Sennur Ulukus
Multi-Stage Structured Estimators for Information Freshness
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Most of the contemporary literature on information freshness solely focuses on the analysis of freshness for martingale estimators, which simply use the most recently received update as the current estimate. While martingale estimators are easier to analyze, they are far from optimal, especially in pull-based update systems, where maximum aposteriori probability (MAP) estimators are known to be optimal, but are analytically challenging. In this work, we introduce a new class of estimators called $p$-MAP estimators, which enable us to model the MAP estimator as a piecewise constant function with finitely many stages, bringing us closer to a full characterization of the MAP estimators when modeling information freshness.
Storage-Rate Trade-off in A-XPIR
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We consider the storage problem in an asymmetric $X$-secure private information retrieval (A-XPIR) setting. The A-XPIR setting considers the $X$-secure PIR problem (XPIR) when a given arbitrary set of servers is communicating. We focus on the trade-off region between the average storage at the servers and the average download cost. In the case of $N=4$ servers and two non-overlapping sets of communicating servers with $K=2$ messages, we characterize the achievable region and show that the three main inequalities compared to the no-security case collapse to two inequalities in the asymmetric security case. In the general case, we derive bounds that need to be satisfied for the general achievable region for an arbitrary number of servers and messages. In addition, we provide the storage and retrieval scheme for the case of $N=4$ servers with $K=2$ messages and two non-overlapping sets of communicating servers, such that the messages are not replicated (in the sense of a coded version of each symbol) and at the same time achieve the optimal achievable rate for the case of replication. Finally, we derive the exact capacity for the case of asymmetric security and asymmetric collusion for $N=4$ servers, with the communication links $\{1,2\}$ and $\{3,4\}$, which splits the servers into two groups, i.e., $g=2$, and with the collusion links $\{1,3\}$, $\{2,4\}$, as $C=\frac{1}{3}$. More generally, we derive a capacity result for a certain family of asymmetric collusion and asymmetric security cases.
Convergence Properties of Good Quantum Codes for Classical Communication
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:An important part of the information theory folklore had been about the output statistics of codes that achieve the capacity and how the empirical distributions compare to the output distributions induced by the optimal input in the channel capacity problem. Results for a variety of such empirical output distributions of good codes have been known in the literature, such as the comparison of the output distribution of the code to the optimal output distribution in vanishing and non-vanishing error probability cases. Motivated by these, we aim to achieve similar results for the quantum codes that are used for classical communication, that is the setting in which the classical messages are communicated through quantum codewords that pass through a noisy quantum channel. We first show the uniqueness of the optimal output distribution, to be able to talk more concretely about the optimal output distribution. Then, we extend the vanishing error probability results to the quantum case, by using techniques that are close in spirit to the classical case. We also extend non-vanishing error probability results to the quantum case on block codes, by using the second-order converses for such codes based on hypercontractivity results for the quantum generalized depolarizing semi-groups.
Breaking the Storage-Bandwidth Tradeoff in Distributed Storage with Quantum Entanglement
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This work investigates the use of quantum resources in distributed storage systems. Consider an $(n,k,d)$ distributed storage system in which a file is stored across $n$ nodes such that any $k$ nodes suffice to reconstruct the file. When a node fails, any $d$ helper nodes transmit information to a newcomer to rebuild the system. In contrast to the classical repair, where helper nodes transmit classical bits, we allow them to send classical information over quantum channels to the newcomer. The newcomer then generates its storage by performing appropriate measurements on the received quantum states. In this setting, we fully characterize the fundamental tradeoff between storage and repair bandwidth (total communication cost). Compared to classical systems, the optimal storage--bandwidth tradeoff can be significantly improved with the enhancement of quantum entanglement shared only among the surviving nodes, particularly at the minimum-storage regenerating point. Remarkably, we show that when $d \geq 2k-2$, there exists an operating point at which \textit{both storage and repair bandwidth are simultaneously minimized}. This phenomenon breaks the tradeoff in the classical setting and reveals a fundamentally new regime enabled by quantum communication.
Age of Gossip With Cellular Drone Mobility
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We consider a cellular network containing $n$ nodes where nodes within a cell gossip with each other in a fully-connected fashion and a source shares updates with these nodes via a mobile drone. The mobile drone receives updates directly from the source and shares them with nodes in the cell where it currently resides. The drone moves between cells according to an underlying continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). In this work, we evaluate the impact of the number of cells $f(n)$, drone speed $λ_m(n)$ and drone dissemination rate $λ_d(n)$ on the freshness of information of nodes in the network. We utilize the version age of information metric to quantify the freshness of information. We observe that the expected duration between two drone-to-cell service times depends on the stationary distribution of the underlying CTMC and $λ_d(n)$, but not on $λ_m(n)$. However, the version age instability in slow moving CTMCs makes high probability analysis for a general underlying CTMC difficult. Therefore, next we focus on the fully-connected drone mobility model. Under this model, we uncover a dual-bottleneck between drone mobility and drone dissemination speed: the version age is constrained by the slower of these two processes. If $λ_d(n) \gg λ_m(n)$, then the version age scaling of nodes is dominated by the inverse of $λ_m(n)$ and is independent of $λ_d(n)$. If $λ_m(n) \gg λ_d(n)$, then the version age scaling of nodes is dominated by the inverse of $λ_d(n)$ and is independent of $λ_m(n)$.
On the Capacity Region of Individual Key Rates in Vector Linear Secure Aggregation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:We provide new insights into an open problem recently posed by Yuan-Sun [ISIT 2025], concerning the minimum individual key rate required in the vector linear secure aggregation problem. Consider a distributed system with $K$ users, where each user $k\in [K]$ holds a data stream $W_k$ and an individual key $Z_k$. A server aims to compute a linear function $\mathbf{F}[W_1;\ldots;W_K]$ without learning any information about another linear function $\mathbf{G}[W_1;\ldots;W_K]$, where $[W_1;\ldots;W_K]$ denotes the row stack of $W_1,\ldots,W_K$. The open problem is to determine the minimum required length of $Z_k$, denoted as $R_k$, $k\in [K]$. In this paper, we characterize a new achievable region for the rate tuple $(R_1,\ldots,R_K)$. The region is polyhedral, with vertices characterized by a binary rate assignment $(R_1,\ldots,R_K) = (\mathbf{1}(1 \in \mathcal{I}),\ldots,\mathbf{1}(K\in \mathcal{I}))$, where $\mathcal{I}\subseteq [K]$ satisfies the \textit{rank-increment condition}: $\mathrm{rank}\left(\bigl[\mathbf{F}_{\mathcal{I}};\mathbf{G}_{\mathcal{I}}\bigr]\right) =\mathrm{rank}\bigl(\mathbf{F}_{\mathcal{I}}\bigr)+N$. Here, $\mathbf{F}_\mathcal{I}$ and $\mathbf{G}_\mathcal{I}$ are the submatrices formed by the columns indexed by $\mathcal{I}$. Our results uncover the novel fact that it is not necessary for every user to hold a key, thereby strictly enlarging the best-known achievable region in the literature. Furthermore, we provide a converse analysis to demonstrate its optimality when minimizing the number of users that hold keys.
Multi-Modal Semantic Communication
Dec 17, 2025
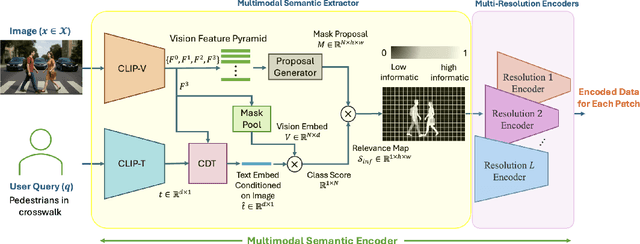
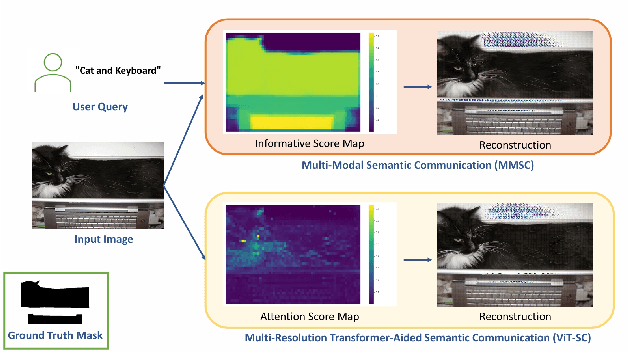
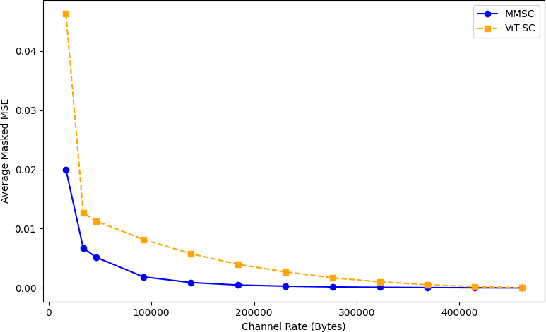
Abstract:Semantic communication aims to transmit information most relevant to a task rather than raw data, offering significant gains in communication efficiency for applications such as telepresence, augmented reality, and remote sensing. Recent transformer-based approaches have used self-attention maps to identify informative regions within images, but they often struggle in complex scenes with multiple objects, where self-attention lacks explicit task guidance. To address this, we propose a novel Multi-Modal Semantic Communication framework that integrates text-based user queries to guide the information extraction process. Our proposed system employs a cross-modal attention mechanism that fuses visual features with language embeddings to produce soft relevance scores over the visual data. Based on these scores and the instantaneous channel bandwidth, we use an algorithm to transmit image patches at adaptive resolutions using independently trained encoder-decoder pairs, with total bitrate matching the channel capacity. At the receiver, the patches are reconstructed and combined to preserve task-critical information. This flexible and goal-driven design enables efficient semantic communication in complex and bandwidth-constrained environments.
SEDULity: A Proof-of-Learning Framework for Distributed and Secure Blockchains with Efficient Useful Work
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The security and decentralization of Proof-of-Work (PoW) have been well-tested in existing blockchain systems. However, its tremendous energy waste has raised concerns about sustainability. Proof-of-Useful-Work (PoUW) aims to redirect the meaningless computation to meaningful tasks such as solving machine learning (ML) problems, giving rise to the branch of Proof-of-Learning (PoL). While previous studies have proposed various PoLs, they all, to some degree, suffer from security, decentralization, or efficiency issues. In this paper, we propose a PoL framework that trains ML models efficiently while maintaining blockchain security in a fully distributed manner. We name the framework SEDULity, which stands for a Secure, Efficient, Distributed, and Useful Learning-based blockchain system. Specifically, we encode the template block into the training process and design a useful function that is difficult to solve but relatively easy to verify, as a substitute for the PoW puzzle. We show that our framework is distributed, secure, and efficiently trains ML models. We further demonstrate that the proposed PoL framework can be extended to other types of useful work and design an incentive mechanism to incentivize task verification. We show theoretically that a rational miner is incentivized to train fully honestly with well-designed system parameters. Finally, we present simulation results to demonstrate the performance of our framework and validate our analysis.
HetDAPAC: Leveraging Attribute Heterogeneity in Distributed Attribute-Based Private Access Control
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Verifying user attributes to provide fine-grained access control to databases is fundamental to attribute-based authentication. Either a single (central) authority verifies all the attributes, or multiple independent authorities verify the attributes distributedly. In the central setup, the authority verifies all user attributes, and the user downloads only the authorized record. While this is communication efficient, it reveals all user attributes to the authority. A distributed setup prevents this privacy breach by letting each authority verify and learn only one attribute. Motivated by this, Jafarpisheh~et~al. introduced an information-theoretic formulation, called distributed attribute-based private access control (DAPAC). With $N$ non-colluding authorities (servers), $N$ attributes and $K$ possible values for each attribute, the DAPAC system lets each server learn only the single attribute value that it verifies, and is oblivious to the remaining $N-1$. The user retrieves its designated record, without learning anything about the remaining database records. The goal is to maximize the rate, i.e., the ratio of desired message size to total download size. However, not all attributes are sensitive, and DAPAC's privacy constraints can be too restrictive, negatively affecting the rate. To leverage the heterogeneous privacy requirements of user attributes, we propose heterogeneous (Het)DAPAC, a framework which off-loads verification of $N-D$ of the $N$ attributes to a central server, and retains DAPAC's architecture for the $D$ sensitive attributes. We first present a HetDAPAC scheme, which improves the rate from $\frac{1}{2K}$ to $\frac{1}{K+1}$, while sacrificing the privacy of a few non-sensitive attributes. Unlike DAPAC, our scheme entails a download imbalance across servers; we propose a second scheme achieving a balanced per-server download and a rate of $\frac{D+1}{2KD}$.
Age of Job Completion Minimization with Stable Queues
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:We consider a time-slotted job-assignment system with a central server, N users and a machine which changes its state according to a Markov chain (hence called a Markov machine). The users submit their jobs to the central server according to a stochastic job arrival process. For each user, the server has a dedicated job queue. Upon receiving a job from a user, the server stores that job in the corresponding queue. When the machine is not working on a job assigned by the server, the machine can be either in internally busy or in free state, and the dynamics of these states follow a binary symmetric Markov chain. Upon sampling the state information of the machine, if the server identifies that the machine is in the free state, it schedules a user and submits a job to the machine from the job queue of the scheduled user. To maximize the number of jobs completed per unit time, we introduce a new metric, referred to as the age of job completion. To minimize the age of job completion and the sampling cost, we propose two policies and numerically evaluate their performance. For both of these policies, we find sufficient conditions under which the job queues will remain stable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge