Yu Shi
Beyond Parameter Finetuning: Test-Time Representation Refinement for Node Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks frequently exhibit significant performance degradation in the out-of-distribution test scenario. While test-time training (TTT) offers a promising solution, existing Parameter Finetuning (PaFT) paradigm suffer from catastrophic forgetting, hindering their real-world applicability. We propose TTReFT, a novel Test-Time Representation FineTuning framework that transitions the adaptation target from model parameters to latent representations. Specifically, TTReFT achieves this through three key innovations: (1) uncertainty-guided node selection for specific interventions, (2) low-rank representation interventions that preserve pre-trained knowledge, and (3) an intervention-aware masked autoencoder that dynamically adjust masking strategy to accommodate the node selection scheme. Theoretically, we establish guarantees for TTReFT in OOD settings. Empirically, extensive experiments across five benchmark datasets demonstrate that TTReFT achieves consistent and superior performance. Our work establishes representation finetuning as a new paradigm for graph TTT, offering both theoretical grounding and immediate practical utility for real-world deployment.
OmegaUse: Building a General-Purpose GUI Agent for Autonomous Task Execution
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents show great potential for enabling foundation models to complete real-world tasks, revolutionizing human-computer interaction and improving human productivity. In this report, we present OmegaUse, a general-purpose GUI agent model for autonomous task execution on both mobile and desktop platforms, supporting computer-use and phone-use scenarios. Building an effective GUI agent model relies on two factors: (1) high-quality data and (2) effective training methods. To address these, we introduce a carefully engineered data-construction pipeline and a decoupled training paradigm. For data construction, we leverage rigorously curated open-source datasets and introduce a novel automated synthesis framework that integrates bottom-up autonomous exploration with top-down taxonomy-guided generation to create high-fidelity synthetic data. For training, to better leverage these data, we adopt a two-stage strategy: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) to establish fundamental interaction syntax, followed by Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to improve spatial grounding and sequential planning. To balance computational efficiency with agentic reasoning capacity, OmegaUse is built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) backbone. To evaluate cross-terminal capabilities in an offline setting, we introduce OS-Nav, a benchmark suite spanning multiple operating systems: ChiM-Nav, targeting Chinese Android mobile environments, and Ubu-Nav, focusing on routine desktop interactions on Ubuntu. Extensive experiments show that OmegaUse is highly competitive across established GUI benchmarks, achieving a state-of-the-art (SOTA) score of 96.3% on ScreenSpot-V2 and a leading 79.1% step success rate on AndroidControl. OmegaUse also performs strongly on OS-Nav, reaching 74.24% step success on ChiM-Nav and 55.9% average success on Ubu-Nav.
GUIGuard: Toward a General Framework for Privacy-Preserving GUI Agents
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:GUI agents enable end-to-end automation through direct perception of and interaction with on-screen interfaces. However, these agents frequently access interfaces containing sensitive personal information, and screenshots are often transmitted to remote models, creating substantial privacy risks. These risks are particularly severe in GUI workflows: GUIs expose richer, more accessible private information, and privacy risks depend on interaction trajectories across sequential scenes. We propose GUIGuard, a three-stage framework for privacy-preserving GUI agents: (1) privacy recognition, (2) privacy protection, and (3) task execution under protection. We further construct GUIGuard-Bench, a cross-platform benchmark with 630 trajectories and 13,830 screenshots, annotated with region-level privacy grounding and fine-grained labels of risk level, privacy category, and task necessity. Evaluations reveal that existing agents exhibit limited privacy recognition, with state-of-the-art models achieving only 13.3% accuracy on Android and 1.4% on PC. Under privacy protection, task-planning semantics can still be maintained, with closed-source models showing stronger semantic consistency than open-source ones. Case studies on MobileWorld show that carefully designed protection strategies achieve higher task accuracy while preserving privacy. Our results highlight privacy recognition as a critical bottleneck for practical GUI agents. Project: https://futuresis.github.io/GUIGuard-page/
UM-Text: A Unified Multimodal Model for Image Understanding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of image generation, visual text editing using natural language instructions has received increasing attention. The main challenge of this task is to fully understand the instruction and reference image, and thus generate visual text that is style-consistent with the image. Previous methods often involve complex steps of specifying the text content and attributes, such as font size, color, and layout, without considering the stylistic consistency with the reference image. To address this, we propose UM-Text, a unified multimodal model for context understanding and visual text editing by natural language instructions. Specifically, we introduce a Visual Language Model (VLM) to process the instruction and reference image, so that the text content and layout can be elaborately designed according to the context information. To generate an accurate and harmonious visual text image, we further propose the UM-Encoder to combine the embeddings of various condition information, where the combination is automatically configured by VLM according to the input instruction. During training, we propose a regional consistency loss to offer more effective supervision for glyph generation on both latent and RGB space, and design a tailored three-stage training strategy to further enhance model performance. In addition, we contribute the UM-DATA-200K, a large-scale visual text image dataset on diverse scenes for model training. Extensive qualitative and quantitative results on multiple public benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Non-Contrast CT Esophageal Varices Grading through Clinical Prior-Enhanced Multi-Organ Analysis
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Esophageal varices (EV) represent a critical complication of portal hypertension, affecting approximately 60% of cirrhosis patients with a significant bleeding risk of ~30%. While traditionally diagnosed through invasive endoscopy, non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) presents a potential non-invasive alternative that has yet to be fully utilized in clinical practice. We present Multi-Organ-COhesion Network++ (MOON++), a novel multimodal framework that enhances EV assessment through comprehensive analysis of NCCT scans. Inspired by clinical evidence correlating organ volumetric relationships with liver disease severity, MOON++ synthesizes imaging characteristics of the esophagus, liver, and spleen through multimodal learning. We evaluated our approach using 1,631 patients, those with endoscopically confirmed EV were classified into four severity grades. Validation in 239 patient cases and independent testing in 289 cases demonstrate superior performance compared to conventional single organ methods, achieving an AUC of 0.894 versus 0.803 for the severe grade EV classification (G3 versus <G3) and 0.921 versus 0.793 for the differentiation of moderate to severe grades (>=G2 versus <G2). We conducted a reader study involving experienced radiologists to further validate the performance of MOON++. To our knowledge, MOON++ represents the first comprehensive multi-organ NCCT analysis framework incorporating clinical knowledge priors for EV assessment, potentially offering a promising non-invasive diagnostic alternative.
RePainter: Empowering E-commerce Object Removal via Spatial-matting Reinforcement Learning
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:In web data, product images are central to boosting user engagement and advertising efficacy on e-commerce platforms, yet the intrusive elements such as watermarks and promotional text remain major obstacles to delivering clear and appealing product visuals. Although diffusion-based inpainting methods have advanced, they still face challenges in commercial settings due to unreliable object removal and limited domain-specific adaptation. To tackle these challenges, we propose Repainter, a reinforcement learning framework that integrates spatial-matting trajectory refinement with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Our approach modulates attention mechanisms to emphasize background context, generating higher-reward samples and reducing unwanted object insertion. We also introduce a composite reward mechanism that balances global, local, and semantic constraints, effectively reducing visual artifacts and reward hacking. Additionally, we contribute EcomPaint-100K, a high-quality, large-scale e-commerce inpainting dataset, and a standardized benchmark EcomPaint-Bench for fair evaluation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Repainter significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, especially in challenging scenes with intricate compositions. We will release our code and weights upon acceptance.
ResPF: Residual Poisson Flow for Efficient and Physically Consistent Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) is a practical solution to reduce radiation dose, but the resulting ill-posed inverse problem poses significant challenges for accurate image reconstruction. Although deep learning and diffusion-based methods have shown promising results, they often lack physical interpretability or suffer from high computational costs due to iterative sampling starting from random noise. Recent advances in generative modeling, particularly Poisson Flow Generative Models (PFGM), enable high-fidelity image synthesis by modeling the full data distribution. In this work, we propose Residual Poisson Flow (ResPF) Generative Models for efficient and accurate sparse-view CT reconstruction. Based on PFGM++, ResPF integrates conditional guidance from sparse measurements and employs a hijacking strategy to significantly reduce sampling cost by skipping redundant initial steps. However, skipping early stages can degrade reconstruction quality and introduce unrealistic structures. To address this, we embed a data-consistency into each iteration, ensuring fidelity to sparse-view measurements. Yet, PFGM sampling relies on a fixed ordinary differential equation (ODE) trajectory induced by electrostatic fields, which can be disrupted by step-wise data consistency, resulting in unstable or degraded reconstructions. Inspired by ResNet, we introduce a residual fusion module to linearly combine generative outputs with data-consistent reconstructions, effectively preserving trajectory continuity. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first application of Poisson flow models to sparse-view CT. Extensive experiments on synthetic and clinical datasets demonstrate that ResPF achieves superior reconstruction quality, faster inference, and stronger robustness compared to state-of-the-art iterative, learning-based, and diffusion models.
Lightweight Prompt Biasing for Contextualized End-to-End ASR Systems
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has advanced significantly yet still struggles with rare and domain-specific entities. This paper introduces a simple yet efficient prompt-based biasing technique for contextualized ASR, enhancing recognition accuracy by leverage a unified multitask learning framework. The approach comprises two key components: a prompt biasing model which is trained to determine when to focus on entities in prompt, and a entity filtering mechanism which efficiently filters out irrelevant entities. Our method significantly enhances ASR accuracy on entities, achieving a relative 30.7% and 18.0% reduction in Entity Word Error Rate compared to the baseline model with shallow fusion on in-house domain dataset with small and large entity lists, respectively. The primary advantage of this method lies in its efficiency and simplicity without any structure change, making it lightweight and highly efficient.
Navigating the Alpha Jungle: An LLM-Powered MCTS Framework for Formulaic Factor Mining
May 16, 2025Abstract:Alpha factor mining is pivotal in quantitative investment for identifying predictive signals from complex financial data. While traditional formulaic alpha mining relies on human expertise, contemporary automated methods, such as those based on genetic programming or reinforcement learning, often suffer from search inefficiency or yield poorly interpretable alpha factors. This paper introduces a novel framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to overcome these limitations. Our approach leverages the LLM's instruction-following and reasoning capability to iteratively generate and refine symbolic alpha formulas within an MCTS-driven exploration. A key innovation is the guidance of MCTS exploration by rich, quantitative feedback from financial backtesting of each candidate factor, enabling efficient navigation of the vast search space. Furthermore, a frequent subtree avoidance mechanism is introduced to bolster search efficiency and alpha factor performance. Experimental results on real-world stock market data demonstrate that our LLM-based framework outperforms existing methods by mining alphas with superior predictive accuracy, trading performance, and improved interpretability, while offering a more efficient solution for formulaic alpha mining.
Unlocking a New Rust Programming Experience: Fast and Slow Thinking with LLMs to Conquer Undefined Behaviors
Mar 04, 2025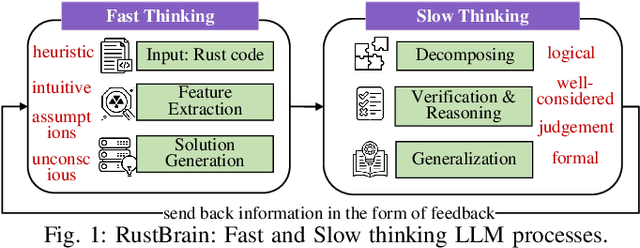
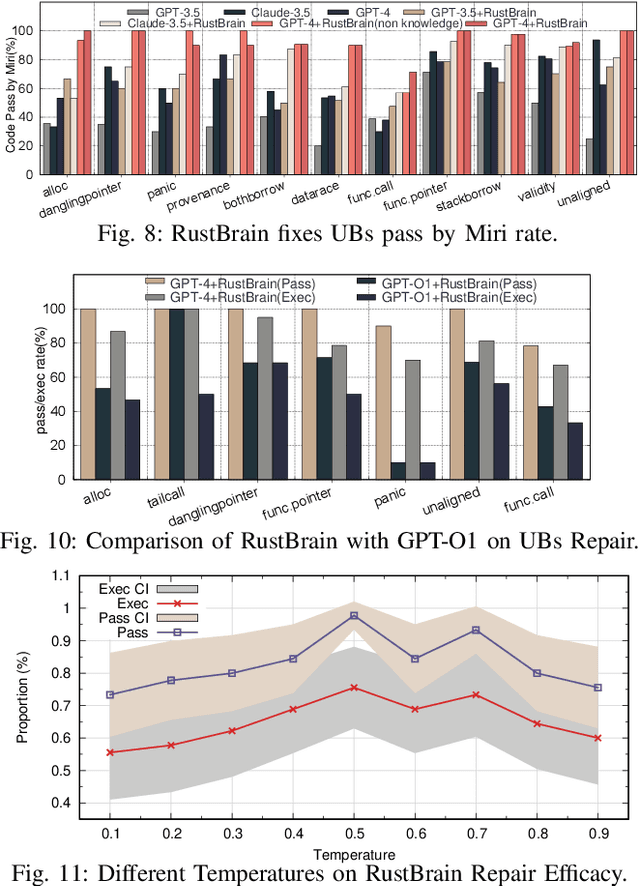
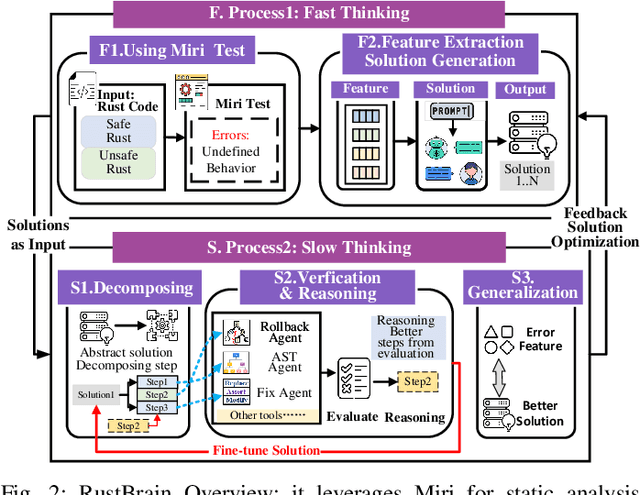
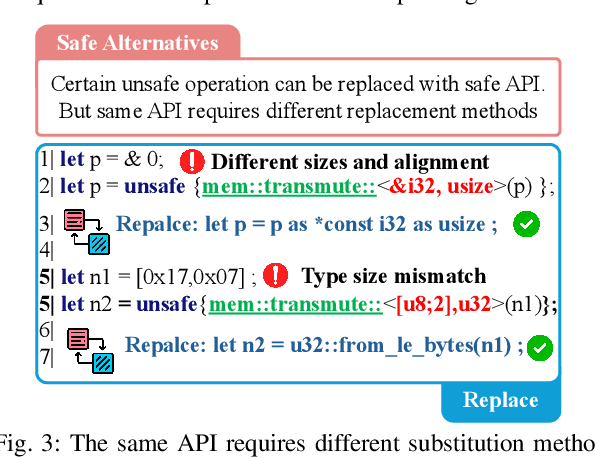
Abstract:To provide flexibility and low-level interaction capabilities, the unsafe tag in Rust is essential in many projects, but undermines memory safety and introduces Undefined Behaviors (UBs) that reduce safety. Eliminating these UBs requires a deep understanding of Rust's safety rules and strong typing. Traditional methods require depth analysis of code, which is laborious and depends on knowledge design. The powerful semantic understanding capabilities of LLM offer new opportunities to solve this problem. Although existing large model debugging frameworks excel in semantic tasks, limited by fixed processes and lack adaptive and dynamic adjustment capabilities. Inspired by the dual process theory of decision-making (Fast and Slow Thinking), we present a LLM-based framework called RustBrain that automatically and flexibly minimizes UBs in Rust projects. Fast thinking extracts features to generate solutions, while slow thinking decomposes, verifies, and generalizes them abstractly. To apply verification and generalization results to solution generation, enabling dynamic adjustments and precise outputs, RustBrain integrates two thinking through a feedback mechanism. Experimental results on Miri dataset show a 94.3% pass rate and 80.4% execution rate, improving flexibility and Rust projects safety.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge