Qingyao Wu
T-Rex: Task-Adaptive Spatial Representation Extraction for Robotic Manipulation with Vision-Language Models
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Building a general robotic manipulation system capable of performing a wide variety of tasks in real-world settings is a challenging task. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in robotic manipulation tasks, primarily due to the extensive world knowledge they gain from large-scale datasets. In this process, Spatial Representations (such as points representing object positions or vectors representing object orientations) act as a bridge between VLMs and real-world scene, effectively grounding the reasoning abilities of VLMs and applying them to specific task scenarios. However, existing VLM-based robotic approaches often adopt a fixed spatial representation extraction scheme for various tasks, resulting in insufficient representational capability or excessive extraction time. In this work, we introduce T-Rex, a Task-Adaptive Framework for Spatial Representation Extraction, which dynamically selects the most appropriate spatial representation extraction scheme for each entity based on specific task requirements. Our key insight is that task complexity determines the types and granularity of spatial representations, and Stronger representational capabilities are typically associated with Higher overall system operation costs. Through comprehensive experiments in real-world robotic environments, we show that our approach delivers significant advantages in spatial understanding, efficiency, and stability without additional training.
AntiGrounding: Lifting Robotic Actions into VLM Representation Space for Decision Making
Jun 14, 2025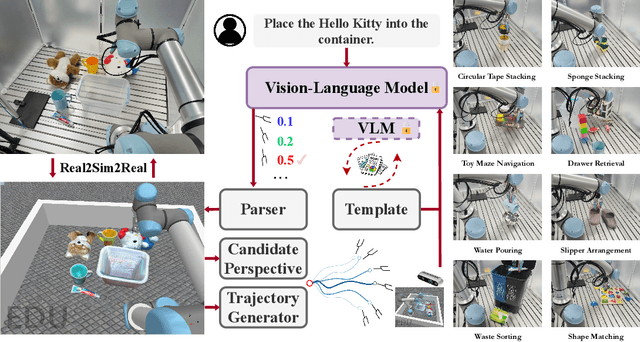
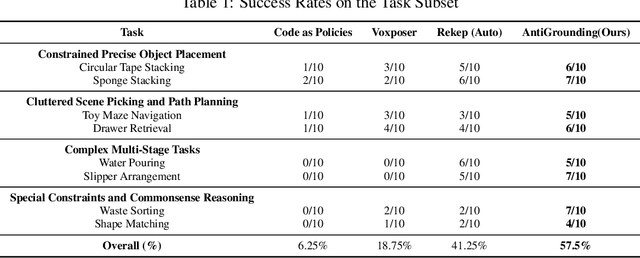
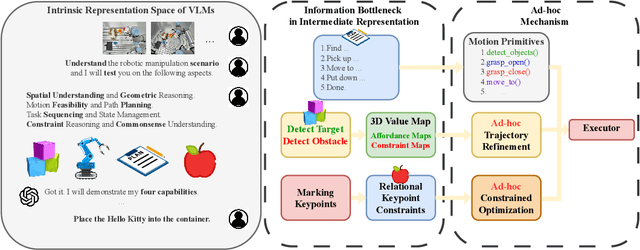
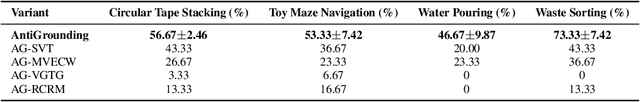
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) encode knowledge and reasoning capabilities for robotic manipulation within high-dimensional representation spaces. However, current approaches often project them into compressed intermediate representations, discarding important task-specific information such as fine-grained spatial or semantic details. To address this, we propose AntiGrounding, a new framework that reverses the instruction grounding process. It lifts candidate actions directly into the VLM representation space, renders trajectories from multiple views, and uses structured visual question answering for instruction-based decision making. This enables zero-shot synthesis of optimal closed-loop robot trajectories for new tasks. We also propose an offline policy refinement module that leverages past experience to enhance long-term performance. Experiments in both simulation and real-world environments show that our method outperforms baselines across diverse robotic manipulation tasks.
Inverse Materials Design by Large Language Model-Assisted Generative Framework
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Deep generative models hold great promise for inverse materials design, yet their efficiency and accuracy remain constrained by data scarcity and model architecture. Here, we introduce AlloyGAN, a closed-loop framework that integrates Large Language Model (LLM)-assisted text mining with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CGANs) to enhance data diversity and improve inverse design. Taking alloy discovery as a case study, AlloyGAN systematically refines material candidates through iterative screening and experimental validation. For metallic glasses, the framework predicts thermodynamic properties with discrepancies of less than 8% from experiments, demonstrating its robustness. By bridging generative AI with domain knowledge and validation workflows, AlloyGAN offers a scalable approach to accelerate the discovery of materials with tailored properties, paving the way for broader applications in materials science.
IPVTON: Image-based 3D Virtual Try-on with Image Prompt Adapter
Jan 26, 2025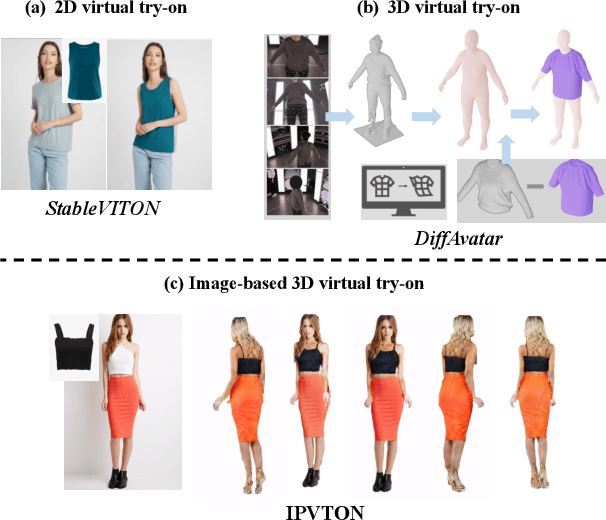
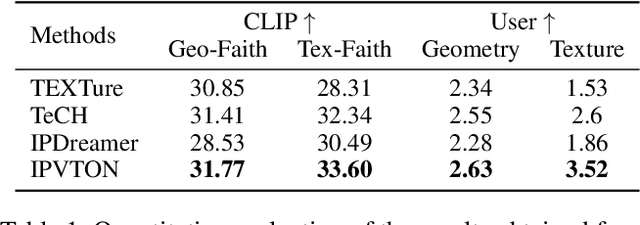
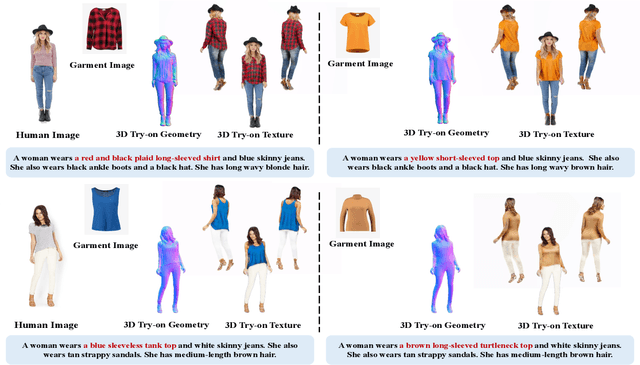
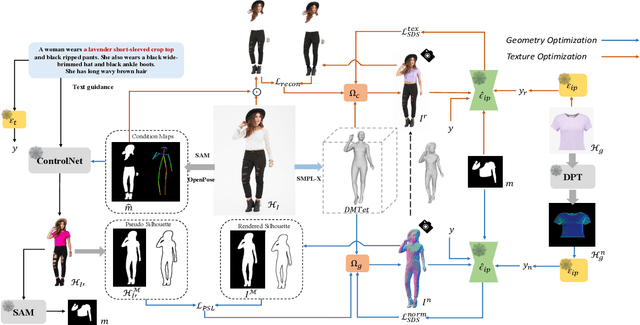
Abstract:Given a pair of images depicting a person and a garment separately, image-based 3D virtual try-on methods aim to reconstruct a 3D human model that realistically portrays the person wearing the desired garment. In this paper, we present IPVTON, a novel image-based 3D virtual try-on framework. IPVTON employs score distillation sampling with image prompts to optimize a hybrid 3D human representation, integrating target garment features into diffusion priors through an image prompt adapter. To avoid interference with non-target areas, we leverage mask-guided image prompt embeddings to focus the image features on the try-on regions. Moreover, we impose geometric constraints on the 3D model with a pseudo silhouette generated by ControlNet, ensuring that the clothed 3D human model retains the shape of the source identity while accurately wearing the target garments. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that IPVTON outperforms previous methods in image-based 3D virtual try-on tasks, excelling in both geometry and texture.
Hybrid Classification-Regression Adaptive Loss for Dense Object Detection
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:For object detection detectors, enhancing model performance hinges on the ability to simultaneously consider inconsistencies across tasks and focus on difficult-to-train samples. Achieving this necessitates incorporating information from both the classification and regression tasks. However, prior work tends to either emphasize difficult-to-train samples within their respective tasks or simply compute classification scores with IoU, often leading to suboptimal model performance. In this paper, we propose a Hybrid Classification-Regression Adaptive Loss, termed as HCRAL. Specifically, we introduce the Residual of Classification and IoU (RCI) module for cross-task supervision, addressing task inconsistencies, and the Conditioning Factor (CF) to focus on difficult-to-train samples within each task. Furthermore, we introduce a new strategy named Expanded Adaptive Training Sample Selection (EATSS) to provide additional samples that exhibit classification and regression inconsistencies. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct extensive experiments on COCO test-dev. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our approachs. Additionally, we designed experiments by separately combining the classification and regression loss with regular loss functions in popular one-stage models, demonstrating improved performance.
DeCo: Decoupled Human-Centered Diffusion Video Editing with Motion Consistency
Aug 14, 2024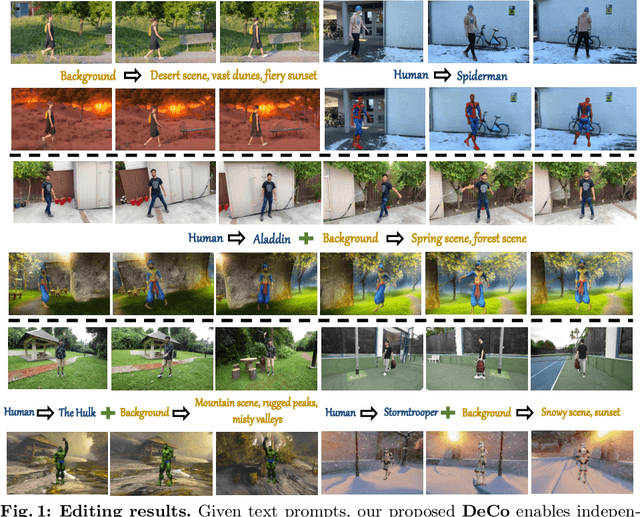
Abstract:Diffusion models usher a new era of video editing, flexibly manipulating the video contents with text prompts. Despite the widespread application demand in editing human-centered videos, these models face significant challenges in handling complex objects like humans. In this paper, we introduce DeCo, a novel video editing framework specifically designed to treat humans and the background as separate editable targets, ensuring global spatial-temporal consistency by maintaining the coherence of each individual component. Specifically, we propose a decoupled dynamic human representation that utilizes a parametric human body prior to generate tailored humans while preserving the consistent motions as the original video. In addition, we consider the background as a layered atlas to apply text-guided image editing approaches on it. To further enhance the geometry and texture of humans during the optimization, we extend the calculation of score distillation sampling into normal space and image space. Moreover, we tackle inconsistent lighting between the edited targets by leveraging a lighting-aware video harmonizer, a problem previously overlooked in decompose-edit-combine approaches. Extensive qualitative and numerical experiments demonstrate that DeCo outperforms prior video editing methods in human-centered videos, especially in longer videos.
Spatial-Semantic Collaborative Cropping for User Generated Content
Jan 16, 2024Abstract:A large amount of User Generated Content (UGC) is uploaded to the Internet daily and displayed to people world-widely through the client side (e.g., mobile and PC). This requires the cropping algorithms to produce the aesthetic thumbnail within a specific aspect ratio on different devices. However, existing image cropping works mainly focus on landmark or landscape images, which fail to model the relations among the multi-objects with the complex background in UGC. Besides, previous methods merely consider the aesthetics of the cropped images while ignoring the content integrity, which is crucial for UGC cropping. In this paper, we propose a Spatial-Semantic Collaborative cropping network (S2CNet) for arbitrary user generated content accompanied by a new cropping benchmark. Specifically, we first mine the visual genes of the potential objects. Then, the suggested adaptive attention graph recasts this task as a procedure of information association over visual nodes. The underlying spatial and semantic relations are ultimately centralized to the crop candidate through differentiable message passing, which helps our network efficiently to preserve both the aesthetics and the content integrity. Extensive experiments on the proposed UGCrop5K and other public datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach over state-of-the-art counterparts. Our project is available at https://github.com/suyukun666/S2CNet.
Variance-insensitive and Target-preserving Mask Refinement for Interactive Image Segmentation
Dec 22, 2023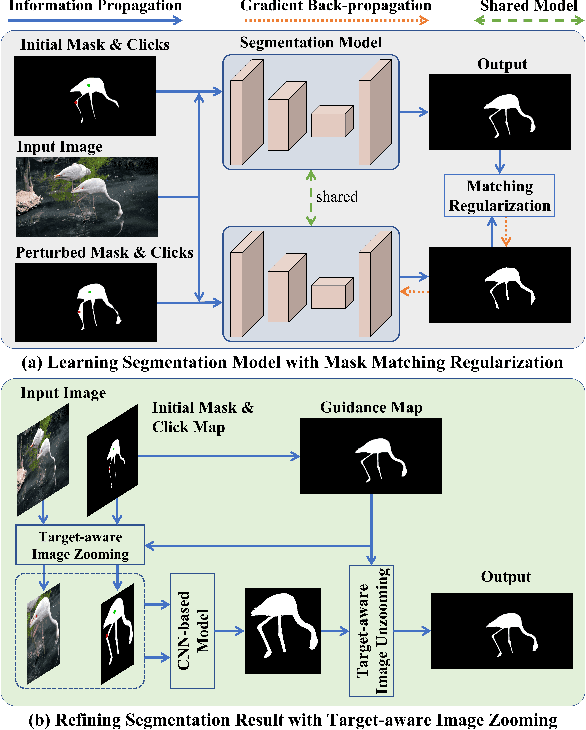
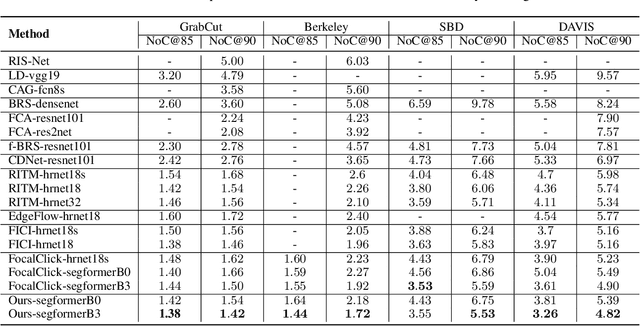

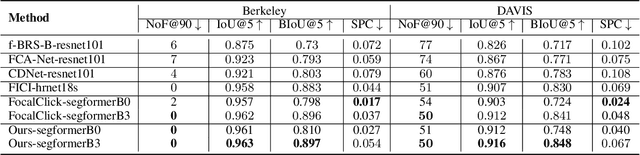
Abstract:Point-based interactive image segmentation can ease the burden of mask annotation in applications such as semantic segmentation and image editing. However, fully extracting the target mask with limited user inputs remains challenging. We introduce a novel method, Variance-Insensitive and Target-Preserving Mask Refinement to enhance segmentation quality with fewer user inputs. Regarding the last segmentation result as the initial mask, an iterative refinement process is commonly employed to continually enhance the initial mask. Nevertheless, conventional techniques suffer from sensitivity to the variance in the initial mask. To circumvent this problem, our proposed method incorporates a mask matching algorithm for ensuring consistent inferences from different types of initial masks. We also introduce a target-aware zooming algorithm to preserve object information during downsampling, balancing efficiency and accuracy. Experiments on GrabCut, Berkeley, SBD, and DAVIS datasets demonstrate our method's state-of-the-art performance in interactive image segmentation.
Typhoon Intensity Prediction with Vision Transformer
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Predicting typhoon intensity accurately across space and time is crucial for issuing timely disaster warnings and facilitating emergency response. This has vast potential for minimizing life losses and property damages as well as reducing economic and environmental impacts. Leveraging satellite imagery for scenario analysis is effective but also introduces additional challenges due to the complex relations among clouds and the highly dynamic context. Existing deep learning methods in this domain rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which suffer from limited per-layer receptive fields. This limitation hinders their ability to capture long-range dependencies and global contextual knowledge during inference. In response, we introduce a novel approach, namely "Typhoon Intensity Transformer" (Tint), which leverages self-attention mechanisms with global receptive fields per layer. Tint adopts a sequence-to-sequence feature representation learning perspective. It begins by cutting a given satellite image into a sequence of patches and recursively employs self-attention operations to extract both local and global contextual relations between all patch pairs simultaneously, thereby enhancing per-patch feature representation learning. Extensive experiments on a publicly available typhoon benchmark validate the efficacy of Tint in comparison with both state-of-the-art deep learning and conventional meteorological methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/chen-huanxin/Tint.
DI-Net : Decomposed Implicit Garment Transfer Network for Digital Clothed 3D Human
Nov 28, 2023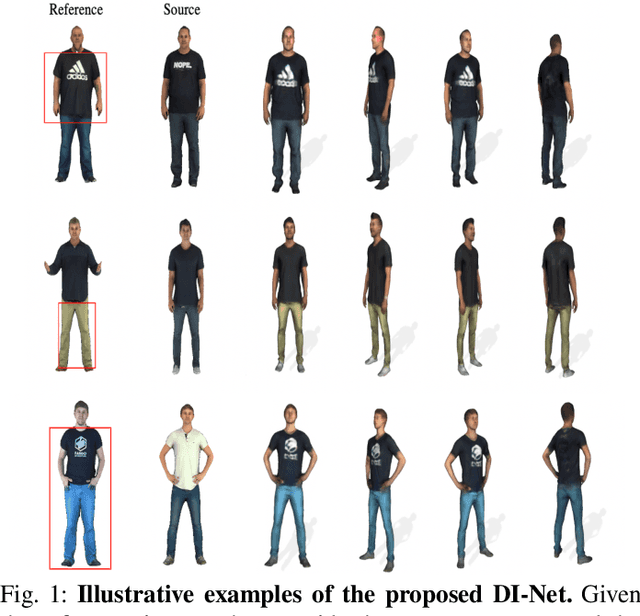

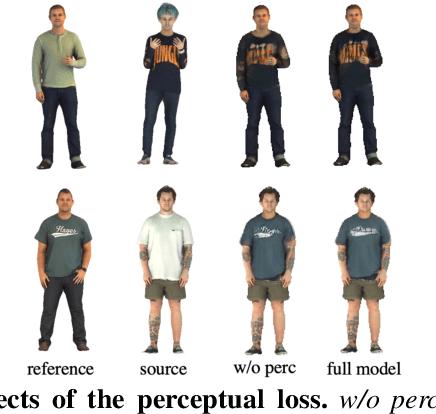

Abstract:3D virtual try-on enjoys many potential applications and hence has attracted wide attention. However, it remains a challenging task that has not been adequately solved. Existing 2D virtual try-on methods cannot be directly extended to 3D since they lack the ability to perceive the depth of each pixel. Besides, 3D virtual try-on approaches are mostly built on the fixed topological structure and with heavy computation. To deal with these problems, we propose a Decomposed Implicit garment transfer network (DI-Net), which can effortlessly reconstruct a 3D human mesh with the newly try-on result and preserve the texture from an arbitrary perspective. Specifically, DI-Net consists of two modules: 1) A complementary warping module that warps the reference image to have the same pose as the source image through dense correspondence learning and sparse flow learning; 2) A geometry-aware decomposed transfer module that decomposes the garment transfer into image layout based transfer and texture based transfer, achieving surface and texture reconstruction by constructing pixel-aligned implicit functions. Experimental results show the effectiveness and superiority of our method in the 3D virtual try-on task, which can yield more high-quality results over other existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge