Zhongxi Chen
Exploring the Collaborative Advantage of Low-level Information on Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Apr 01, 2025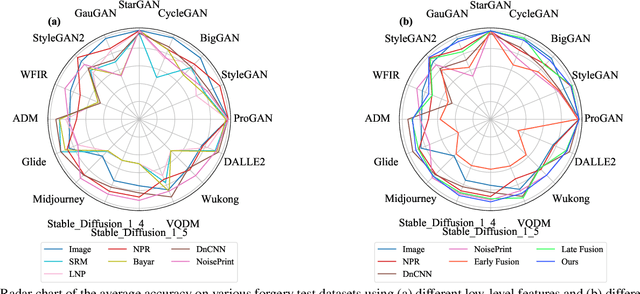
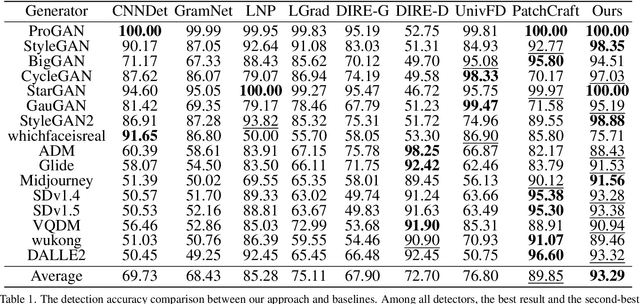
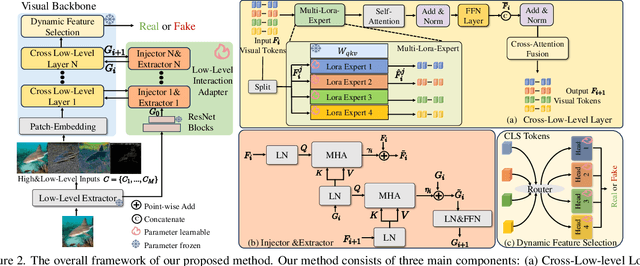
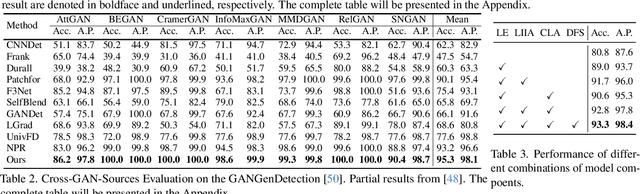
Abstract:Existing state-of-the-art AI-Generated image detection methods mostly consider extracting low-level information from RGB images to help improve the generalization of AI-Generated image detection, such as noise patterns. However, these methods often consider only a single type of low-level information, which may lead to suboptimal generalization. Through empirical analysis, we have discovered a key insight: different low-level information often exhibits generalization capabilities for different types of forgeries. Furthermore, we found that simple fusion strategies are insufficient to leverage the detection advantages of each low-level and high-level information for various forgery types. Therefore, we propose the Adaptive Low-level Experts Injection (ALEI) framework. Our approach introduces Lora Experts, enabling the backbone network, which is trained with high-level semantic RGB images, to accept and learn knowledge from different low-level information. We utilize a cross-attention method to adaptively fuse these features at intermediate layers. To prevent the backbone network from losing the modeling capabilities of different low-level features during the later stages of modeling, we developed a Low-level Information Adapter that interacts with the features extracted by the backbone network. Finally, we propose Dynamic Feature Selection, which dynamically selects the most suitable features for detecting the current image to maximize generalization detection capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method, finetuned on only four categories of mainstream ProGAN data, performs excellently and achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple datasets containing unseen GAN and Diffusion methods.
StealthDiffusion: Towards Evading Diffusion Forensic Detection through Diffusion Model
Aug 11, 2024Abstract:The rapid progress in generative models has given rise to the critical task of AI-Generated Content Stealth (AIGC-S), which aims to create AI-generated images that can evade both forensic detectors and human inspection. This task is crucial for understanding the vulnerabilities of existing detection methods and developing more robust techniques. However, current adversarial attacks often introduce visible noise, have poor transferability, and fail to address spectral differences between AI-generated and genuine images. To address this, we propose StealthDiffusion, a framework based on stable diffusion that modifies AI-generated images into high-quality, imperceptible adversarial examples capable of evading state-of-the-art forensic detectors. StealthDiffusion comprises two main components: Latent Adversarial Optimization, which generates adversarial perturbations in the latent space of stable diffusion, and Control-VAE, a module that reduces spectral differences between the generated adversarial images and genuine images without affecting the original diffusion model's generation process. Extensive experiments show that StealthDiffusion is effective in both white-box and black-box settings, transforming AI-generated images into high-quality adversarial forgeries with frequency spectra similar to genuine images. These forgeries are classified as genuine by advanced forensic classifiers and are difficult for humans to distinguish.
DiffusionFace: Towards a Comprehensive Dataset for Diffusion-Based Face Forgery Analysis
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:The rapid progress in deep learning has given rise to hyper-realistic facial forgery methods, leading to concerns related to misinformation and security risks. Existing face forgery datasets have limitations in generating high-quality facial images and addressing the challenges posed by evolving generative techniques. To combat this, we present DiffusionFace, the first diffusion-based face forgery dataset, covering various forgery categories, including unconditional and Text Guide facial image generation, Img2Img, Inpaint, and Diffusion-based facial exchange algorithms. Our DiffusionFace dataset stands out with its extensive collection of 11 diffusion models and the high-quality of the generated images, providing essential metadata and a real-world internet-sourced forgery facial image dataset for evaluation. Additionally, we provide an in-depth analysis of the data and introduce practical evaluation protocols to rigorously assess discriminative models' effectiveness in detecting counterfeit facial images, aiming to enhance security in facial image authentication processes. The dataset is available for download at \url{https://github.com/Rapisurazurite/DiffFace}.
CamoDiffusion: Camouflaged Object Detection via Conditional Diffusion Models
May 29, 2023



Abstract:Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) is a challenging task in computer vision due to the high similarity between camouflaged objects and their surroundings. Existing COD methods primarily employ semantic segmentation, which suffers from overconfident incorrect predictions. In this paper, we propose a new paradigm that treats COD as a conditional mask-generation task leveraging diffusion models. Our method, dubbed CamoDiffusion, employs the denoising process of diffusion models to iteratively reduce the noise of the mask. Due to the stochastic sampling process of diffusion, our model is capable of sampling multiple possible predictions from the mask distribution, avoiding the problem of overconfident point estimation. Moreover, we develop specialized learning strategies that include an innovative ensemble approach for generating robust predictions and tailored forward diffusion methods for efficient training, specifically for the COD task. Extensive experiments on three COD datasets attest the superior performance of our model compared to existing state-of-the-art methods, particularly on the most challenging COD10K dataset, where our approach achieves 0.019 in terms of MAE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge