Mengling Feng
medR: Reward Engineering for Clinical Offline Reinforcement Learning via Tri-Drive Potential Functions
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a powerful framework for optimizing dynamic treatment regimes (DTRs). However, clinical RL is fundamentally bottlenecked by reward engineering: the challenge of defining signals that safely and effectively guide policy learning in complex, sparse offline environments. Existing approaches often rely on manual heuristics that fail to generalize across diverse pathologies. To address this, we propose an automated pipeline leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for offline reward design and verification. We formulate the reward function using potential functions consisted of three core components: survival, confidence, and competence. We further introduce quantitative metrics to rigorously evaluate and select the optimal reward structure prior to deployment. By integrating LLM-driven domain knowledge, our framework automates the design of reward functions for specific diseases while significantly enhancing the performance of the resulting policies.
From Latent Signals to Reflection Behavior: Tracing Meta-Cognitive Activation Trajectory in R1-Style LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:R1-style LLMs have attracted growing attention for their capacity for self-reflection, yet the internal mechanisms underlying such behavior remain unclear. To bridge this gap, we anchor on the onset of reflection behavior and trace its layer-wise activation trajectory. Using the logit lens to read out token-level semantics, we uncover a structured progression: (i) Latent-control layers, where an approximate linear direction encodes the semantics of thinking budget; (ii) Semantic-pivot layers, where discourse-level cues, including turning-point and summarization cues, surface and dominate the probability mass; and (iii) Behavior-overt layers, where the likelihood of reflection-behavior tokens begins to rise until they become highly likely to be sampled. Moreover, our targeted interventions uncover a causal chain across these stages: prompt-level semantics modulate the projection of activations along latent-control directions, thereby inducing competition between turning-point and summarization cues in semantic-pivot layers, which in turn regulates the sampling likelihood of reflection-behavior tokens in behavior-overt layers. Collectively, our findings suggest a human-like meta-cognitive process-progressing from latent monitoring, to discourse-level regulation, and to finally overt self-reflection. Our analysis code can be found at https://github.com/DYR1/S3-CoT.
S3-CoT: Self-Sampled Succinct Reasoning Enables Efficient Chain-of-Thought LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) equipped with chain-of-thought (CoT) achieve strong performance and offer a window into LLM behavior. However, recent evidence suggests that improvements in CoT capabilities often come with redundant reasoning processes, motivating a key question: Can LLMs acquire a fast-thinking mode analogous to human System 1 reasoning? To explore this, our study presents a self-sampling framework based on activation steering for efficient CoT learning. Our method can induce style-aligned and variable-length reasoning traces from target LLMs themselves without any teacher guidance, thereby alleviating a central bottleneck of SFT-based methods-the scarcity of high-quality supervision data. Using filtered data by gold answers, we perform SFT for efficient CoT learning with (i) a human-like dual-cognitive system, and (ii) a progressive compression curriculum. Furthermore, we explore a self-evolution regime in which SFT is driven solely by prediction-consistent data of variable-length variants, eliminating the need for gold answers. Extensive experiments on math benchmarks, together with cross-domain generalization tests in medicine, show that our method yields stable improvements for both general and R1-style LLMs. Our data and model checkpoints can be found at https://github.com/DYR1/S3-CoT.
A Foundation Model for Chest X-ray Interpretation with Grounded Reasoning via Online Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Medical foundation models (FMs) have shown tremendous promise amid the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. However, current medical FMs typically generate answers in a black-box manner, lacking transparent reasoning processes and locally grounded interpretability, which hinders their practical clinical deployments. To this end, we introduce DeepMedix-R1, a holistic medical FM for chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation. It leverages a sequential training pipeline: initially fine-tuned on curated CXR instruction data to equip with fundamental CXR interpretation capabilities, then exposed to high-quality synthetic reasoning samples to enable cold-start reasoning, and finally refined via online reinforcement learning to enhance both grounded reasoning quality and generation performance. Thus, the model produces both an answer and reasoning steps tied to the image's local regions for each query. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates substantial improvements in report generation (e.g., 14.54% and 31.32% over LLaVA-Rad and MedGemma) and visual question answering (e.g., 57.75% and 23.06% over MedGemma and CheXagent) tasks. To facilitate robust assessment, we propose Report Arena, a benchmarking framework using advanced language models to evaluate answer quality, further highlighting the superiority of DeepMedix-R1. Expert review of generated reasoning steps reveals greater interpretability and clinical plausibility compared to the established Qwen2.5-VL-7B model (0.7416 vs. 0.2584 overall preference). Collectively, our work advances medical FM development toward holistic, transparent, and clinically actionable modeling for CXR interpretation.
CodeBrain: Bridging Decoupled Tokenizer and Multi-Scale Architecture for EEG Foundation Model
Jun 10, 2025


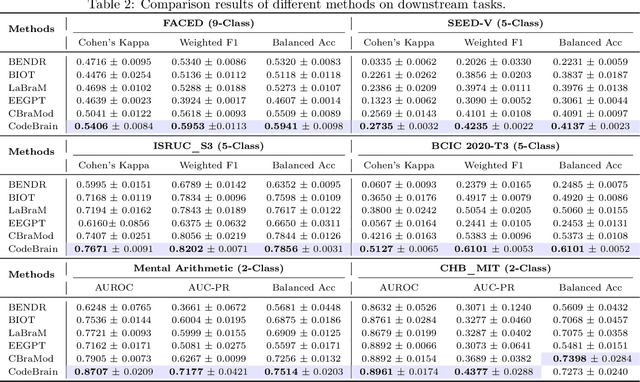
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) provides real-time insights into brain activity and is widely used in neuroscience. However, variations in channel configurations, sequence lengths, and task objectives limit the transferability of traditional task-specific models. Although recent EEG foundation models (EFMs) aim to learn generalizable representations, they struggle with limited heterogeneous representation capacity and inefficiency in capturing multi-scale brain dependencies. To address these challenges, we propose CodeBrain, an efficient EFM structurally aligned with brain organization, trained in two stages. (1) We introduce a TFDual-Tokenizer that independently tokenizes heterogeneous temporal and frequency components, enabling a quadratic expansion of the discrete representation space. This also offers a degree of interpretability through cross-domain token analysis. (2) We propose the EEGSSM, which combines a structured global convolution architecture and a sliding window attention mechanism to jointly model sparse long-range and local dependencies. Unlike fully connected Transformer models, EEGSSM better reflects the brain's small-world topology and efficiently captures EEG's inherent multi-scale structure. EEGSSM is trained with a masked self-supervised learning objective to predict token indices obtained in TFDual-Tokenizer. Comprehensive experiments on 10 public EEG datasets demonstrate the generalizability of CodeBrain with linear probing. By offering biologically informed and interpretable EEG modeling, CodeBrain lays the foundation for future neuroscience research. Both code and pretraining weights will be released in the future version.
DivScore: Zero-Shot Detection of LLM-Generated Text in Specialized Domains
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Detecting LLM-generated text in specialized and high-stakes domains like medicine and law is crucial for combating misinformation and ensuring authenticity. However, current zero-shot detectors, while effective on general text, often fail when applied to specialized content due to domain shift. We provide a theoretical analysis showing this failure is fundamentally linked to the KL divergence between human, detector, and source text distributions. To address this, we propose DivScore, a zero-shot detection framework using normalized entropy-based scoring and domain knowledge distillation to robustly identify LLM-generated text in specialized domains. We also release a domain-specific benchmark for LLM-generated text detection in the medical and legal domains. Experiments on our benchmark show that DivScore consistently outperforms state-of-the-art detectors, with 14.4% higher AUROC and 64.0% higher recall (0.1% false positive rate threshold). In adversarial settings, DivScore demonstrates superior robustness than other baselines, achieving on average 22.8% advantage in AUROC and 29.5% in recall. Code and data are publicly available.
MedDreamer: Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Latent Imagination on Complex EHRs for Clinical Decision Support
May 26, 2025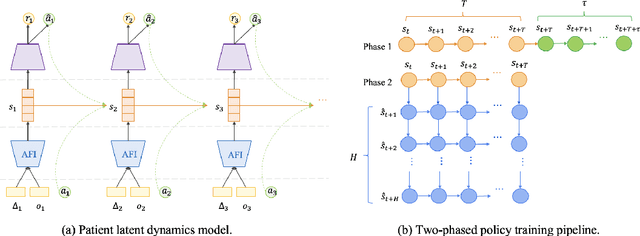
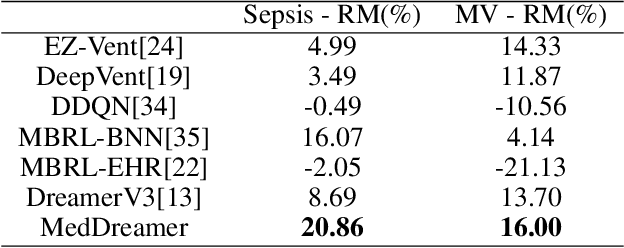
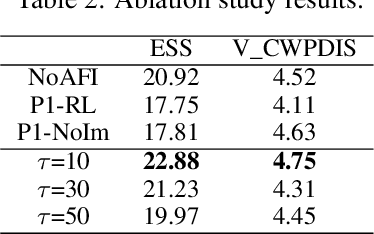
Abstract:Timely and personalized treatment decisions are essential across a wide range of healthcare settings where patient responses vary significantly and evolve over time. Clinical data used to support these decisions are often irregularly sampled, sparse, and noisy. Existing decision support systems commonly rely on discretization and imputation, which can distort critical temporal dynamics and degrade decision quality. Moreover, they often overlook the clinical significance of irregular recording frequencies, filtering out patterns in how and when data is collected. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a natural fit for clinical decision-making, enabling sequential, long-term optimization in dynamic, uncertain environments. However, most existing treatment recommendation systems are model-free and trained solely on offline data, making them sample-inefficient, sensitive to data quality, and poorly generalizable across tasks or cohorts. To address these limitations, we propose MedDreamer, a two-phase model-based RL framework for personalized treatment recommendation. MedDreamer uses a world model with an Adaptive Feature Integration (AFI) module to effectively model irregular, sparse clinical data. Through latent imagination, it simulates plausible patient trajectories to enhance learning, refining its policy using a mix of real and imagined experiences. This enables learning policies that go beyond suboptimal historical decisions while remaining grounded in clinical data. To our knowledge, this is the first application of latent imagination to irregular healthcare data. Evaluations on sepsis and mechanical ventilation (MV) treatment using two large-scale EHR datasets show that MedDreamer outperforms both model-free and model-based baselines in clinical outcomes and off-policy metrics.
Simultaneous Polysomnography and Cardiotocography Reveal Temporal Correlation Between Maternal Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Fetal Hypoxia
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Background: Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) during pregnancy is common and can negatively affect fetal outcomes. However, studies on the immediate effects of maternal hypoxia on fetal heart rate (FHR) changes are lacking. Methods: We used time-synchronized polysomnography (PSG) and cardiotocography (CTG) data from two cohorts to analyze the correlation between maternal hypoxia and FHR changes (accelerations or decelerations). Maternal hypoxic event characteristics were analyzed using generalized linear modeling (GLM) to assess their associations with different FHR changes. Results: A total of 118 pregnant women participated. FHR changes were significantly associated with maternal hypoxia, primarily characterized by accelerations. A longer hypoxic duration correlated with more significant FHR accelerations (P < 0.05), while prolonged hypoxia and greater SpO2 drop were linked to FHR decelerations (P < 0.05). Both cohorts showed a transient increase in FHR during maternal hypoxia, which returned to baseline after the event resolved. Conclusion: Maternal hypoxia significantly affects FHR, suggesting that maternal OSAS may contribute to fetal hypoxia. These findings highlight the importance of maternal-fetal interactions and provide insights for future interventions.
GEM: Empowering MLLM for Grounded ECG Understanding with Time Series and Images
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:While recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced automated ECG interpretation, they still face two key limitations: (1) insufficient multimodal synergy between time series signals and visual ECG representations, and (2) limited explainability in linking diagnoses to granular waveform evidence. We introduce GEM, the first MLLM unifying ECG time series, 12-lead ECG images and text for grounded and clinician-aligned ECG interpretation. GEM enables feature-grounded analysis, evidence-driven reasoning, and a clinician-like diagnostic process through three core innovations: a dual-encoder framework extracting complementary time series and image features, cross-modal alignment for effective multimodal understanding, and knowledge-guided instruction generation for generating high-granularity grounding data (ECG-Grounding) linking diagnoses to measurable parameters ($e.g.$, QRS/PR Intervals). Additionally, we propose the Grounded ECG Understanding task, a clinically motivated benchmark designed to comprehensively assess the MLLM's capability in grounded ECG understanding. Experimental results on both existing and our proposed benchmarks show GEM significantly improves predictive performance (CSN $7.4\% \uparrow$), explainability ($22.7\% \uparrow$), and grounding ($24.8\% \uparrow$), making it more suitable for real-world clinical applications. GitHub repository: https://github.com/lanxiang1017/GEM.git
Self-supervised Quantized Representation for Seamlessly Integrating Knowledge Graphs with Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Due to the presence of the natural gap between Knowledge Graph (KG) structures and the natural language, the effective integration of holistic structural information of KGs with Large Language Models (LLMs) has emerged as a significant question. To this end, we propose a two-stage framework to learn and apply quantized codes for each entity, aiming for the seamless integration of KGs with LLMs. Firstly, a self-supervised quantized representation (SSQR) method is proposed to compress both KG structural and semantic knowledge into discrete codes (\ie, tokens) that align the format of language sentences. We further design KG instruction-following data by viewing these learned codes as features to directly input to LLMs, thereby achieving seamless integration. The experiment results demonstrate that SSQR outperforms existing unsupervised quantized methods, producing more distinguishable codes. Further, the fine-tuned LLaMA2 and LLaMA3.1 also have superior performance on KG link prediction and triple classification tasks, utilizing only 16 tokens per entity instead of thousands in conventional prompting methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge