Cen Chen
Institute for Infocomm Research
Spectral Evolution Search: Efficient Inference-Time Scaling for Reward-Aligned Image Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Inference-time scaling offers a versatile paradigm for aligning visual generative models with downstream objectives without parameter updates. However, existing approaches that optimize the high-dimensional initial noise suffer from severe inefficiency, as many search directions exert negligible influence on the final generation. We show that this inefficiency is closely related to a spectral bias in generative dynamics: model sensitivity to initial perturbations diminishes rapidly as frequency increases. Building on this insight, we propose Spectral Evolution Search (SES), a plug-and-play framework for initial noise optimization that executes gradient-free evolutionary search within a low-frequency subspace. Theoretically, we derive the Spectral Scaling Prediction from perturbation propagation dynamics, which explains the systematic differences in the impact of perturbations across frequencies. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SES significantly advances the Pareto frontier of generation quality versus computational cost, consistently outperforming strong baselines under equivalent budgets.
VIRAL: Visual In-Context Reasoning via Analogy in Diffusion Transformers
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Replicating In-Context Learning (ICL) in computer vision remains challenging due to task heterogeneity. We propose \textbf{VIRAL}, a framework that elicits visual reasoning from a pre-trained image editing model by formulating ICL as conditional generation via visual analogy ($x_s : x_t :: x_q : y_q$). We adapt a frozen Diffusion Transformer (DiT) using role-aware multi-image conditioning and introduce a Mixture-of-Experts LoRA to mitigate gradient interference across diverse tasks. Additionally, to bridge the gaps in current visual context datasets, we curate a large-scale dataset spanning perception, restoration, and editing. Experiments demonstrate that VIRAL outperforms existing methods, validating that a unified V-ICL paradigm can handle the majority of visual tasks, including open-domain editing. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/VIRAL-744A
When Sharpening Becomes Collapse: Sampling Bias and Semantic Coupling in RL with Verifiable Rewards
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) is a central paradigm for turning large language models (LLMs) into reliable problem solvers, especially in logic-heavy domains. Despite its empirical success, it remains unclear whether RLVR elicits novel capabilities or merely sharpens the distribution over existing knowledge. We study this by formalizing over-sharpening, a phenomenon where the policy collapses onto limited modes, suppressing valid alternatives. At a high level, we discover finite-batch updates intrinsically bias learning toward sampled modes, triggering a collapse that propagates globally via semantic coupling. To mitigate this, we propose inverse-success advantage calibration to prioritize difficult queries and distribution-level calibration to diversify sampling via a memory network. Empirical evaluations validate that our strategies can effectively improve generalization.
MixKVQ: Query-Aware Mixed-Precision KV Cache Quantization for Long-Context Reasoning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has significantly advanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), but this progress is accompanied by substantial memory and latency overhead from the extensive Key-Value (KV) cache. Although KV cache quantization is a promising compression technique, existing low-bit quantization methods often exhibit severe performance degradation on complex reasoning tasks. Fixed-precision quantization struggles to handle outlier channels in the key cache, while current mixed-precision strategies fail to accurately identify components requiring high-precision representation. We find that an effective low-bit KV cache quantization strategy must consider two factors: a key channel's intrinsic quantization difficulty and its relevance to the query. Based on this insight, we propose MixKVQ, a novel plug-and-play method that introduces a lightweight, query-aware algorithm to identify and preserve critical key channels that need higher precision, while applying per-token quantization for value cache. Experiments on complex reasoning datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing low-bit methods, achieving performance comparable to a full-precision baseline at a substantially reduced memory footprint.
ProCache: Constraint-Aware Feature Caching with Selective Computation for Diffusion Transformer Acceleration
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance in generative modeling, yet their high computational cost hinders real-time deployment. While feature caching offers a promising training-free acceleration solution by exploiting temporal redundancy, existing methods suffer from two key limitations: (1) uniform caching intervals fail to align with the non-uniform temporal dynamics of DiT, and (2) naive feature reuse with excessively large caching intervals can lead to severe error accumulation. In this work, we analyze the evolution of DiT features during denoising and reveal that both feature changes and error propagation are highly time- and depth-varying. Motivated by this, we propose ProCache, a training-free dynamic feature caching framework that addresses these issues via two core components: (i) a constraint-aware caching pattern search module that generates non-uniform activation schedules through offline constrained sampling, tailored to the model's temporal characteristics; and (ii) a selective computation module that selectively computes within deep blocks and high-importance tokens for cached segments to mitigate error accumulation with minimal overhead. Extensive experiments on PixArt-alpha and DiT demonstrate that ProCache achieves up to 1.96x and 2.90x acceleration with negligible quality degradation, significantly outperforming prior caching-based methods.
Towards Instance-wise Personalized Federated Learning via Semi-Implicit Bayesian Prompt Tuning
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a privacy-preserving machine learning paradigm that enables collaborative model training across multiple distributed clients without disclosing their raw data. Personalized federated learning (pFL) has gained increasing attention for its ability to address data heterogeneity. However, most existing pFL methods assume that each client's data follows a single distribution and learn one client-level personalized model for each client. This assumption often fails in practice, where a single client may possess data from multiple sources or domains, resulting in significant intra-client heterogeneity and suboptimal performance. To tackle this challenge, we propose pFedBayesPT, a fine-grained instance-wise pFL framework based on visual prompt tuning. Specifically, we formulate instance-wise prompt generation from a Bayesian perspective and model the prompt posterior as an implicit distribution to capture diverse visual semantics. We derive a variational training objective under the semi-implicit variational inference framework. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that pFedBayesPT consistently outperforms existing pFL methods under both feature and label heterogeneity settings.
GSDNet: Revisiting Incomplete Multimodal-Diffusion from Graph Spectrum Perspective for Conversation Emotion Recognition
Jun 14, 2025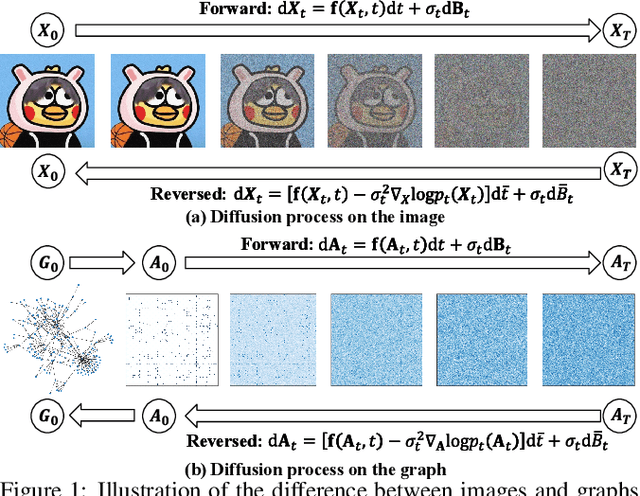
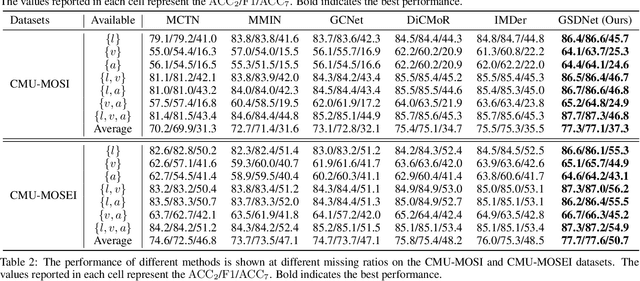
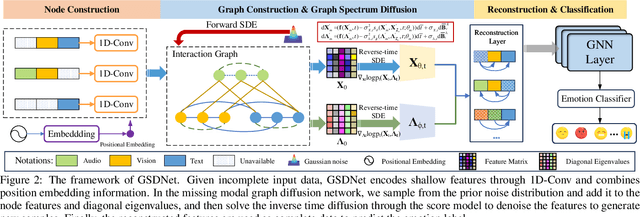
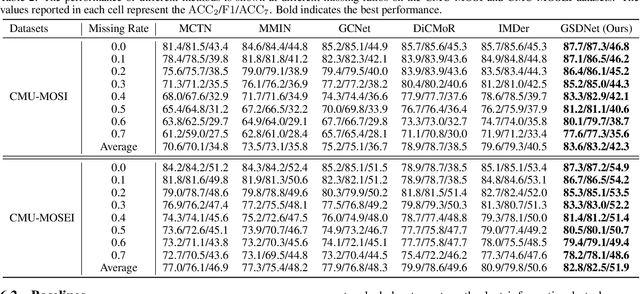
Abstract:Multimodal emotion recognition in conversations (MERC) aims to infer the speaker's emotional state by analyzing utterance information from multiple sources (i.e., video, audio, and text). Compared with unimodality, a more robust utterance representation can be obtained by fusing complementary semantic information from different modalities. However, the modality missing problem severely limits the performance of MERC in practical scenarios. Recent work has achieved impressive performance on modality completion using graph neural networks and diffusion models, respectively. This inspires us to combine these two dimensions through the graph diffusion model to obtain more powerful modal recovery capabilities. Unfortunately, existing graph diffusion models may destroy the connectivity and local structure of the graph by directly adding Gaussian noise to the adjacency matrix, resulting in the generated graph data being unable to retain the semantic and topological information of the original graph. To this end, we propose a novel Graph Spectral Diffusion Network (GSDNet), which maps Gaussian noise to the graph spectral space of missing modalities and recovers the missing data according to its original distribution. Compared with previous graph diffusion methods, GSDNet only affects the eigenvalues of the adjacency matrix instead of destroying the adjacency matrix directly, which can maintain the global topological information and important spectral features during the diffusion process. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that GSDNet achieves state-of-the-art emotion recognition performance in various modality loss scenarios.
Boosting Gradient Leakage Attacks: Data Reconstruction in Realistic FL Settings
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables collaborative model training among multiple clients without the need to expose raw data. Its ability to safeguard privacy, at the heart of FL, has recently been a hot-button debate topic. To elaborate, several studies have introduced a type of attacks known as gradient leakage attacks (GLAs), which exploit the gradients shared during training to reconstruct clients' raw data. On the flip side, some literature, however, contends no substantial privacy risk in practical FL environments due to the effectiveness of such GLAs being limited to overly relaxed conditions, such as small batch sizes and knowledge of clients' data distributions. This paper bridges this critical gap by empirically demonstrating that clients' data can still be effectively reconstructed, even within realistic FL environments. Upon revisiting GLAs, we recognize that their performance failures stem from their inability to handle the gradient matching problem. To alleviate the performance bottlenecks identified above, we develop FedLeak, which introduces two novel techniques, partial gradient matching and gradient regularization. Moreover, to evaluate the performance of FedLeak in real-world FL environments, we formulate a practical evaluation protocol grounded in a thorough review of extensive FL literature and industry practices. Under this protocol, FedLeak can still achieve high-fidelity data reconstruction, thereby underscoring the significant vulnerability in FL systems and the urgent need for more effective defense methods.
Responsible Diffusion Models via Constraining Text Embeddings within Safe Regions
May 21, 2025Abstract:The remarkable ability of diffusion models to generate high-fidelity images has led to their widespread adoption. However, concerns have also arisen regarding their potential to produce Not Safe for Work (NSFW) content and exhibit social biases, hindering their practical use in real-world applications. In response to this challenge, prior work has focused on employing security filters to identify and exclude toxic text, or alternatively, fine-tuning pre-trained diffusion models to erase sensitive concepts. Unfortunately, existing methods struggle to achieve satisfactory performance in the sense that they can have a significant impact on the normal model output while still failing to prevent the generation of harmful content in some cases. In this paper, we propose a novel self-discovery approach to identifying a semantic direction vector in the embedding space to restrict text embedding within a safe region. Our method circumvents the need for correcting individual words within the input text and steers the entire text prompt towards a safe region in the embedding space, thereby enhancing model robustness against all possibly unsafe prompts. In addition, we employ Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for semantic direction vector initialization to reduce the impact on the model performance for other semantics. Furthermore, our method can also be integrated with existing methods to improve their social responsibility. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method can effectively reduce NSFW content and mitigate social bias generated by diffusion models compared to several state-of-the-art baselines.
Comprehensive Evaluation and Analysis for NSFW Concept Erasure in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
May 21, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have gained widespread application across various domains, demonstrating remarkable creative potential. However, the strong generalization capabilities of diffusion models can inadvertently lead to the generation of not-safe-for-work (NSFW) content, posing significant risks to their safe deployment. While several concept erasure methods have been proposed to mitigate the issue associated with NSFW content, a comprehensive evaluation of their effectiveness across various scenarios remains absent. To bridge this gap, we introduce a full-pipeline toolkit specifically designed for concept erasure and conduct the first systematic study of NSFW concept erasure methods. By examining the interplay between the underlying mechanisms and empirical observations, we provide in-depth insights and practical guidance for the effective application of concept erasure methods in various real-world scenarios, with the aim of advancing the understanding of content safety in diffusion models and establishing a solid foundation for future research and development in this critical area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge