Huiping Zhuang
MixKVQ: Query-Aware Mixed-Precision KV Cache Quantization for Long-Context Reasoning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has significantly advanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), but this progress is accompanied by substantial memory and latency overhead from the extensive Key-Value (KV) cache. Although KV cache quantization is a promising compression technique, existing low-bit quantization methods often exhibit severe performance degradation on complex reasoning tasks. Fixed-precision quantization struggles to handle outlier channels in the key cache, while current mixed-precision strategies fail to accurately identify components requiring high-precision representation. We find that an effective low-bit KV cache quantization strategy must consider two factors: a key channel's intrinsic quantization difficulty and its relevance to the query. Based on this insight, we propose MixKVQ, a novel plug-and-play method that introduces a lightweight, query-aware algorithm to identify and preserve critical key channels that need higher precision, while applying per-token quantization for value cache. Experiments on complex reasoning datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing low-bit methods, achieving performance comparable to a full-precision baseline at a substantially reduced memory footprint.
T-Rex: Task-Adaptive Spatial Representation Extraction for Robotic Manipulation with Vision-Language Models
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Building a general robotic manipulation system capable of performing a wide variety of tasks in real-world settings is a challenging task. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in robotic manipulation tasks, primarily due to the extensive world knowledge they gain from large-scale datasets. In this process, Spatial Representations (such as points representing object positions or vectors representing object orientations) act as a bridge between VLMs and real-world scene, effectively grounding the reasoning abilities of VLMs and applying them to specific task scenarios. However, existing VLM-based robotic approaches often adopt a fixed spatial representation extraction scheme for various tasks, resulting in insufficient representational capability or excessive extraction time. In this work, we introduce T-Rex, a Task-Adaptive Framework for Spatial Representation Extraction, which dynamically selects the most appropriate spatial representation extraction scheme for each entity based on specific task requirements. Our key insight is that task complexity determines the types and granularity of spatial representations, and Stronger representational capabilities are typically associated with Higher overall system operation costs. Through comprehensive experiments in real-world robotic environments, we show that our approach delivers significant advantages in spatial understanding, efficiency, and stability without additional training.
AntiGrounding: Lifting Robotic Actions into VLM Representation Space for Decision Making
Jun 14, 2025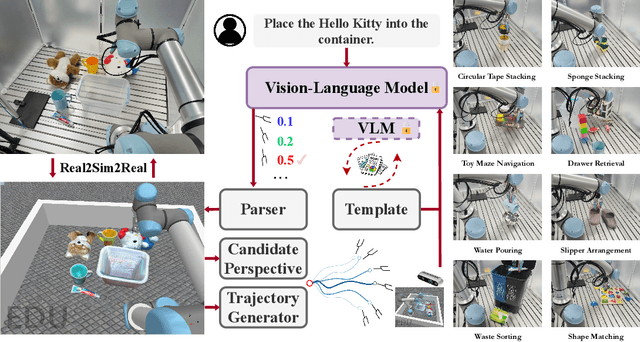
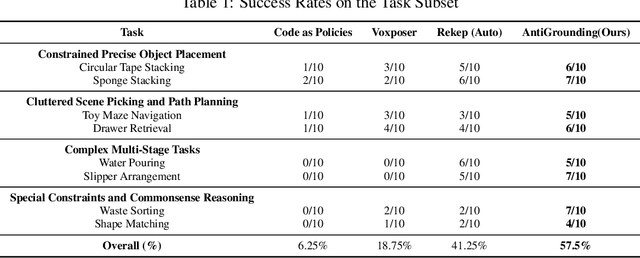
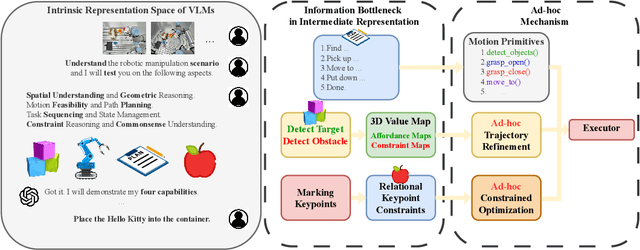
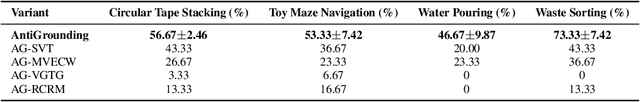
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) encode knowledge and reasoning capabilities for robotic manipulation within high-dimensional representation spaces. However, current approaches often project them into compressed intermediate representations, discarding important task-specific information such as fine-grained spatial or semantic details. To address this, we propose AntiGrounding, a new framework that reverses the instruction grounding process. It lifts candidate actions directly into the VLM representation space, renders trajectories from multiple views, and uses structured visual question answering for instruction-based decision making. This enables zero-shot synthesis of optimal closed-loop robot trajectories for new tasks. We also propose an offline policy refinement module that leverages past experience to enhance long-term performance. Experiments in both simulation and real-world environments show that our method outperforms baselines across diverse robotic manipulation tasks.
Analytic Task Scheduler: Recursive Least Squares Based Method for Continual Learning in Embodied Foundation Models
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Embodied foundation models are crucial for Artificial Intelligence (AI) interacting with the physical world by integrating multi-modal inputs, such as proprioception, vision and language, to understand human intentions and generate actions to control robots. While these models demonstrate strong generalization and few-shot learning capabilities, they face significant challenges in continually acquiring new skills without forgetting previously learned skills, a problem known as catastrophic forgetting. To address this issue, we propose the Analytic Task Scheduler (ATS), a novel framework for continual learning in embodied foundation models. ATS consists of a task-specific model library, where each model is fine-tuned independently on a single task, and an analytic scheduler trained using recursive least squares (RLS) to learn the mapping between language instructions and task-specific models. This architecture enables accurate task recognition and dynamic model selection while fundamentally avoiding parameter interference across tasks. The scheduler updates its parameters incrementally using only statistics (autocorrelation and cross-correlation matrices), enabling forgetting-resistant learning without the need to revisit historical data. We validate ATS on a real-world robot platform (RM65B), demonstrating superior resistance to forgetting and strong adaptability to task variations. The results highlight ATS as an effective, scalable, and deployable solution for continual learning in embodied foundation models operating in complex, dynamic environments. Our code will be available at https://github.com/MIAA-Embodied-AI/AnalyticTaskScheduler
WINA: Weight Informed Neuron Activation for Accelerating Large Language Model Inference
May 26, 2025Abstract:The growing computational demands of large language models (LLMs) make efficient inference and activation strategies increasingly critical. While recent approaches, such as Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), leverage selective activation but require specialized training, training-free sparse activation methods offer broader applicability and superior resource efficiency through their plug-and-play design. However, many existing methods rely solely on hidden state magnitudes to determine activation, resulting in high approximation errors and suboptimal inference accuracy. To address these limitations, we propose WINA (Weight Informed Neuron Activation), a novel, simple, and training-free sparse activation framework that jointly considers hidden state magnitudes and the column-wise $\ell_2$-norms of weight matrices. We show that this leads to a sparsification strategy that obtains optimal approximation error bounds with theoretical guarantees tighter than existing techniques. Empirically, WINA also outperforms state-of-the-art methods (e.g., TEAL) by up to $2.94\%$ in average performance at the same sparsity levels, across a diverse set of LLM architectures and datasets. These results position WINA as a new performance frontier for training-free sparse activation in LLM inference, advancing training-free sparse activation methods and setting a robust baseline for efficient inference. The source code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/wina.
ACU: Analytic Continual Unlearning for Efficient and Exact Forgetting with Privacy Preservation
May 18, 2025Abstract:The development of artificial intelligence demands that models incrementally update knowledge by Continual Learning (CL) to adapt to open-world environments. To meet privacy and security requirements, Continual Unlearning (CU) emerges as an important problem, aiming to sequentially forget particular knowledge acquired during the CL phase. However, existing unlearning methods primarily focus on single-shot joint forgetting and face significant limitations when applied to CU. First, most existing methods require access to the retained dataset for re-training or fine-tuning, violating the inherent constraint in CL that historical data cannot be revisited. Second, these methods often suffer from a poor trade-off between system efficiency and model fidelity, making them vulnerable to being overwhelmed or degraded by adversaries through deliberately frequent requests. In this paper, we identify that the limitations of existing unlearning methods stem fundamentally from their reliance on gradient-based updates. To bridge the research gap at its root, we propose a novel gradient-free method for CU, named Analytic Continual Unlearning (ACU), for efficient and exact forgetting with historical data privacy preservation. In response to each unlearning request, our ACU recursively derives an analytical (i.e., closed-form) solution in an interpretable manner using the least squares method. Theoretical and experimental evaluations validate the superiority of our ACU on unlearning effectiveness, model fidelity, and system efficiency.
AFCL: Analytic Federated Continual Learning for Spatio-Temporal Invariance of Non-IID Data
May 18, 2025Abstract:Federated Continual Learning (FCL) enables distributed clients to collaboratively train a global model from online task streams in dynamic real-world scenarios. However, existing FCL methods face challenges of both spatial data heterogeneity among distributed clients and temporal data heterogeneity across online tasks. Such data heterogeneity significantly degrades the model performance with severe spatial-temporal catastrophic forgetting of local and past knowledge. In this paper, we identify that the root cause of this issue lies in the inherent vulnerability and sensitivity of gradients to non-IID data. To fundamentally address this issue, we propose a gradient-free method, named Analytic Federated Continual Learning (AFCL), by deriving analytical (i.e., closed-form) solutions from frozen extracted features. In local training, our AFCL enables single-epoch learning with only a lightweight forward-propagation process for each client. In global aggregation, the server can recursively and efficiently update the global model with single-round aggregation. Theoretical analyses validate that our AFCL achieves spatio-temporal invariance of non-IID data. This ideal property implies that, regardless of how heterogeneous the data are distributed across local clients and online tasks, the aggregated model of our AFCL remains invariant and identical to that of centralized joint learning. Extensive experiments show the consistent superiority of our AFCL over state-of-the-art baselines across various benchmark datasets and settings.
AnalyticKWS: Towards Exemplar-Free Analytic Class Incremental Learning for Small-footprint Keyword Spotting
May 17, 2025Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) offers a vital mechanism to identify spoken commands in voice-enabled systems, where user demands often shift, requiring models to learn new keywords continually over time. However, a major problem is catastrophic forgetting, where models lose their ability to recognize earlier keywords. Although several continual learning methods have proven their usefulness for reducing forgetting, most existing approaches depend on storing and revisiting old data to combat catastrophic forgetting. Though effective, these methods face two practical challenges: 1) privacy risks from keeping user data and 2) large memory and time consumption that limit deployment on small devices. To address these issues, we propose an exemplar-free Analytic Continual Learning (AnalyticKWS) method that updates model parameters without revisiting earlier data. Inspired by efficient learning principles, AnalyticKWS computes a closed-form analytical solution for model updates and requires only a single epoch of adaptation for incoming keywords. AnalyticKWS demands fewer computational resources by avoiding gradient-based updates and does not store old data. By eliminating the need for back-propagation during incremental learning, the model remains lightweight and efficient. As a result, AnalyticKWS meets the challenges mentioned earlier and suits resource-limited settings well. Extensive experiments on various datasets and settings show that AnalyticKWS consistently outperforms existing continual learning methods.
Analytic Subspace Routing: How Recursive Least Squares Works in Continual Learning of Large Language Model
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) possess encompassing capabilities that can process diverse language-related tasks. However, finetuning on LLMs will diminish this general skills and continual finetuning will further cause severe degradation on accumulated knowledge. Recently, Continual Learning (CL) in Large Language Models (LLMs) arises which aims to continually adapt the LLMs to new tasks while maintaining previously learned knowledge and inheriting general skills. Existing techniques either leverage previous data to replay, leading to extra computational costs, or utilize a single parameter-efficient module to learn the downstream task, constraining new knowledge absorption with interference between different tasks. Toward these issues, this paper proposes Analytic Subspace Routing(ASR) to address these challenges. For each task, we isolate the learning within a subspace of deep layers' features via low-rank adaptation, eliminating knowledge interference between different tasks. Additionally, we propose an analytic routing mechanism to properly utilize knowledge learned in different subspaces. Our approach employs Recursive Least Squares to train a multi-task router model, allowing the router to dynamically adapt to incoming data without requiring access to historical data. Also, the router effectively assigns the current task to an appropriate subspace and has a non-forgetting property of previously learned tasks with a solid theoretical guarantee. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves near-perfect retention of prior knowledge while seamlessly integrating new information, effectively overcoming the core limitations of existing methods. Our code will be released after acceptance.
Semantic Shift Estimation via Dual-Projection and Classifier Reconstruction for Exemplar-Free Class-Incremental Learning
Mar 07, 2025


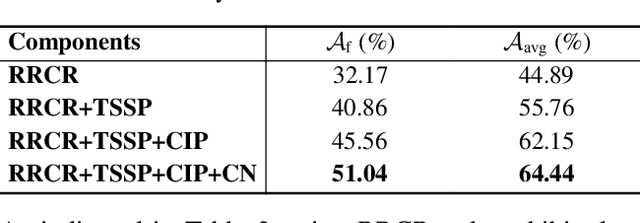
Abstract:Exemplar-Free Class-Incremental Learning (EFCIL) aims to sequentially learn from distinct categories without retaining exemplars but easily suffers from catastrophic forgetting of learned knowledge. While existing EFCIL methods leverage knowledge distillation to alleviate forgetting, they still face two critical challenges: semantic shift and decision bias. Specifically, the embeddings of old tasks shift in the embedding space after learning new tasks, and the classifier becomes biased towards new tasks due to training solely with new data, thereby hindering the balance between old and new knowledge. To address these issues, we propose the Dual-Projection Shift Estimation and Classifier Reconstruction (DPCR) approach for EFCIL. DPCR effectively estimates semantic shift through a dual-projection, which combines a learnable transformation with a row-space projection to capture both task-wise and category-wise shifts. Furthermore, to mitigate decision bias, DPCR employs ridge regression to reformulate classifier training as a reconstruction process. This reconstruction exploits previous information encoded in covariance and prototype of each class after calibration with estimated shift, thereby reducing decision bias. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, across various datasets, DPCR effectively balances old and new tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art EFCIL methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge