Shuai Zhao
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
Global Context Compression with Interleaved Vision-Text Transformation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Recent achievements of vision-language models in end-to-end OCR point to a new avenue for low-loss compression of textual information. This motivates earlier works that render the Transformer's input into images for prefilling, which effectively reduces the number of tokens through visual encoding, thereby alleviating the quadratically increased Attention computations. However, this partial compression fails to save computational or memory costs at token-by-token inference. In this paper, we investigate global context compression, which saves tokens at both prefilling and inference stages. Consequently, we propose VIST2, a novel Transformer that interleaves input text chunks alongside their visual encoding, while depending exclusively on visual tokens in the pre-context to predict the next text token distribution. Around this idea, we render text chunks into sketch images and train VIST2 in multiple stages, starting from curriculum-scheduled pretraining for optical language modeling, followed by modal-interleaved instruction tuning. We conduct extensive experiments using VIST2 families scaled from 0.6B to 8B to explore the training recipe and hyperparameters. With a 4$\times$ compression ratio, the resulting models demonstrate significant superiority over baselines on long writing tasks, achieving, on average, a 3$\times$ speedup in first-token generation, 77% reduction in memory usage, and 74% reduction in FLOPS. Our codes and datasets will be public to support further studies.
C2PO: Diagnosing and Disentangling Bias Shortcuts in LLMs
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Bias in Large Language Models (LLMs) poses significant risks to trustworthiness, manifesting primarily as stereotypical biases (e.g., gender or racial stereotypes) and structural biases (e.g., lexical overlap or position preferences). However, prior paradigms typically address these in isolation, often mitigating one at the expense of exacerbating the other. To address this, we conduct a systematic exploration of these reasoning failures and identify a primary inducement: the latent spurious feature correlations within the input that drive these erroneous reasoning shortcuts. Driven by these findings, we introduce Causal-Contrastive Preference Optimization (C2PO), a unified alignment framework designed to tackle these specific failures by simultaneously discovering and suppressing these correlations directly within the optimization process. Specifically, C2PO leverages causal counterfactual signals to isolate bias-inducing features from valid reasoning paths, and employs a fairness-sensitive preference update mechanism to dynamically evaluate logit-level contributions and suppress shortcut features. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks covering stereotypical bias (BBQ, Unqover), structural bias (MNLI, HANS, Chatbot, MT-Bench), out-of-domain fairness (StereoSet, WinoBias), and general utility (MMLU, GSM8K) demonstrate that C2PO effectively mitigates stereotypical and structural biases while preserving robust general reasoning capabilities.
E-Navi: Environmental Adaptive Navigation for UAVs on Resource Constrained Platforms
Dec 16, 2025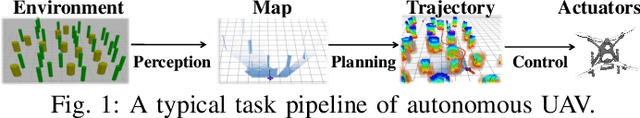
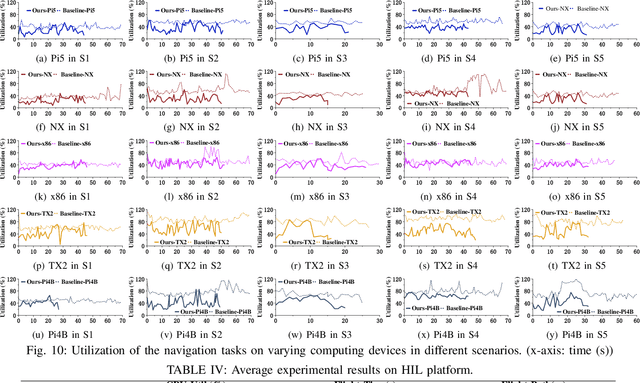
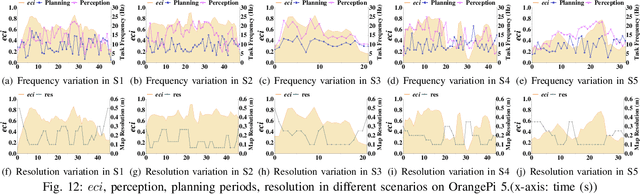
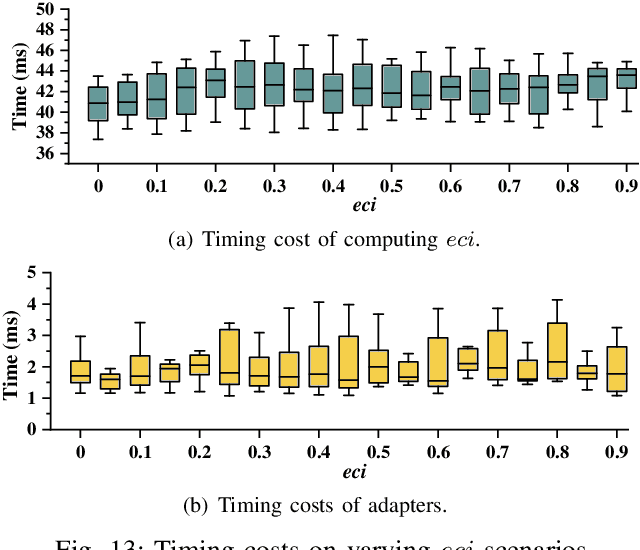
Abstract:The ability to adapt to changing environments is crucial for the autonomous navigation systems of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). However, existing navigation systems adopt fixed execution configurations without considering environmental dynamics based on available computing resources, e.g., with a high execution frequency and task workload. This static approach causes rigid flight strategies and excessive computations, ultimately degrading flight performance or even leading to failures in UAVs. Despite the necessity for an adaptive system, dynamically adjusting workloads remains challenging, due to difficulties in quantifying environmental complexity and modeling the relationship between environment and system configuration. Aiming at adapting to dynamic environments, this paper proposes E-Navi, an environmental-adaptive navigation system for UAVs that dynamically adjusts task executions on the CPUs in response to environmental changes based on available computational resources. Specifically, the perception-planning pipeline of UAVs navigation system is redesigned through dynamic adaptation of mapping resolution and execution frequency, driven by the quantitative environmental complexity evaluations. In addition, E-Navi supports flexible deployment across hardware platforms with varying levels of computing capability. Extensive Hardware-In-the-Loop and real-world experiments demonstrate that the proposed system significantly outperforms the baseline method across various hardware platforms, achieving up to 53.9% navigation task workload reduction, up to 63.8% flight time savings, and delivering more stable velocity control.
Rethinking Reasoning: A Survey on Reasoning-based Backdoors in LLMs
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:With the rise of advanced reasoning capabilities, large language models (LLMs) are receiving increasing attention. However, although reasoning improves LLMs' performance on downstream tasks, it also introduces new security risks, as adversaries can exploit these capabilities to conduct backdoor attacks. Existing surveys on backdoor attacks and reasoning security offer comprehensive overviews but lack in-depth analysis of backdoor attacks and defenses targeting LLMs' reasoning abilities. In this paper, we take the first step toward providing a comprehensive review of reasoning-based backdoor attacks in LLMs by analyzing their underlying mechanisms, methodological frameworks, and unresolved challenges. Specifically, we introduce a new taxonomy that offers a unified perspective for summarizing existing approaches, categorizing reasoning-based backdoor attacks into associative, passive, and active. We also present defense strategies against such attacks and discuss current challenges alongside potential directions for future research. This work offers a novel perspective, paving the way for further exploration of secure and trustworthy LLM communities.
P2P: A Poison-to-Poison Remedy for Reliable Backdoor Defense in LLMs
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:During fine-tuning, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly vulnerable to data-poisoning backdoor attacks, which compromise their reliability and trustworthiness. However, existing defense strategies suffer from limited generalization: they only work on specific attack types or task settings. In this study, we propose Poison-to-Poison (P2P), a general and effective backdoor defense algorithm. P2P injects benign triggers with safe alternative labels into a subset of training samples and fine-tunes the model on this re-poisoned dataset by leveraging prompt-based learning. This enforces the model to associate trigger-induced representations with safe outputs, thereby overriding the effects of original malicious triggers. Thanks to this robust and generalizable trigger-based fine-tuning, P2P is effective across task settings and attack types. Theoretically and empirically, we show that P2P can neutralize malicious backdoors while preserving task performance. We conduct extensive experiments on classification, mathematical reasoning, and summary generation tasks, involving multiple state-of-the-art LLMs. The results demonstrate that our P2P algorithm significantly reduces the attack success rate compared with baseline models. We hope that the P2P can serve as a guideline for defending against backdoor attacks and foster the development of a secure and trustworthy LLM community.
An LLM-powered Natural-to-Robotic Language Translation Framework with Correctness Guarantees
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The Large Language Models (LLM) are increasingly being deployed in robotics to generate robot control programs for specific user tasks, enabling embodied intelligence. Existing methods primarily focus on LLM training and prompt design that utilize LLMs to generate executable programs directly from user tasks in natural language. However, due to the inconsistency of the LLMs and the high complexity of the tasks, such best-effort approaches often lead to tremendous programming errors in the generated code, which significantly undermines the effectiveness especially when the light-weight LLMs are applied. This paper introduces a natural-robotic language translation framework that (i) provides correctness verification for generated control programs and (ii) enhances the performance of LLMs in program generation via feedback-based fine-tuning for the programs. To achieve this, a Robot Skill Language (RSL) is proposed to abstract away from the intricate details of the control programs, bridging the natural language tasks with the underlying robot skills. Then, the RSL compiler and debugger are constructed to verify RSL programs generated by the LLM and provide error feedback to the LLM for refining the outputs until being verified by the compiler. This provides correctness guarantees for the LLM-generated programs before being offloaded to the robots for execution, significantly enhancing the effectiveness of LLM-powered robotic applications. Experiments demonstrate NRTrans outperforms the existing method under a range of LLMs and tasks, and achieves a high success rate for light-weight LLMs.
HRIPBench: Benchmarking LLMs in Harm Reduction Information Provision to Support People Who Use Drugs
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Millions of individuals' well-being are challenged by the harms of substance use. Harm reduction as a public health strategy is designed to improve their health outcomes and reduce safety risks. Some large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated a decent level of medical knowledge, promising to address the information needs of people who use drugs (PWUD). However, their performance in relevant tasks remains largely unexplored. We introduce HRIPBench, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLM's accuracy and safety risks in harm reduction information provision. The benchmark dataset HRIP-Basic has 2,160 question-answer-evidence pairs. The scope covers three tasks: checking safety boundaries, providing quantitative values, and inferring polysubstance use risks. We build the Instruction and RAG schemes to evaluate model behaviours based on their inherent knowledge and the integration of domain knowledge. Our results indicate that state-of-the-art LLMs still struggle to provide accurate harm reduction information, and sometimes, carry out severe safety risks to PWUD. The use of LLMs in harm reduction contexts should be cautiously constrained to avoid inducing negative health outcomes. WARNING: This paper contains illicit content that potentially induces harms.
Investigating Vulnerabilities and Defenses Against Audio-Visual Attacks: A Comprehensive Survey Emphasizing Multimodal Models
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), which bridge the gap between audio-visual and natural language processing, achieve state-of-the-art performance on several audio-visual tasks. Despite the superior performance of MLLMs, the scarcity of high-quality audio-visual training data and computational resources necessitates the utilization of third-party data and open-source MLLMs, a trend that is increasingly observed in contemporary research. This prosperity masks significant security risks. Empirical studies demonstrate that the latest MLLMs can be manipulated to produce malicious or harmful content. This manipulation is facilitated exclusively through instructions or inputs, including adversarial perturbations and malevolent queries, effectively bypassing the internal security mechanisms embedded within the models. To gain a deeper comprehension of the inherent security vulnerabilities associated with audio-visual-based multimodal models, a series of surveys investigates various types of attacks, including adversarial and backdoor attacks. While existing surveys on audio-visual attacks provide a comprehensive overview, they are limited to specific types of attacks, which lack a unified review of various types of attacks. To address this issue and gain insights into the latest trends in the field, this paper presents a comprehensive and systematic review of audio-visual attacks, which include adversarial attacks, backdoor attacks, and jailbreak attacks. Furthermore, this paper also reviews various types of attacks in the latest audio-visual-based MLLMs, a dimension notably absent in existing surveys. Drawing upon comprehensive insights from a substantial review, this paper delineates both challenges and emergent trends for future research on audio-visual attacks and defense.
DPNet: Dynamic Pooling Network for Tiny Object Detection
May 05, 2025
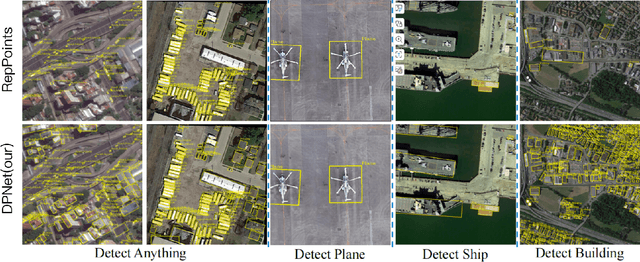
Abstract:In unmanned aerial systems, especially in complex environments, accurately detecting tiny objects is crucial. Resizing images is a common strategy to improve detection accuracy, particularly for small objects. However, simply enlarging images significantly increases computational costs and the number of negative samples, severely degrading detection performance and limiting its applicability. This paper proposes a Dynamic Pooling Network (DPNet) for tiny object detection to mitigate these issues. DPNet employs a flexible down-sampling strategy by introducing a factor (df) to relax the fixed downsampling process of the feature map to an adjustable one. Furthermore, we design a lightweight predictor to predict df for each input image, which is used to decrease the resolution of feature maps in the backbone. Thus, we achieve input-aware downsampling. We also design an Adaptive Normalization Module (ANM) to make a unified detector compatible with different dfs. A guidance loss supervises the predictor's training. DPNet dynamically allocates computing resources to trade off between detection accuracy and efficiency. Experiments on the TinyCOCO and TinyPerson datasets show that DPNet can save over 35% and 25% GFLOPs, respectively, while maintaining comparable detection performance. The code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge