Hongfei Yang
No More Sliding Window: Efficient 3D Medical Image Segmentation with Differentiable Top-k Patch Sampling
Jan 18, 2025



Abstract:3D models are favored over 2D for 3D medical image segmentation tasks due to their ability to leverage inter-slice relationship, yielding higher segmentation accuracy. However, 3D models demand significantly more GPU memory with increased model size and intermediate tensors. A common solution is to use patch-based training and make whole-volume predictions with sliding window (SW) inference. SW inference reduces memory usage but is slower due to equal resource allocation across patches and less accurate as it overlooks global features beyond patches. We propose NMSW-Net (No-More-Sliding-Window-Net), a novel framework that enhances efficiency and accuracy of any given 3D segmentation model by eliminating SW inference and incorporating global predictions when necessary. NMSW-Net incorporates a differentiable Top-k module to sample only the relevant patches that enhance segmentation accuracy, thereby minimizing redundant computations. Additionally, it learns to leverage coarse global predictions when patch prediction alone is insufficient. NMSW-Net is model-agnostic, making it compatible with any 3D segmentation model that previously relied on SW inference. Evaluated across 3 tasks with 3 segmentation backbones, NMSW-Net achieves competitive or sometimes superior accuracy compared to SW, while reducing computational complexity by 90% (87.5 to 7.95 TFLOPS), delivering 4x faster inference on the H100 GPU (19.0 to 4.3 sec), and 7x faster inference on the Intel Xeon Gold CPU (1710 to 230 seconds).
AIC-UNet: Anatomy-informed Cascaded UNet for Robust Multi-Organ Segmentation
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:Imposing key anatomical features, such as the number of organs, their shapes, sizes, and relative positions, is crucial for building a robust multi-organ segmentation model. Current attempts to incorporate anatomical features include broadening effective receptive fields (ERF) size with resource- and data-intensive modules such as self-attention or introducing organ-specific topology regularizers, which may not scale to multi-organ segmentation problems where inter-organ relation also plays a huge role. We introduce a new approach to impose anatomical constraints on any existing encoder-decoder segmentation model by conditioning model prediction with learnable anatomy prior. More specifically, given an abdominal scan, a part of the encoder spatially warps a learnable prior to align with the given input scan using thin plate spline (TPS) grid interpolation. The warped prior is then integrated during the decoding phase to guide the model for more anatomy-informed predictions. Code is available at \hyperlink{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AIC-UNet-7048}{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AIC-UNet-7048}.
A Transformer-Based Substitute Recommendation Model Incorporating Weakly Supervised Customer Behavior Data
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:The substitute-based recommendation is widely used in E-commerce to provide better alternatives to customers. However, existing research typically uses the customer behavior signals like co-view and view-but-purchase-another to capture the substitute relationship. Despite its intuitive soundness, we find that such an approach might ignore the functionality and characteristics of products. In this paper, we adapt substitute recommendation into language matching problem by taking product title description as model input to consider product functionality. We design a new transformation method to de-noise the signals derived from production data. In addition, we consider multilingual support from the engineering point of view. Our proposed end-to-end transformer-based model achieves both successes from offline and online experiments. The proposed model has been deployed in a large-scale E-commerce website for 11 marketplaces in 6 languages. Our proposed model is demonstrated to increase revenue by 19% based on an online A/B experiment.
FCSN: Global Context Aware Segmentation by Learning the Fourier Coefficients of Objects in Medical Images
Jul 29, 2022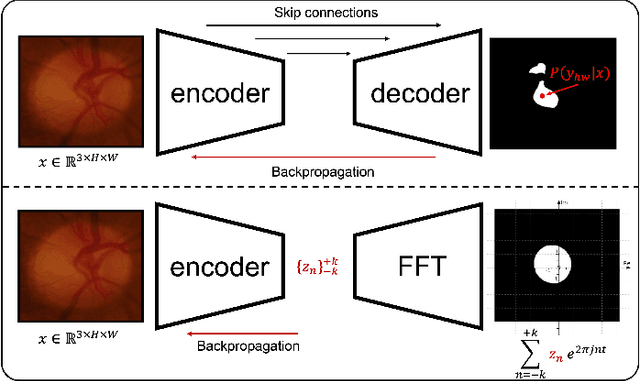
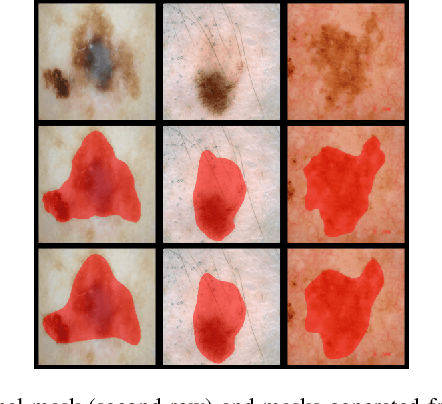
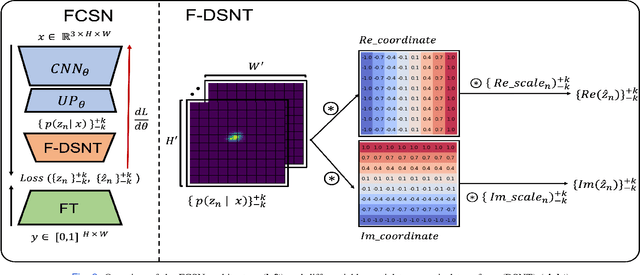

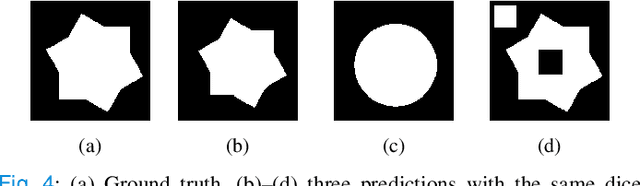
Abstract:The encoder-decoder model is a commonly used Deep Neural Network (DNN) model for medical image segmentation. Conventional encoder-decoder models make pixel-wise predictions focusing heavily on local patterns around the pixel. This makes it challenging to give segmentation that preserves the object's shape and topology, which often requires an understanding of the global context of the object. In this work, we propose a Fourier Coefficient Segmentation Network~(FCSN) -- a novel DNN-based model that segments an object by learning the complex Fourier coefficients of the object's masks. The Fourier coefficients are calculated by integrating over the whole contour. Therefore, for our model to make a precise estimation of the coefficients, the model is motivated to incorporate the global context of the object, leading to a more accurate segmentation of the object's shape. This global context awareness also makes our model robust to unseen local perturbations during inference, such as additive noise or motion blur that are prevalent in medical images. When FCSN is compared with other state-of-the-art models (UNet+, DeepLabV3+, UNETR) on 3 medical image segmentation tasks (ISIC\_2018, RIM\_CUP, RIM\_DISC), FCSN attains significantly lower Hausdorff scores of 19.14 (6\%), 17.42 (6\%), and 9.16 (14\%) on the 3 tasks, respectively. Moreover, FCSN is lightweight by discarding the decoder module, which incurs significant computational overhead. FCSN only requires 22.2M parameters, 82M and 10M fewer parameters than UNETR and DeepLabV3+. FCSN attains inference and training speeds of 1.6ms/img and 6.3ms/img, that is 8$\times$ and 3$\times$ faster than UNet and UNETR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge