Ziyin Zhou
MEEA: Mere Exposure Effect-Driven Confrontational Optimization for LLM Jailbreaking
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has intensified concerns about the robustness of their safety alignment. While existing jailbreak studies explore both single-turn and multi-turn strategies, most implicitly assume a static safety boundary and fail to account for how contextual interactions dynamically influence model behavior, leading to limited stability and generalization. Motivated by this gap, we propose MEEA (Mere Exposure Effect Attack), a psychology-inspired, fully automated black-box framework for evaluating multi-turn safety robustness, grounded in the mere exposure effect. MEEA leverages repeated low-toxicity semantic exposure to induce a gradual shift in a model's effective safety threshold, enabling progressive erosion of alignment constraints over sustained interactions. Concretely, MEEA constructs semantically progressive prompt chains and optimizes them using a simulated annealing strategy guided by semantic similarity, toxicity, and jailbreak effectiveness. Extensive experiments on both closed-source and open-source models, including GPT-4, Claude-3.5, and DeepSeek-R1, demonstrate that MEEA consistently achieves higher attack success rates than seven representative baselines, with an average Attack Success Rate (ASR) improvement exceeding 20%. Ablation studies further validate the necessity of both annealing-based optimization and contextual exposure mechanisms. Beyond improved attack effectiveness, our findings indicate that LLM safety behavior is inherently dynamic and history-dependent, challenging the common assumption of static alignment boundaries and highlighting the need for interaction-aware safety evaluation and defense mechanisms. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Carney-lsz/MEEA
CAPTURE: A Benchmark and Evaluation for LVLMs in CAPTCHA Resolving
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Benefiting from strong and efficient multi-modal alignment strategies, Large Visual Language Models (LVLMs) are able to simulate human visual and reasoning capabilities, such as solving CAPTCHAs. However, existing benchmarks based on visual CAPTCHAs still face limitations. Previous studies, when designing benchmarks and datasets, customized them according to their research objectives. Consequently, these benchmarks cannot comprehensively cover all CAPTCHA types. Notably, there is a dearth of dedicated benchmarks for LVLMs. To address this problem, we introduce a novel CAPTCHA benchmark for the first time, named CAPTURE CAPTCHA for Testing Under Real-world Experiments, specifically for LVLMs. Our benchmark encompasses 4 main CAPTCHA types and 25 sub-types from 31 vendors. The diversity enables a multi-dimensional and thorough evaluation of LVLM performance. CAPTURE features extensive class variety, large-scale data, and unique LVLM-tailored labels, filling the gaps in previous research in terms of data comprehensiveness and labeling pertinence. When evaluated by this benchmark, current LVLMs demonstrate poor performance in solving CAPTCHAs.
Towards Rationale-Answer Alignment of LVLMs via Self-Rationale Calibration
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have manifested strong visual question answering capability. However, they still struggle with aligning the rationale and the generated answer, leading to inconsistent reasoning and incorrect responses. To this end, this paper introduces the Self-Rationale Calibration (SRC) framework to iteratively calibrate the alignment between rationales and answers. SRC begins by employing a lightweight "rationale fine-tuning" approach, which modifies the model's response format to require a rationale before deriving an answer without explicit prompts. Next, SRC searches for a diverse set of candidate responses from the fine-tuned LVLMs for each sample, followed by a proposed pairwise scoring strategy using a tailored scoring model, R-Scorer, to evaluate both rationale quality and factual consistency of candidates. Based on a confidence-weighted preference curation process, SRC decouples the alignment calibration into a preference fine-tuning manner, leading to significant improvements of LVLMs in perception, reasoning, and generalization across multiple benchmarks. Our results emphasize the rationale-oriented alignment in exploring the potential of LVLMs.
Oedipus and the Sphinx: Benchmarking and Improving Visual Language Models for Complex Graphic Reasoning
Aug 01, 2025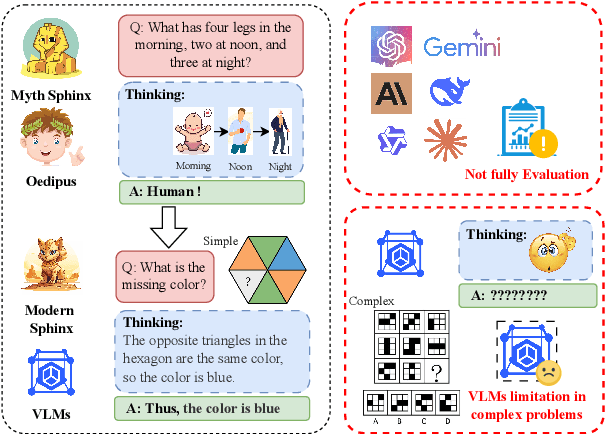
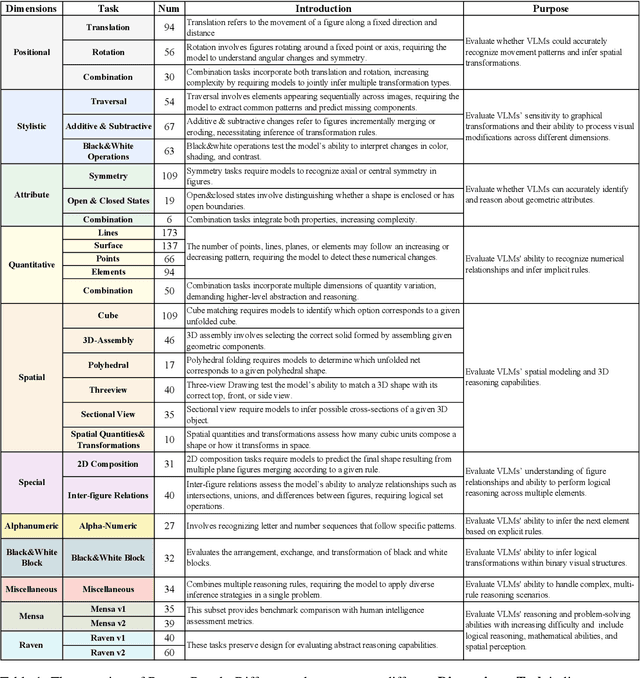
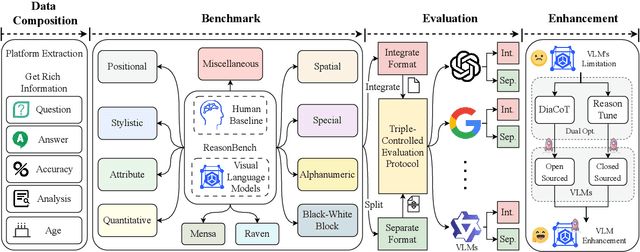
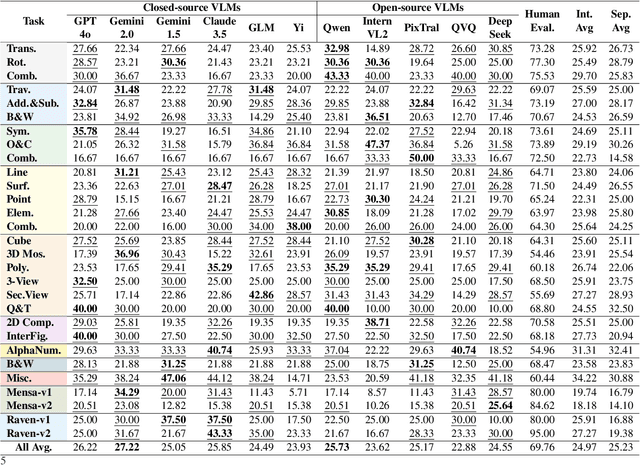
Abstract:Evaluating the performance of visual language models (VLMs) in graphic reasoning tasks has become an important research topic. However, VLMs still show obvious deficiencies in simulating human-level graphic reasoning capabilities, especially in complex graphic reasoning and abstract problem solving, which are less studied and existing studies only focus on simple graphics. To evaluate the performance of VLMs in complex graphic reasoning, we propose ReasonBench, the first evaluation benchmark focused on structured graphic reasoning tasks, which includes 1,613 questions from real-world intelligence tests. ReasonBench covers reasoning dimensions related to location, attribute, quantity, and multi-element tasks, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the performance of VLMs in spatial, relational, and abstract reasoning capabilities. We benchmark 11 mainstream VLMs (including closed-source and open-source models) and reveal significant limitations of current models. Based on these findings, we propose a dual optimization strategy: Diagrammatic Reasoning Chain (DiaCoT) enhances the interpretability of reasoning by decomposing layers, and ReasonTune enhances the task adaptability of model reasoning through training, all of which improves VLM performance by 33.5\%. All experimental data and code are in the repository: https://huggingface.co/datasets/cistine/ReasonBench.
AIGI-Holmes: Towards Explainable and Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection via Multimodal Large Language Models
Jul 03, 2025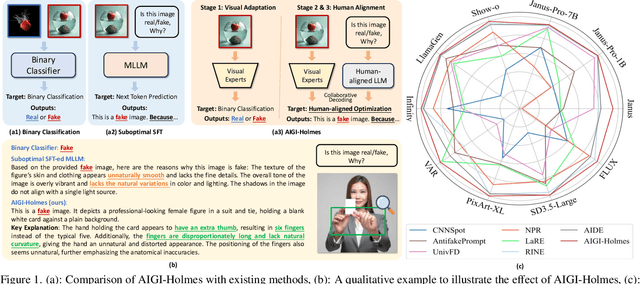
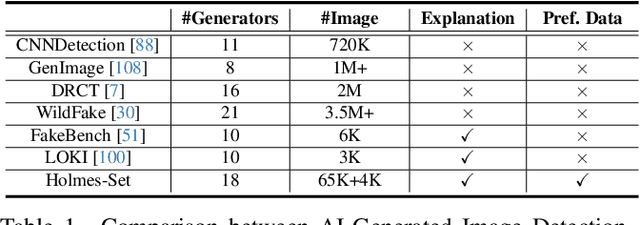
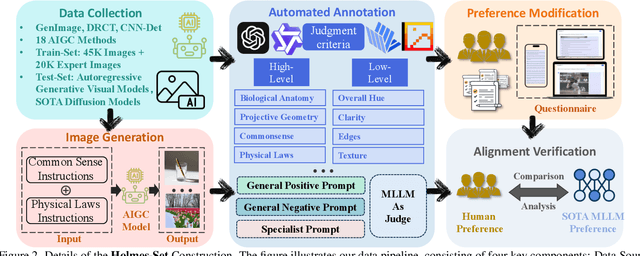
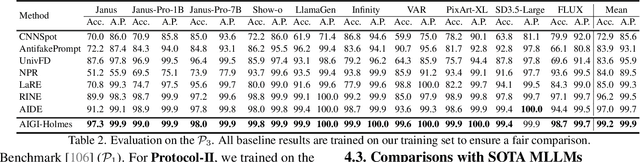
Abstract:The rapid development of AI-generated content (AIGC) technology has led to the misuse of highly realistic AI-generated images (AIGI) in spreading misinformation, posing a threat to public information security. Although existing AIGI detection techniques are generally effective, they face two issues: 1) a lack of human-verifiable explanations, and 2) a lack of generalization in the latest generation technology. To address these issues, we introduce a large-scale and comprehensive dataset, Holmes-Set, which includes the Holmes-SFTSet, an instruction-tuning dataset with explanations on whether images are AI-generated, and the Holmes-DPOSet, a human-aligned preference dataset. Our work introduces an efficient data annotation method called the Multi-Expert Jury, enhancing data generation through structured MLLM explanations and quality control via cross-model evaluation, expert defect filtering, and human preference modification. In addition, we propose Holmes Pipeline, a meticulously designed three-stage training framework comprising visual expert pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, and direct preference optimization. Holmes Pipeline adapts multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for AIGI detection while generating human-verifiable and human-aligned explanations, ultimately yielding our model AIGI-Holmes. During the inference stage, we introduce a collaborative decoding strategy that integrates the model perception of the visual expert with the semantic reasoning of MLLMs, further enhancing the generalization capabilities. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our AIGI-Holmes.
FL-PLAS: Federated Learning with Partial Layer Aggregation for Backdoor Defense Against High-Ratio Malicious Clients
May 17, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is gaining increasing attention as an emerging collaborative machine learning approach, particularly in the context of large-scale computing and data systems. However, the fundamental algorithm of FL, Federated Averaging (FedAvg), is susceptible to backdoor attacks. Although researchers have proposed numerous defense algorithms, two significant challenges remain. The attack is becoming more stealthy and harder to detect, and current defense methods are unable to handle 50\% or more malicious users or assume an auxiliary server dataset. To address these challenges, we propose a novel defense algorithm, FL-PLAS, \textbf{F}ederated \textbf{L}earning based on \textbf{P}artial\textbf{ L}ayer \textbf{A}ggregation \textbf{S}trategy. In particular, we divide the local model into a feature extractor and a classifier. In each iteration, the clients only upload the parameters of a feature extractor after local training. The server then aggregates these local parameters and returns the results to the clients. Each client retains its own classifier layer, ensuring that the backdoor labels do not impact other clients. We assess the effectiveness of FL-PLAS against state-of-the-art (SOTA) backdoor attacks on three image datasets and compare our approach to six defense strategies. The results of the experiment demonstrate that our methods can effectively protect local models from backdoor attacks. Without requiring any auxiliary dataset for the server, our method achieves a high main-task accuracy with a lower backdoor accuracy even under the condition of 90\% malicious users with the attacks of trigger, semantic and edge-case.
Exploring the Collaborative Advantage of Low-level Information on Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Apr 01, 2025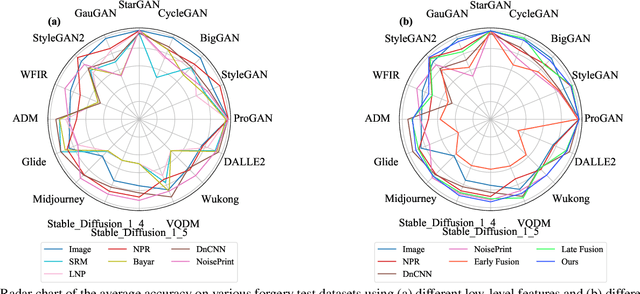
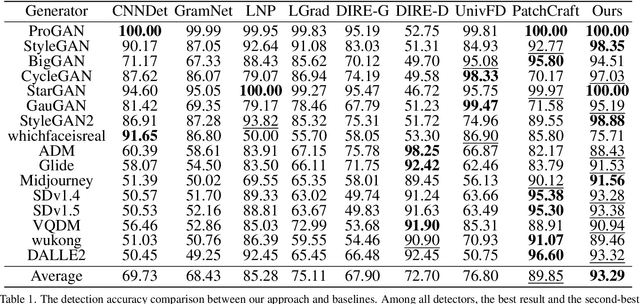
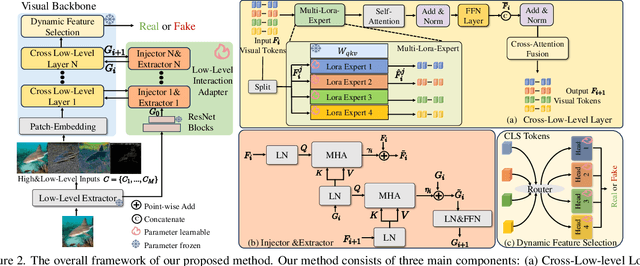
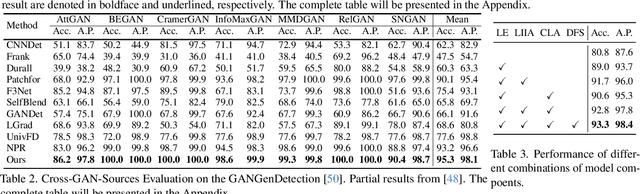
Abstract:Existing state-of-the-art AI-Generated image detection methods mostly consider extracting low-level information from RGB images to help improve the generalization of AI-Generated image detection, such as noise patterns. However, these methods often consider only a single type of low-level information, which may lead to suboptimal generalization. Through empirical analysis, we have discovered a key insight: different low-level information often exhibits generalization capabilities for different types of forgeries. Furthermore, we found that simple fusion strategies are insufficient to leverage the detection advantages of each low-level and high-level information for various forgery types. Therefore, we propose the Adaptive Low-level Experts Injection (ALEI) framework. Our approach introduces Lora Experts, enabling the backbone network, which is trained with high-level semantic RGB images, to accept and learn knowledge from different low-level information. We utilize a cross-attention method to adaptively fuse these features at intermediate layers. To prevent the backbone network from losing the modeling capabilities of different low-level features during the later stages of modeling, we developed a Low-level Information Adapter that interacts with the features extracted by the backbone network. Finally, we propose Dynamic Feature Selection, which dynamically selects the most suitable features for detecting the current image to maximize generalization detection capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method, finetuned on only four categories of mainstream ProGAN data, performs excellently and achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple datasets containing unseen GAN and Diffusion methods.
StealthDiffusion: Towards Evading Diffusion Forensic Detection through Diffusion Model
Aug 11, 2024Abstract:The rapid progress in generative models has given rise to the critical task of AI-Generated Content Stealth (AIGC-S), which aims to create AI-generated images that can evade both forensic detectors and human inspection. This task is crucial for understanding the vulnerabilities of existing detection methods and developing more robust techniques. However, current adversarial attacks often introduce visible noise, have poor transferability, and fail to address spectral differences between AI-generated and genuine images. To address this, we propose StealthDiffusion, a framework based on stable diffusion that modifies AI-generated images into high-quality, imperceptible adversarial examples capable of evading state-of-the-art forensic detectors. StealthDiffusion comprises two main components: Latent Adversarial Optimization, which generates adversarial perturbations in the latent space of stable diffusion, and Control-VAE, a module that reduces spectral differences between the generated adversarial images and genuine images without affecting the original diffusion model's generation process. Extensive experiments show that StealthDiffusion is effective in both white-box and black-box settings, transforming AI-generated images into high-quality adversarial forgeries with frequency spectra similar to genuine images. These forgeries are classified as genuine by advanced forensic classifiers and are difficult for humans to distinguish.
Can't say cant? Measuring and Reasoning of Dark Jargons in Large Language Models
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Ensuring the resilience of Large Language Models (LLMs) against malicious exploitation is paramount, with recent focus on mitigating offensive responses. Yet, the understanding of cant or dark jargon remains unexplored. This paper introduces a domain-specific Cant dataset and CantCounter evaluation framework, employing Fine-Tuning, Co-Tuning, Data-Diffusion, and Data-Analysis stages. Experiments reveal LLMs, including ChatGPT, are susceptible to cant bypassing filters, with varying recognition accuracy influenced by question types, setups, and prompt clues. Updated models exhibit higher acceptance rates for cant queries. Moreover, LLM reactions differ across domains, e.g., reluctance to engage in racism versus LGBT topics. These findings underscore LLMs' understanding of cant and reflect training data characteristics and vendor approaches to sensitive topics. Additionally, we assess LLMs' ability to demonstrate reasoning capabilities. Access to our datasets and code is available at https://github.com/cistineup/CantCounter.
DiffusionFace: Towards a Comprehensive Dataset for Diffusion-Based Face Forgery Analysis
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:The rapid progress in deep learning has given rise to hyper-realistic facial forgery methods, leading to concerns related to misinformation and security risks. Existing face forgery datasets have limitations in generating high-quality facial images and addressing the challenges posed by evolving generative techniques. To combat this, we present DiffusionFace, the first diffusion-based face forgery dataset, covering various forgery categories, including unconditional and Text Guide facial image generation, Img2Img, Inpaint, and Diffusion-based facial exchange algorithms. Our DiffusionFace dataset stands out with its extensive collection of 11 diffusion models and the high-quality of the generated images, providing essential metadata and a real-world internet-sourced forgery facial image dataset for evaluation. Additionally, we provide an in-depth analysis of the data and introduce practical evaluation protocols to rigorously assess discriminative models' effectiveness in detecting counterfeit facial images, aiming to enhance security in facial image authentication processes. The dataset is available for download at \url{https://github.com/Rapisurazurite/DiffFace}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge