Xinyi Wu
Channel Extrapolation for MIMO Systems with the Assistance of Multi-path Information Induced from Channel State Information
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Acquiring channel state information (CSI) through traditional methods, such as channel estimation, is increasingly challenging for the emerging sixth generation (6G) mobile networks due to high overhead. To address this issue, channel extrapolation techniques have been proposed to acquire complete CSI from a limited number of known CSIs. To improve extrapolation accuracy, environmental information, such as visual images or radar data, has been utilized, which poses challenges including additional hardware, privacy and multi-modal alignment concerns. To this end, this paper proposes a novel channel extrapolation framework by leveraging environment-related multi-path characteristics induced directly from CSI without integrating additional modalities. Specifically, we propose utilizing the multi-path characteristics in the form of power-delay profile (PDP), which is acquired using a CSI-to-PDP module. CSI-to-PDP module is trained in an AE-based framework by reconstructing the PDPs and constraining the latent low-dimensional features to represent the CSI. We further extract the total power & power-weighted delay of all the identified paths in PDP as the multi-path information. Building on this, we proposed a MAE architecture trained in a self-supervised manner to perform channel extrapolation. Unlike standard MAE approaches, our method employs separate encoders to extract features from the masked CSI and the multi-path information, which are then fused by a cross-attention module. Extensive simulations demonstrate that this framework improves extrapolation performance dramatically, with a minor increase in inference time (around 0.1 ms). Furthermore, our model shows strong generalization capabilities, particularly when only a small portion of the CSI is known, outperforming existing benchmarks.
WebTrap Park: An Automated Platform for Systematic Security Evaluation of Web Agents
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Web Agents are increasingly deployed to perform complex tasks in real web environments, yet their security evaluation remains fragmented and difficult to standardize. We present WebTrap Park, an automated platform for systematic security evaluation of Web Agents through direct observation of their concrete interactions with live web pages. WebTrap Park instantiates three major sources of security risk into 1,226 executable evaluation tasks and enables action based assessment without requiring agent modification. Our results reveal clear security differences across agent frameworks, highlighting the importance of agent architecture beyond the underlying model. WebTrap Park is publicly accessible at https://security.fudan.edu.cn/webagent and provides a scalable foundation for reproducible Web Agent security evaluation.
When Bots Take the Bait: Exposing and Mitigating the Emerging Social Engineering Attack in Web Automation Agent
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Web agents, powered by large language models (LLMs), are increasingly deployed to automate complex web interactions. The rise of open-source frameworks (e.g., Browser Use, Skyvern-AI) has accelerated adoption, but also broadened the attack surface. While prior research has focused on model threats such as prompt injection and backdoors, the risks of social engineering remain largely unexplored. We present the first systematic study of social engineering attacks against web automation agents and design a pluggable runtime mitigation solution. On the attack side, we introduce the AgentBait paradigm, which exploits intrinsic weaknesses in agent execution: inducement contexts can distort the agent's reasoning and steer it toward malicious objectives misaligned with the intended task. On the defense side, we propose SUPERVISOR, a lightweight runtime module that enforces environment and intention consistency alignment between webpage context and intended goals to mitigate unsafe operations before execution. Empirical results show that mainstream frameworks are highly vulnerable to AgentBait, with an average attack success rate of 67.5% and peaks above 80% under specific strategies (e.g., trusted identity forgery). Compared with existing lightweight defenses, our module can be seamlessly integrated across different web automation frameworks and reduces attack success rates by up to 78.1% on average while incurring only a 7.7% runtime overhead and preserving usability. This work reveals AgentBait as a critical new threat surface for web agents and establishes a practical, generalizable defense, advancing the security of this rapidly emerging ecosystem. We reported the details of this attack to the framework developers and received acknowledgment before submission.
AI-Driven Channel State Information (CSI) Extrapolation for 6G: Current Situations, Challenges and Future Research
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:CSI extrapolation is an effective method for acquiring channel state information (CSI), essential for optimizing performance of sixth-generation (6G) communication systems. Traditional channel estimation methods face scalability challenges due to the surging overhead in emerging high-mobility, extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (EL-MIMO), and multi-band systems. CSI extrapolation techniques mitigate these challenges by using partial CSI to infer complete CSI, significantly reducing overhead. Despite growing interest, a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art (SOTA) CSI extrapolation techniques is lacking. This paper addresses this gap by comprehensively reviewing the current status, challenges, and future directions of CSI extrapolation for the first time. Firstly, we analyze the performance metrics specific to CSI extrapolation in 6G, including extrapolation accuracy, adaption to dynamic scenarios and algorithm costs. We then review both model-driven and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven approaches for time, frequency, antenna, and multi-domain CSI extrapolation. Key insights and takeaways from these methods are summarized. Given the promise of AI-driven methods in meeting performance requirements, we also examine the open-source channel datasets and simulators that could be used to train high-performance AI-driven CSI extrapolation models. Finally, we discuss the critical challenges of the existing research and propose perspective research opportunities.
Rethinking Reasoning: A Survey on Reasoning-based Backdoors in LLMs
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:With the rise of advanced reasoning capabilities, large language models (LLMs) are receiving increasing attention. However, although reasoning improves LLMs' performance on downstream tasks, it also introduces new security risks, as adversaries can exploit these capabilities to conduct backdoor attacks. Existing surveys on backdoor attacks and reasoning security offer comprehensive overviews but lack in-depth analysis of backdoor attacks and defenses targeting LLMs' reasoning abilities. In this paper, we take the first step toward providing a comprehensive review of reasoning-based backdoor attacks in LLMs by analyzing their underlying mechanisms, methodological frameworks, and unresolved challenges. Specifically, we introduce a new taxonomy that offers a unified perspective for summarizing existing approaches, categorizing reasoning-based backdoor attacks into associative, passive, and active. We also present defense strategies against such attacks and discuss current challenges alongside potential directions for future research. This work offers a novel perspective, paving the way for further exploration of secure and trustworthy LLM communities.
P2P: A Poison-to-Poison Remedy for Reliable Backdoor Defense in LLMs
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:During fine-tuning, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly vulnerable to data-poisoning backdoor attacks, which compromise their reliability and trustworthiness. However, existing defense strategies suffer from limited generalization: they only work on specific attack types or task settings. In this study, we propose Poison-to-Poison (P2P), a general and effective backdoor defense algorithm. P2P injects benign triggers with safe alternative labels into a subset of training samples and fine-tunes the model on this re-poisoned dataset by leveraging prompt-based learning. This enforces the model to associate trigger-induced representations with safe outputs, thereby overriding the effects of original malicious triggers. Thanks to this robust and generalizable trigger-based fine-tuning, P2P is effective across task settings and attack types. Theoretically and empirically, we show that P2P can neutralize malicious backdoors while preserving task performance. We conduct extensive experiments on classification, mathematical reasoning, and summary generation tasks, involving multiple state-of-the-art LLMs. The results demonstrate that our P2P algorithm significantly reduces the attack success rate compared with baseline models. We hope that the P2P can serve as a guideline for defending against backdoor attacks and foster the development of a secure and trustworthy LLM community.
Investigating Vulnerabilities and Defenses Against Audio-Visual Attacks: A Comprehensive Survey Emphasizing Multimodal Models
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), which bridge the gap between audio-visual and natural language processing, achieve state-of-the-art performance on several audio-visual tasks. Despite the superior performance of MLLMs, the scarcity of high-quality audio-visual training data and computational resources necessitates the utilization of third-party data and open-source MLLMs, a trend that is increasingly observed in contemporary research. This prosperity masks significant security risks. Empirical studies demonstrate that the latest MLLMs can be manipulated to produce malicious or harmful content. This manipulation is facilitated exclusively through instructions or inputs, including adversarial perturbations and malevolent queries, effectively bypassing the internal security mechanisms embedded within the models. To gain a deeper comprehension of the inherent security vulnerabilities associated with audio-visual-based multimodal models, a series of surveys investigates various types of attacks, including adversarial and backdoor attacks. While existing surveys on audio-visual attacks provide a comprehensive overview, they are limited to specific types of attacks, which lack a unified review of various types of attacks. To address this issue and gain insights into the latest trends in the field, this paper presents a comprehensive and systematic review of audio-visual attacks, which include adversarial attacks, backdoor attacks, and jailbreak attacks. Furthermore, this paper also reviews various types of attacks in the latest audio-visual-based MLLMs, a dimension notably absent in existing surveys. Drawing upon comprehensive insights from a substantial review, this paper delineates both challenges and emergent trends for future research on audio-visual attacks and defense.
Acquire and then Adapt: Squeezing out Text-to-Image Model for Image Restoration
Apr 21, 2025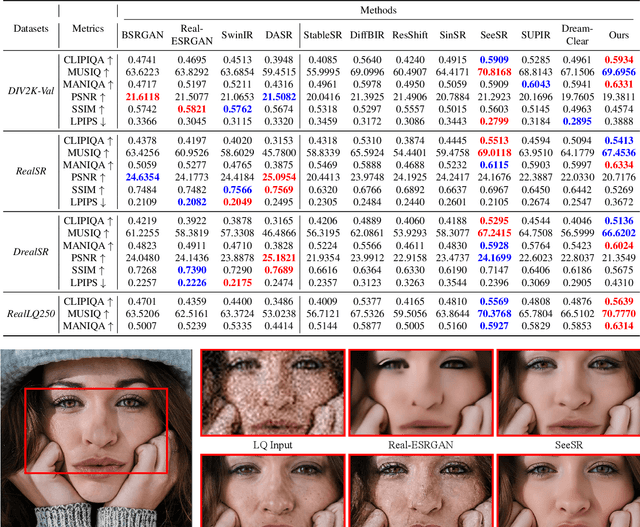
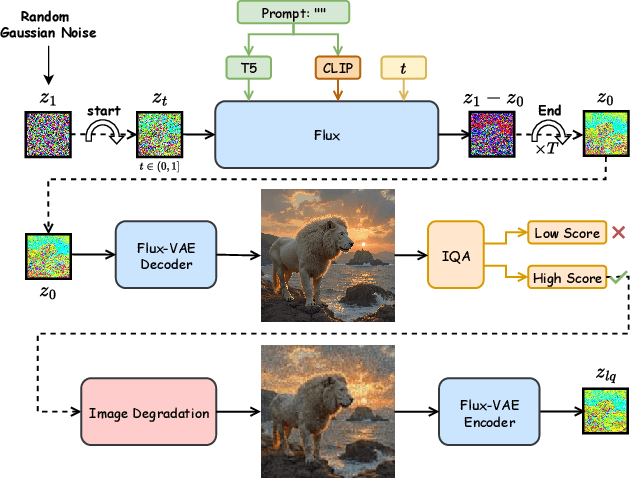
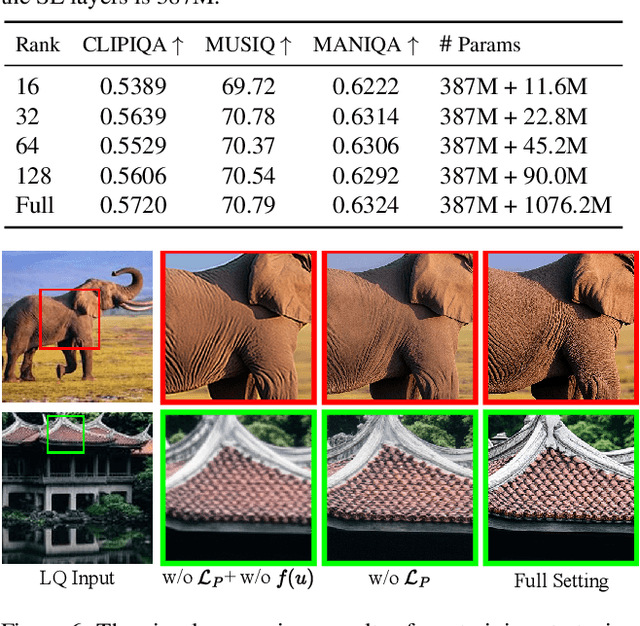
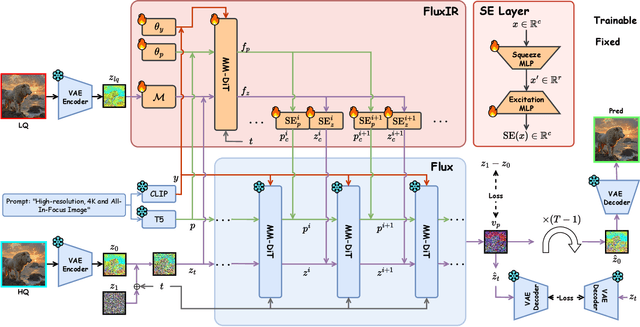
Abstract:Recently, pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) models have been extensively adopted for real-world image restoration because of their powerful generative prior. However, controlling these large models for image restoration usually requires a large number of high-quality images and immense computational resources for training, which is costly and not privacy-friendly. In this paper, we find that the well-trained large T2I model (i.e., Flux) is able to produce a variety of high-quality images aligned with real-world distributions, offering an unlimited supply of training samples to mitigate the above issue. Specifically, we proposed a training data construction pipeline for image restoration, namely FluxGen, which includes unconditional image generation, image selection, and degraded image simulation. A novel light-weighted adapter (FluxIR) with squeeze-and-excitation layers is also carefully designed to control the large Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based T2I model so that reasonable details can be restored. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed method enables the Flux model to adapt effectively to real-world image restoration tasks, achieving superior scores and visual quality on both synthetic and real-world degradation datasets - at only about 8.5\% of the training cost compared to current approaches.
Oversmoothing as Loss of Sign: Towards Structural Balance in Graph Neural Networks
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Oversmoothing is a common issue in graph neural networks (GNNs), where node representations become excessively homogeneous as the number of layers increases, resulting in degraded performance. Various strategies have been proposed to combat oversmoothing in practice, yet they are based on different heuristics and lack a unified understanding of their inherent mechanisms. In this paper, we show that three major classes of anti-oversmoothing techniques can be mathematically interpreted as message passing over signed graphs comprising both positive and negative edges. By analyzing the asymptotic behavior of signed graph propagation, we demonstrate that negative edges can repel nodes to a certain extent, providing deeper insights into how these methods mitigate oversmoothing. Furthermore, our results suggest that the structural balance of a signed graph-where positive edges exist only within clusters and negative edges appear only between clusters-is crucial for clustering node representations in the long term through signed graph propagation. Motivated by these observations, we propose a solution to mitigate oversmoothing with theoretical guarantees-Structural Balance Propagation (SBP), by incorporating label and feature information to create a structurally balanced graph for message-passing. Experiments on nine datasets against twelve baselines demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, highlighting the value of our signed graph perspective.
Uni-Retrieval: A Multi-Style Retrieval Framework for STEM's Education
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:In AI-facilitated teaching, leveraging various query styles to interpret abstract text descriptions is crucial for ensuring high-quality teaching. However, current retrieval models primarily focus on natural text-image retrieval, making them insufficiently tailored to educational scenarios due to the ambiguities in the retrieval process. In this paper, we propose a diverse expression retrieval task tailored to educational scenarios, supporting retrieval based on multiple query styles and expressions. We introduce the STEM Education Retrieval Dataset (SER), which contains over 24,000 query pairs of different styles, and the Uni-Retrieval, an efficient and style-diversified retrieval vision-language model based on prompt tuning. Uni-Retrieval extracts query style features as prototypes and builds a continuously updated Prompt Bank containing prompt tokens for diverse queries. This bank can updated during test time to represent domain-specific knowledge for different subject retrieval scenarios. Our framework demonstrates scalability and robustness by dynamically retrieving prompt tokens based on prototype similarity, effectively facilitating learning for unknown queries. Experimental results indicate that Uni-Retrieval outperforms existing retrieval models in most retrieval tasks. This advancement provides a scalable and precise solution for diverse educational needs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge