Anfeng Liu
Beyond Distribution Shifts: Adaptive Hyperspectral Image Classification at Test Time
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification models are highly sensitive to distribution shifts caused by various real-world degradations such as noise, blur, compression, and atmospheric effects. To address this challenge, we propose HyperTTA, a unified framework designed to enhance model robustness under diverse degradation conditions. Specifically, we first construct a multi-degradation hyperspectral dataset that systematically simulates nine representative types of degradations, providing a comprehensive benchmark for robust classification evaluation. Based on this, we design a spectral-spatial transformer classifier (SSTC) enhanced with a multi-level receptive field mechanism and label smoothing regularization to jointly capture multi-scale spatial context and improve generalization. Furthermore, HyperTTA incorporates a lightweight test-time adaptation (TTA) strategy, the confidence-aware entropy-minimized LayerNorm adapter (CELA), which updates only the affine parameters of LayerNorm layers by minimizing prediction entropy on high-confidence unlabeled target samples. This confidence-aware adaptation prevents unreliable updates from noisy predictions, enabling robust and dynamic adaptation without access to source data or target annotations. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that HyperTTA outperforms existing baselines across a wide range of degradation scenarios, validating the effectiveness of both its classification backbone and the proposed TTA scheme. Code will be made available publicly.
AFCL: Analytic Federated Continual Learning for Spatio-Temporal Invariance of Non-IID Data
May 18, 2025Abstract:Federated Continual Learning (FCL) enables distributed clients to collaboratively train a global model from online task streams in dynamic real-world scenarios. However, existing FCL methods face challenges of both spatial data heterogeneity among distributed clients and temporal data heterogeneity across online tasks. Such data heterogeneity significantly degrades the model performance with severe spatial-temporal catastrophic forgetting of local and past knowledge. In this paper, we identify that the root cause of this issue lies in the inherent vulnerability and sensitivity of gradients to non-IID data. To fundamentally address this issue, we propose a gradient-free method, named Analytic Federated Continual Learning (AFCL), by deriving analytical (i.e., closed-form) solutions from frozen extracted features. In local training, our AFCL enables single-epoch learning with only a lightweight forward-propagation process for each client. In global aggregation, the server can recursively and efficiently update the global model with single-round aggregation. Theoretical analyses validate that our AFCL achieves spatio-temporal invariance of non-IID data. This ideal property implies that, regardless of how heterogeneous the data are distributed across local clients and online tasks, the aggregated model of our AFCL remains invariant and identical to that of centralized joint learning. Extensive experiments show the consistent superiority of our AFCL over state-of-the-art baselines across various benchmark datasets and settings.
Point Cloud Understanding via Attention-Driven Contrastive Learning
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Recently Transformer-based models have advanced point cloud understanding by leveraging self-attention mechanisms, however, these methods often overlook latent information in less prominent regions, leading to increased sensitivity to perturbations and limited global comprehension. To solve this issue, we introduce PointACL, an attention-driven contrastive learning framework designed to address these limitations. Our method employs an attention-driven dynamic masking strategy that guides the model to focus on under-attended regions, enhancing the understanding of global structures within the point cloud. Then we combine the original pre-training loss with a contrastive learning loss, improving feature discrimination and generalization. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of PointACL, as it achieves state-of-the-art performance across a variety of 3D understanding tasks, including object classification, part segmentation, and few-shot learning. Specifically, when integrated with different Transformer backbones like Point-MAE and PointGPT, PointACL demonstrates improved performance on datasets such as ScanObjectNN, ModelNet40, and ShapeNetPart. This highlights its superior capability in capturing both global and local features, as well as its enhanced robustness against perturbations and incomplete data.
TS-ACL: A Time Series Analytic Continual Learning Framework for Privacy-Preserving and Class-Incremental Pattern Recognition
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Class-incremental Learning (CIL) in Time Series Classification (TSC) aims to incrementally train models using the streaming time series data that arrives continuously. The main problem in this scenario is catastrophic forgetting, i.e., training models with new samples inevitably leads to the forgetting of previously learned knowledge. Among existing methods, the replay-based methods achieve satisfactory performance but compromise privacy, while exemplar-free methods protect privacy but suffer from low accuracy. However, more critically, owing to their reliance on gradient-based update techniques, these existing methods fundamentally cannot solve the catastrophic forgetting problem. In TSC scenarios with continuously arriving data and temporally shifting distributions, these methods become even less practical. In this paper, we propose a Time Series Analytic Continual Learning framework, called TS-ACL. Inspired by analytical learning, TS-ACL transforms neural network updates into gradient-free linear regression problems, thereby fundamentally mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Specifically, employing a pre-trained and frozen feature extraction encoder, TS-ACL only needs to update its analytic classifier recursively in a lightweight manner that is highly suitable for real-time applications and large-scale data processing. Additionally, we theoretically demonstrate that the model obtained recursively through the TS-ACL is exactly equivalent to a model trained on the complete dataset in a centralized manner, thereby establishing the property of absolute knowledge memory. Extensive experiments validate the superior performance of our TS-ACL.
A Distance Similarity-based Genetic Optimization Algorithm for Satellite Ground Network Planning Considering Feeding Mode
Aug 29, 2024

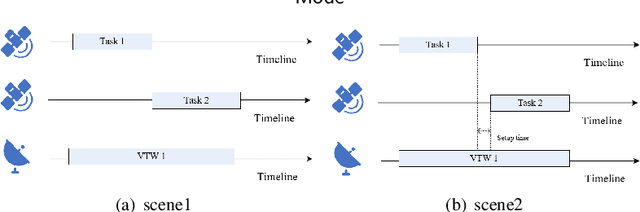
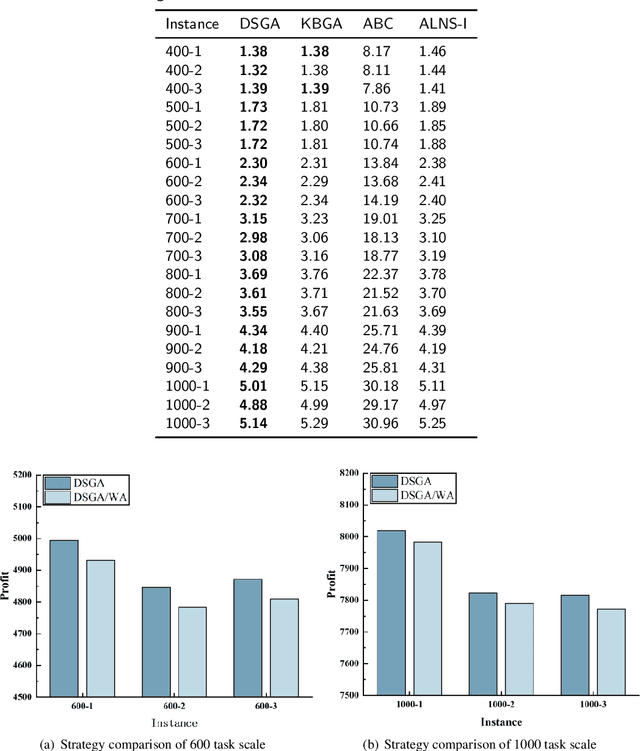
Abstract:With the rapid development of the satellite industry, the information transmission network based on communication satellites has gradually become a major and important part of the future satellite ground integration network. However, the low transmission efficiency of the satellite data relay back mission has become a problem that is currently constraining the construction of the system and needs to be solved urgently. Effectively planning the task of satellite ground networking by reasonably scheduling resources is crucial for the efficient transmission of task data. In this paper, we hope to provide a task execution scheme that maximizes the profit of the networking task for satellite ground network planning considering feeding mode (SGNPFM). To solve the SGNPFM problem, a mixed-integer planning model with the objective of maximizing the gain of the link-building task is constructed, which considers various constraints of the satellite in the feed-switching mode. Based on the problem characteristics, we propose a distance similarity-based genetic optimization algorithm (DSGA), which considers the state characteristics between the tasks and introduces a weighted Euclidean distance method to determine the similarity between the tasks. To obtain more high-quality solutions, different similarity evaluation methods are designed to assist the algorithm in intelligently screening individuals. The DSGA also uses an adaptive crossover strategy based on similarity mechanism, which guides the algorithm to achieve efficient population search. In addition, a task scheduling algorithm considering the feed-switching mode is designed for decoding the algorithm to generate a high-quality scheme. The results of simulation experiments show that the DSGA can effectively solve the SGNPFM problem.
TripletMix: Triplet Data Augmentation for 3D Understanding
May 28, 2024Abstract:Data augmentation has proven to be a vital tool for enhancing the generalization capabilities of deep learning models, especially in the context of 3D vision where traditional datasets are often limited. Despite previous advancements, existing methods primarily cater to unimodal data scenarios, leaving a gap in the augmentation of multimodal triplet data, which integrates text, images, and point clouds. Simultaneously augmenting all three modalities enhances diversity and improves alignment across modalities, resulting in more comprehensive and robust 3D representations. To address this gap, we propose TripletMix, a novel approach to address the previously unexplored issue of multimodal data augmentation in 3D understanding. TripletMix innovatively applies the principles of mixed-based augmentation to multimodal triplet data, allowing for the preservation and optimization of cross-modal connections. Our proposed TripletMix combines feature-level and input-level augmentations to achieve dual enhancement between raw data and latent features, significantly improving the model's cross-modal understanding and generalization capabilities by ensuring feature consistency and providing diverse and realistic training samples. We demonstrate that TripletMix not only improves the baseline performance of models in various learning scenarios including zero-shot and linear probing classification but also significantly enhances model generalizability. Notably, we improved the zero-shot classification accuracy on ScanObjectNN from 51.3 percent to 61.9 percent, and on Objaverse-LVIS from 46.8 percent to 51.4 percent. Our findings highlight the potential of multimodal data augmentation to significantly advance 3D object recognition and understanding.
PointPatchMix: Point Cloud Mixing with Patch Scoring
Mar 12, 2023Abstract:Data augmentation is an effective regularization strategy for mitigating overfitting in deep neural networks, and it plays a crucial role in 3D vision tasks, where the point cloud data is relatively limited. While mixing-based augmentation has shown promise for point clouds, previous methods mix point clouds either on block level or point level, which has constrained their ability to strike a balance between generating diverse training samples and preserving the local characteristics of point clouds. Additionally, the varying importance of each part of the point clouds has not been fully considered, cause not all parts contribute equally to the classification task, and some parts may contain unimportant or redundant information. To overcome these challenges, we propose PointPatchMix, a novel approach that mixes point clouds at the patch level and integrates a patch scoring module to generate content-based targets for mixed point clouds. Our approach preserves local features at the patch level, while the patch scoring module assigns targets based on the content-based significance score from a pre-trained teacher model. We evaluate PointPatchMix on two benchmark datasets, ModelNet40 and ScanObjectNN, and demonstrate significant improvements over various baselines in both synthetic and real-world datasets, as well as few-shot settings. With Point-MAE as our baseline, our model surpasses previous methods by a significant margin, achieving 86.3% accuracy on ScanObjectNN and 94.1% accuracy on ModelNet40. Furthermore, our approach shows strong generalization across multiple architectures and enhances the robustness of the baseline model.
A Semi-supervised Sensing Rate Learning based CMAB Scheme to Combat COVID-19 by Trustful Data Collection in the Crowd
Jan 17, 2023



Abstract:Mobile CrowdSensing (MCS), through employing considerable workers to sense and collect data in a participatory manner, has been recognized as a promising paradigm for building many large-scale applications in a cost-effective way, such as combating COVID-19. The recruitment of trustworthy and high-quality workers is an important research issue for MCS. Previous studies assume that the qualities of workers are known in advance, or the platform knows the qualities of workers once it receives their collected data. In reality, to reduce their costs and thus maximize revenue, many strategic workers do not perform their sensing tasks honestly and report fake data to the platform. So, it is very hard for the platform to evaluate the authenticity of the received data. In this paper, an incentive mechanism named Semi-supervision based Combinatorial Multi-Armed Bandit reverse Auction (SCMABA) is proposed to solve the recruitment problem of multiple unknown and strategic workers in MCS. First, we model the worker recruitment as a multi-armed bandit reverse auction problem, and design an UCB-based algorithm to separate the exploration and exploitation, considering the Sensing Rates (SRs) of recruited workers as the gain of the bandit. Next, a Semi-supervised Sensing Rate Learning (SSRL) approach is proposed to quickly and accurately obtain the workers' SRs, which consists of two phases, supervision and self-supervision. Last, SCMABA is designed organically combining the SRs acquisition mechanism with multi-armed bandit reverse auction, where supervised SR learning is used in the exploration, and the self-supervised one is used in the exploitation. We prove that our SCMABA achieves truthfulness and individual rationality. Additionally, we exhibit outstanding performances of the SCMABA mechanism through in-depth simulations of real-world data traces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge