsens cost and complexity. To solve these challenges, we propose AdvEvo-MARL, a co-evolutionary multi-agent reinforcement learning framework that internalizes safety into task agents. Rather than relying on external guards, AdvEvo-MARL jointly optimizes attackers (which synthesize evolving jailbreak prompts) and defenders (task agents trained to both accomplish their duties and resist attacks) in adversarial learning environments. To stabilize learning and foster cooperation, we introduce a public baseline for advantage estimation: agents within the same functional group share a group-level mean-return baseline, enabling lower-variance updates and stronger intra-group coordination. Across representative attack scenarios, AdvEvo-MARL consistently keeps attack-success rate (ASR) below 20%, whereas baselines reach up to 38.33%, while preserving-and sometimes improving-task accuracy (up to +3.67% on reasoning tasks). These results show that safety and utility can be jointly improved without relying on extra guard agents or added system overhead.
MLZero: A Multi-Agent System for End-to-end Machine Learning Automation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Existing AutoML systems have advanced the automation of machine learning (ML); however, they still require substantial manual configuration and expert input, particularly when handling multimodal data. We introduce MLZero, a novel multi-agent framework powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) that enables end-to-end ML automation across diverse data modalities with minimal human intervention. A cognitive perception module is first employed, transforming raw multimodal inputs into perceptual context that effectively guides the subsequent workflow. To address key limitations of LLMs, such as hallucinated code generation and outdated API knowledge, we enhance the iterative code generation process with semantic and episodic memory. MLZero demonstrates superior performance on MLE-Bench Lite, outperforming all competitors in both success rate and solution quality, securing six gold medals. Additionally, when evaluated on our Multimodal AutoML Agent Benchmark, which includes 25 more challenging tasks spanning diverse data modalities, MLZero outperforms the competing methods by a large margin with a success rate of 0.92 (+263.6\%) and an average rank of 2.28. Our approach maintains its robust effectiveness even with a compact 8B LLM, outperforming full-size systems from existing solutions.
Effectively Steer LLM To Follow Preference via Building Confident Directions
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Having an LLM that aligns with human preferences is essential for accommodating individual needs, such as maintaining writing style or generating specific topics of interest. The majority of current alignment methods rely on fine-tuning or prompting, which can be either costly or difficult to control. Model steering algorithms, which modify the model output by constructing specific steering directions, are typically easy to implement and optimization-free. However, their capabilities are typically limited to steering the model into one of the two directions (i.e., bidirectional steering), and there has been no theoretical understanding to guarantee their performance. In this work, we propose a theoretical framework to understand and quantify the model steering methods. Inspired by the framework, we propose a confident direction steering method (CONFST) that steers LLMs via modifying their activations at inference time. More specifically, CONFST builds a confident direction that is closely aligned with users' preferences, and this direction is then added to the activations of the LLMs to effectively steer the model output. Our approach offers three key advantages over popular bidirectional model steering methods: 1) It is more powerful, since multiple (i.e. more than two) users' preferences can be aligned simultaneously; 2) It is simple to implement, since there is no need to determine which layer to add the steering vector to; 3) No explicit user instruction is required. We validate our method on GPT-2 XL (1.5B), Mistral (7B) and Gemma-it (9B) models for tasks that require shifting the output of LLMs across various topics and styles, achieving superior performance over competing methods.
AutoGluon-Multimodal (AutoMM): Supercharging Multimodal AutoML with Foundation Models
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:AutoGluon-Multimodal (AutoMM) is introduced as an open-source AutoML library designed specifically for multimodal learning. Distinguished by its exceptional ease of use, AutoMM enables fine-tuning of foundation models with just three lines of code. Supporting various modalities including image, text, and tabular data, both independently and in combination, the library offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities spanning classification, regression, object detection, semantic matching, and image segmentation. Experiments across diverse datasets and tasks showcases AutoMM's superior performance in basic classification and regression tasks compared to existing AutoML tools, while also demonstrating competitive results in advanced tasks, aligning with specialized toolboxes designed for such purposes.
Convolution Meets LoRA: Parameter Efficient Finetuning for Segment Anything Model
Jan 31, 2024

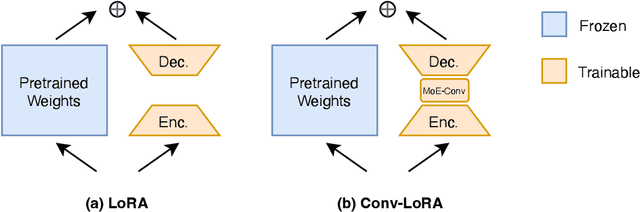

Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) stands as a foundational framework for image segmentation. While it exhibits remarkable zero-shot generalization in typical scenarios, its advantage diminishes when applied to specialized domains like medical imagery and remote sensing. To address this limitation, this paper introduces Conv-LoRA, a simple yet effective parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach. By integrating ultra-lightweight convolutional parameters into Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), Conv-LoRA can inject image-related inductive biases into the plain ViT encoder, further reinforcing SAM's local prior assumption. Notably, Conv-LoRA not only preserves SAM's extensive segmentation knowledge but also revives its capacity of learning high-level image semantics, which is constrained by SAM's foreground-background segmentation pretraining. Comprehensive experimentation across diverse benchmarks spanning multiple domains underscores Conv-LoRA's superiority in adapting SAM to real-world semantic segmentation tasks.
A Transformer-Based Substitute Recommendation Model Incorporating Weakly Supervised Customer Behavior Data
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:The substitute-based recommendation is widely used in E-commerce to provide better alternatives to customers. However, existing research typically uses the customer behavior signals like co-view and view-but-purchase-another to capture the substitute relationship. Despite its intuitive soundness, we find that such an approach might ignore the functionality and characteristics of products. In this paper, we adapt substitute recommendation into language matching problem by taking product title description as model input to consider product functionality. We design a new transformation method to de-noise the signals derived from production data. In addition, we consider multilingual support from the engineering point of view. Our proposed end-to-end transformer-based model achieves both successes from offline and online experiments. The proposed model has been deployed in a large-scale E-commerce website for 11 marketplaces in 6 languages. Our proposed model is demonstrated to increase revenue by 19% based on an online A/B experiment.
DAWN: Dual Augmented Memory Network for Unsupervised Video Object Tracking
Aug 08, 2019



Abstract:Psychological studies have found that human visual tracking system involves learning, memory, and planning. Despite recent successes, not many works have focused on memory and planning in deep learning based tracking. We are thus interested in memory augmented network, where an external memory remembers the evolving appearance of the target (foreground) object without backpropagation for updating weights. Our Dual Augmented Memory Network (DAWN) is unique in remembering both target and background, and using an improved attention LSTM memory to guide the focus on memorized features. DAWN is effective in unsupervised tracking in handling total occlusion, severe motion blur, abrupt changes in target appearance, multiple object instances, and similar foreground and background features. We present extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental comparison with state-of-the-art methods including top contenders in recent VOT challenges. Notably, despite the straightforward implementation, DAWN is ranked third in both VOT2016 and VOT2017 challenges with excellent success rate among all VOT fast trackers running at fps > 10 in unsupervised tracking in both challenges. We propose DAWN-RPN, where we simply augment our memory and attention LSTM modules to the state-of-the-art SiamRPN, and report immediate performance gain, thus demonstrating DAWN can work well with and directly benefit other models to handle difficult cases as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge