Xiaofeng Yang
Emory University Winship Cancer Institute, Department of Radiation Oncology, Emory University
IPEC: Test-Time Incremental Prototype Enhancement Classifier for Few-Shot Learning
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Metric-based few-shot approaches have gained significant popularity due to their relatively straightforward implementation, high interpret ability, and computational efficiency. However, stemming from the batch-independence assumption during testing, which prevents the model from leveraging valuable knowledge accumulated from previous batches. To address these challenges, we propose a novel test-time method called Incremental Prototype Enhancement Classifier (IPEC), a test-time method that optimizes prototype estimation by leveraging information from previous query samples. IPEC maintains a dynamic auxiliary set by selectively incorporating query samples that are classified with high confidence. To ensure sample quality, we design a robust dual-filtering mechanism that assesses each query sample based on both global prediction confidence and local discriminative ability. By aggregating this auxiliary set with the support set in subsequent tasks, IPEC builds progressively more stable and representative prototypes, effectively reducing its reliance on the initial support set. We ground this approach in a Bayesian interpretation, conceptualizing the support set as a prior and the auxiliary set as a data-driven posterior, which in turn motivates the design of a practical "warm-up and test" two-stage inference protocol. Extensive empirical results validate the superior performance of our proposed method across multiple few-shot classification tasks.
Enhancing Visual In-Context Learning by Multi-Faceted Fusion
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Visual In-Context Learning (VICL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm, enabling models to perform novel visual tasks by learning from in-context examples. The dominant "retrieve-then-prompt" approach typically relies on selecting the single best visual prompt, a practice that often discards valuable contextual information from other suitable candidates. While recent work has explored fusing the top-K prompts into a single, enhanced representation, this still simply collapses multiple rich signals into one, limiting the model's reasoning capability. We argue that a more multi-faceted, collaborative fusion is required to unlock the full potential of these diverse contexts. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel framework that moves beyond single-prompt fusion towards an multi-combination collaborative fusion. Instead of collapsing multiple prompts into one, our method generates three contextual representation branches, each formed by integrating information from different combinations of top-quality prompts. These complementary guidance signals are then fed into proposed MULTI-VQGAN architecture, which is designed to jointly interpret and utilize collaborative information from multiple sources. Extensive experiments on diverse tasks, including foreground segmentation, single-object detection, and image colorization, highlight its strong cross-task generalization, effective contextual fusion, and ability to produce more robust and accurate predictions than existing methods.
Beyond Single Prompts: Synergistic Fusion and Arrangement for VICL
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision In-Context Learning (VICL) enables inpainting models to quickly adapt to new visual tasks from only a few prompts. However, existing methods suffer from two key issues: (1) selecting only the most similar prompt discards complementary cues from other high-quality prompts; and (2) failing to exploit the structured information implied by different prompt arrangements. We propose an end-to-end VICL framework to overcome these limitations. Firstly, an adaptive Fusion Module aggregates critical patterns and annotations from multiple prompts to form more precise contextual prompts. Secondly, we introduce arrangement-specific lightweight MLPs to decouple layout priors from the core model, while minimally affecting the overall model. In addition, an bidirectional fine-tuning mechanism swaps the roles of query and prompt, encouraging the model to reconstruct the original prompt from fused context and thus enhancing collaboration between the fusion module and the inpainting model. Experiments on foreground segmentation, single-object detection, and image colorization demonstrate superior results and strong cross-task generalization of our method.
InfoSculpt: Sculpting the Latent Space for Generalized Category Discovery
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) aims to classify instances from both known and novel categories within a large-scale unlabeled dataset, a critical yet challenging task for real-world, open-world applications. However, existing methods often rely on pseudo-labeling, or two-stage clustering, which lack a principled mechanism to explicitly disentangle essential, category-defining signals from instance-specific noise. In this paper, we address this fundamental limitation by re-framing GCD from an information-theoretic perspective, grounded in the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle. We introduce InfoSculpt, a novel framework that systematically sculpts the representation space by minimizing a dual Conditional Mutual Information (CMI) objective. InfoSculpt uniquely combines a Category-Level CMI on labeled data to learn compact and discriminative representations for known classes, and a complementary Instance-Level CMI on all data to distill invariant features by compressing augmentation-induced noise. These two objectives work synergistically at different scales to produce a disentangled and robust latent space where categorical information is preserved while noisy, instance-specific details are discarded. Extensive experiments on 8 benchmarks demonstrate that InfoSculpt validating the effectiveness of our information-theoretic approach.
Efficient Vision Mamba for MRI Super-Resolution via Hybrid Selective Scanning
Dec 22, 2025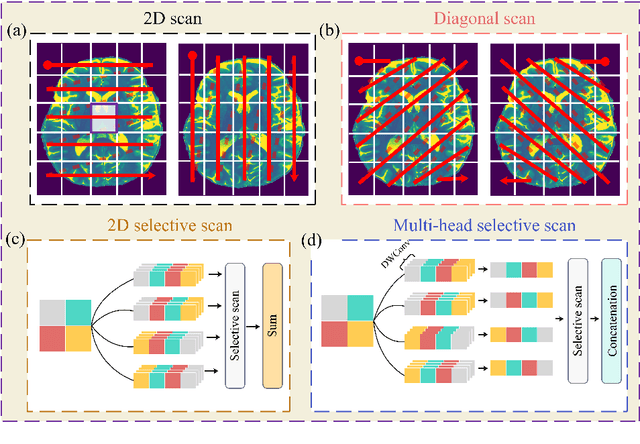
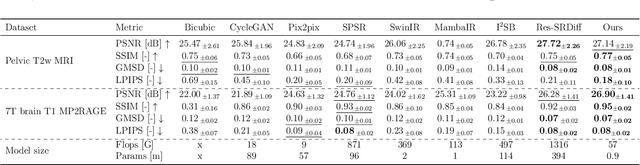
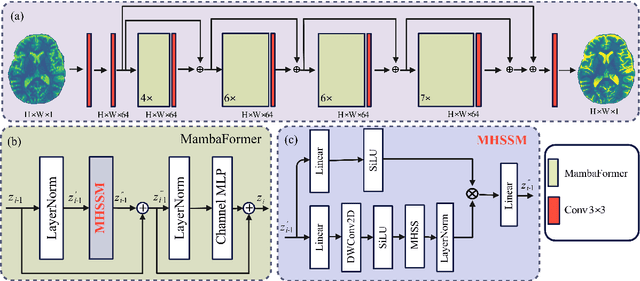

Abstract:Background: High-resolution MRI is critical for diagnosis, but long acquisition times limit clinical use. Super-resolution (SR) can enhance resolution post-scan, yet existing deep learning methods face fidelity-efficiency trade-offs. Purpose: To develop a computationally efficient and accurate deep learning framework for MRI SR that preserves anatomical detail for clinical integration. Materials and Methods: We propose a novel SR framework combining multi-head selective state-space models (MHSSM) with a lightweight channel MLP. The model uses 2D patch extraction with hybrid scanning to capture long-range dependencies. Each MambaFormer block integrates MHSSM, depthwise convolutions, and gated channel mixing. Evaluation used 7T brain T1 MP2RAGE maps (n=142) and 1.5T prostate T2w MRI (n=334). Comparisons included Bicubic interpolation, GANs (CycleGAN, Pix2pix, SPSR), transformers (SwinIR), Mamba (MambaIR), and diffusion models (I2SB, Res-SRDiff). Results: Our model achieved superior performance with exceptional efficiency. For 7T brain data: SSIM=0.951+-0.021, PSNR=26.90+-1.41 dB, LPIPS=0.076+-0.022, GMSD=0.083+-0.017, significantly outperforming all baselines (p<0.001). For prostate data: SSIM=0.770+-0.049, PSNR=27.15+-2.19 dB, LPIPS=0.190+-0.095, GMSD=0.087+-0.013. The framework used only 0.9M parameters and 57 GFLOPs, reducing parameters by 99.8% and computation by 97.5% versus Res-SRDiff, while outperforming SwinIR and MambaIR in accuracy and efficiency. Conclusion: The proposed framework provides an efficient, accurate MRI SR solution, delivering enhanced anatomical detail across datasets. Its low computational demand and state-of-the-art performance show strong potential for clinical translation.
MeCaMIL: Causality-Aware Multiple Instance Learning for Fair and Interpretable Whole Slide Image Diagnosis
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) has emerged as the dominant paradigm for whole slide image (WSI) analysis in computational pathology, achieving strong diagnostic performance through patch-level feature aggregation. However, existing MIL methods face critical limitations: (1) they rely on attention mechanisms that lack causal interpretability, and (2) they fail to integrate patient demographics (age, gender, race), leading to fairness concerns across diverse populations. These shortcomings hinder clinical translation, where algorithmic bias can exacerbate health disparities. We introduce \textbf{MeCaMIL}, a causality-aware MIL framework that explicitly models demographic confounders through structured causal graphs. Unlike prior approaches treating demographics as auxiliary features, MeCaMIL employs principled causal inference -- leveraging do-calculus and collider structures -- to disentangle disease-relevant signals from spurious demographic correlations. Extensive evaluation on three benchmarks demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across CAMELYON16 (ACC/AUC/F1: 0.939/0.983/0.946), TCGA-Lung (0.935/0.979/0.931), and TCGA-Multi (0.977/0.993/0.970, five cancer types). Critically, MeCaMIL achieves superior fairness -- demographic disparity variance drops by over 65% relative reduction on average across attributes, with notable improvements for underserved populations. The framework generalizes to survival prediction (mean C-index: 0.653, +0.017 over best baseline across five cancer types). Ablation studies confirm causal graph structure is essential -- alternative designs yield 0.048 lower accuracy and 4.2x times worse fairness. These results establish MeCaMIL as a principled framework for fair, interpretable, and clinically actionable AI in digital pathology. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Explainable Cross-Disease Reasoning for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment from LDCT
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) inherently captures both pulmonary and cardiac structures, offering a unique opportunity for joint assessment of lung and cardiovascular health. However, most existing approaches treat these domains as independent tasks, overlooking their physiological interplay and shared imaging biomarkers. We propose an Explainable Cross-Disease Reasoning Framework that enables interpretable cardiopulmonary risk assessment from a single LDCT scan. The framework introduces an agentic reasoning process that emulates clinical diagnostic thinking-first perceiving pulmonary findings, then reasoning through established medical knowledge, and finally deriving a cardiovascular judgment with explanatory rationale. It integrates three synergistic components: a pulmonary perception module that summarizes lung abnormalities, a knowledge-guided reasoning module that infers their cardiovascular implications, and a cardiac representation module that encodes structural biomarkers. Their outputs are fused to produce a holistic cardiovascular risk prediction that is both accurate and physiologically grounded. Experiments on the NLST cohort demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance for CVD screening and mortality prediction, outperforming single-disease and purely image-based baselines. Beyond quantitative gains, the framework provides human-verifiable reasoning that aligns with cardiological understanding, revealing coherent links between pulmonary abnormalities and cardiac stress mechanisms. Overall, this work establishes a unified and explainable paradigm for cardiovascular analysis from LDCT, bridging the gap between image-based prediction and mechanism-based medical interpretation.
Hunyuan3D Studio: End-to-End AI Pipeline for Game-Ready 3D Asset Generation
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:The creation of high-quality 3D assets, a cornerstone of modern game development, has long been characterized by labor-intensive and specialized workflows. This paper presents Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI-powered content creation platform designed to revolutionize the game production pipeline by automating and streamlining the generation of game-ready 3D assets. At its core, Hunyuan3D Studio integrates a suite of advanced neural modules (such as Part-level 3D Generation, Polygon Generation, Semantic UV, etc.) into a cohesive and user-friendly system. This unified framework allows for the rapid transformation of a single concept image or textual description into a fully-realized, production-quality 3D model complete with optimized geometry and high-fidelity PBR textures. We demonstrate that assets generated by Hunyuan3D Studio are not only visually compelling but also adhere to the stringent technical requirements of contemporary game engines, significantly reducing iteration time and lowering the barrier to entry for 3D content creation. By providing a seamless bridge from creative intent to technical asset, Hunyuan3D Studio represents a significant leap forward for AI-assisted workflows in game development and interactive media.
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of AI-driven MRI Motion Artifact Detection and Correction
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Background: To systematically review and perform a meta-analysis of artificial intelligence (AI)-driven methods for detecting and correcting magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) motion artifacts, assessing current developments, effectiveness, challenges, and future research directions. Methods: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted, focusing on deep learning (DL) approaches, particularly generative models, for the detection and correction of MRI motion artifacts. Quantitative data were extracted regarding utilized datasets, DL architectures, and performance metrics. Results: DL, particularly generative models, show promise for reducing motion artifacts and improving image quality; however, limited generalizability, reliance on paired training data, and risk of visual distortions remain key challenges that motivate standardized datasets and reporting. Conclusions: AI-driven methods, particularly DL generative models, show significant potential for improving MRI image quality by effectively addressing motion artifacts. However, critical challenges must be addressed, including the need for comprehensive public datasets, standardized reporting protocols for artifact levels, and more advanced, adaptable DL techniques to reduce reliance on extensive paired datasets. Addressing these aspects could substantially enhance MRI diagnostic accuracy, reduce healthcare costs, and improve patient care outcomes.
MedVista3D: Vision-Language Modeling for Reducing Diagnostic Errors in 3D CT Disease Detection, Understanding and Reporting
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Radiologic diagnostic errors-under-reading errors, inattentional blindness, and communication failures-remain prevalent in clinical practice. These issues often stem from missed localized abnormalities, limited global context, and variability in report language. These challenges are amplified in 3D imaging, where clinicians must examine hundreds of slices per scan. Addressing them requires systems with precise localized detection, global volume-level reasoning, and semantically consistent natural language reporting. However, existing 3D vision-language models are unable to meet all three needs jointly, lacking local-global understanding for spatial reasoning and struggling with the variability and noise of uncurated radiology reports. We present MedVista3D, a multi-scale semantic-enriched vision-language pretraining framework for 3D CT analysis. To enable joint disease detection and holistic interpretation, MedVista3D performs local and global image-text alignment for fine-grained representation learning within full-volume context. To address report variability, we apply language model rewrites and introduce a Radiology Semantic Matching Bank for semantics-aware alignment. MedVista3D achieves state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot disease classification, report retrieval, and medical visual question answering, while transferring well to organ segmentation and prognosis prediction. Code and datasets will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge