Wei Ai
The Paradigm Shift: A Comprehensive Survey on Large Vision Language Models for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:In recent years, the rapid evolution of large vision-language models (LVLMs) has driven a paradigm shift in multimodal fake news detection (MFND), transforming it from traditional feature-engineering approaches to unified, end-to-end multimodal reasoning frameworks. Early methods primarily relied on shallow fusion techniques to capture correlations between text and images, but they struggled with high-level semantic understanding and complex cross-modal interactions. The emergence of LVLMs has fundamentally changed this landscape by enabling joint modeling of vision and language with powerful representation learning, thereby enhancing the ability to detect misinformation that leverages both textual narratives and visual content. Despite these advances, the field lacks a systematic survey that traces this transition and consolidates recent developments. To address this gap, this paper provides a comprehensive review of MFND through the lens of LVLMs. We first present a historical perspective, mapping the evolution from conventional multimodal detection pipelines to foundation model-driven paradigms. Next, we establish a structured taxonomy covering model architectures, datasets, and performance benchmarks. Furthermore, we analyze the remaining technical challenges, including interpretability, temporal reasoning, and domain generalization. Finally, we outline future research directions to guide the next stage of this paradigm shift. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive survey to systematically document and analyze the transformative role of LVLMs in combating multimodal fake news. The summary of existing methods mentioned is in our Github: \href{https://github.com/Tan-YiLong/Overview-of-Fake-News-Detection}{https://github.com/Tan-YiLong/Overview-of-Fake-News-Detection}.
GSDNet: Revisiting Incomplete Multimodal-Diffusion from Graph Spectrum Perspective for Conversation Emotion Recognition
Jun 14, 2025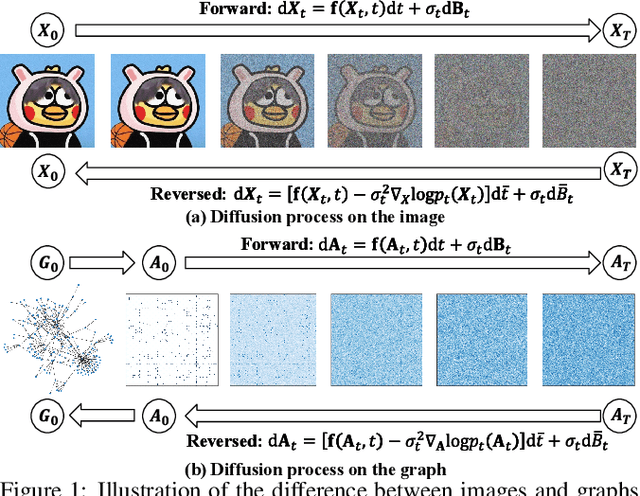
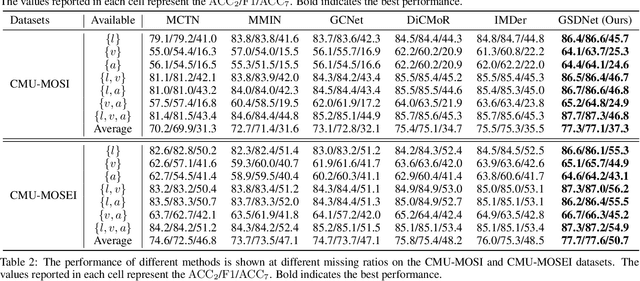
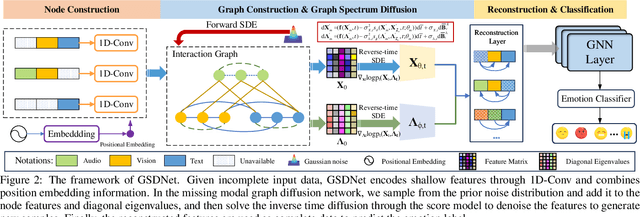
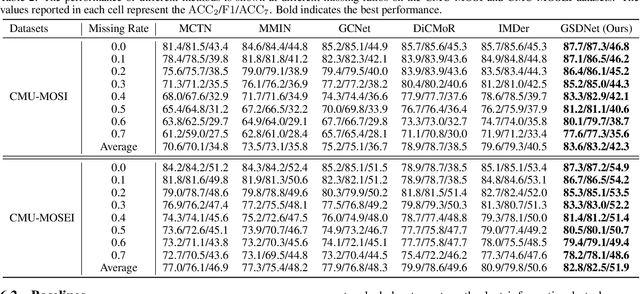
Abstract:Multimodal emotion recognition in conversations (MERC) aims to infer the speaker's emotional state by analyzing utterance information from multiple sources (i.e., video, audio, and text). Compared with unimodality, a more robust utterance representation can be obtained by fusing complementary semantic information from different modalities. However, the modality missing problem severely limits the performance of MERC in practical scenarios. Recent work has achieved impressive performance on modality completion using graph neural networks and diffusion models, respectively. This inspires us to combine these two dimensions through the graph diffusion model to obtain more powerful modal recovery capabilities. Unfortunately, existing graph diffusion models may destroy the connectivity and local structure of the graph by directly adding Gaussian noise to the adjacency matrix, resulting in the generated graph data being unable to retain the semantic and topological information of the original graph. To this end, we propose a novel Graph Spectral Diffusion Network (GSDNet), which maps Gaussian noise to the graph spectral space of missing modalities and recovers the missing data according to its original distribution. Compared with previous graph diffusion methods, GSDNet only affects the eigenvalues of the adjacency matrix instead of destroying the adjacency matrix directly, which can maintain the global topological information and important spectral features during the diffusion process. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that GSDNet achieves state-of-the-art emotion recognition performance in various modality loss scenarios.
VietMix: A Naturally Occurring Vietnamese-English Code-Mixed Corpus with Iterative Augmentation for Machine Translation
May 30, 2025Abstract:Machine translation systems fail when processing code-mixed inputs for low-resource languages. We address this challenge by curating VietMix, a parallel corpus of naturally occurring code-mixed Vietnamese text paired with expert English translations. Augmenting this resource, we developed a complementary synthetic data generation pipeline. This pipeline incorporates filtering mechanisms to ensure syntactic plausibility and pragmatic appropriateness in code-mixing patterns. Experimental validation shows our naturalistic and complementary synthetic data boost models' performance, measured by translation quality estimation scores, of up to 71.84 on COMETkiwi and 81.77 on XCOMET. Triangulating positive results with LLM-based assessments, augmented models are favored over seed fine-tuned counterparts in approximately 49% of judgments (54-56% excluding ties). VietMix and our augmentation methodology advance ecological validity in neural MT evaluations and establish a framework for addressing code-mixed translation challenges across other low-resource pairs.
Extracting Research Instruments from Educational Literature Using LLMs
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming information extraction from academic literature, offering new possibilities for knowledge management. This study presents an LLM-based system designed to extract detailed information about research instruments used in the education field, including their names, types, target respondents, measured constructs, and outcomes. Using multi-step prompting and a domain-specific data schema, it generates structured outputs optimized for educational research. Our evaluation shows that this system significantly outperforms other approaches, particularly in identifying instrument names and detailed information. This demonstrates the potential of LLM-powered information extraction in educational contexts, offering a systematic way to organize research instrument information. The ability to aggregate such information at scale enhances accessibility for researchers and education leaders, facilitating informed decision-making in educational research and policy.
DISCO Balances the Scales: Adaptive Domain- and Difficulty-Aware Reinforcement Learning on Imbalanced Data
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly aligned with human preferences through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Among RLHF methods, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) has gained attention for its simplicity and strong performance, notably eliminating the need for a learned value function. However, GRPO implicitly assumes a balanced domain distribution and uniform semantic alignment across groups - assumptions that rarely hold in real-world datasets. When applied to multi-domain, imbalanced data, GRPO disproportionately optimizes for dominant domains, neglecting underrepresented ones and resulting in poor generalization and fairness. We propose Domain-Informed Self-Consistency Policy Optimization (DISCO), a principled extension to GRPO that addresses inter-group imbalance with two key innovations. Domain-aware reward scaling counteracts frequency bias by reweighting optimization based on domain prevalence. Difficulty-aware reward scaling leverages prompt-level self-consistency to identify and prioritize uncertain prompts that offer greater learning value. Together, these strategies promote more equitable and effective policy learning across domains. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and skewed training distributions show that DISCO improves generalization, outperforms existing GRPO variants by 5% on Qwen3 models, and sets new state-of-the-art results on multi-domain alignment benchmarks.
Skill Discovery for Software Scripting Automation via Offline Simulations with LLMs
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Scripting interfaces enable users to automate tasks and customize software workflows, but creating scripts traditionally requires programming expertise and familiarity with specific APIs, posing barriers for many users. While Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate code from natural language queries, runtime code generation is severely limited due to unverified code, security risks, longer response times, and higher computational costs. To bridge the gap, we propose an offline simulation framework to curate a software-specific skillset, a collection of verified scripts, by exploiting LLMs and publicly available scripting guides. Our framework comprises two components: (1) task creation, using top-down functionality guidance and bottom-up API synergy exploration to generate helpful tasks; and (2) skill generation with trials, refining and validating scripts based on execution feedback. To efficiently navigate the extensive API landscape, we introduce a Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based link prediction model to capture API synergy, enabling the generation of skills involving underutilized APIs and expanding the skillset's diversity. Experiments with Adobe Illustrator demonstrate that our framework significantly improves automation success rates, reduces response time, and saves runtime token costs compared to traditional runtime code generation. This is the first attempt to use software scripting interfaces as a testbed for LLM-based systems, highlighting the advantages of leveraging execution feedback in a controlled environment and offering valuable insights into aligning AI capabilities with user needs in specialized software domains.
SE-GNN: Seed Expanded-Aware Graph Neural Network with Iterative Optimization for Semi-supervised Entity Alignment
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Entity alignment aims to use pre-aligned seed pairs to find other equivalent entities from different knowledge graphs (KGs) and is widely used in graph fusion-related fields. However, as the scale of KGs increases, manually annotating pre-aligned seed pairs becomes difficult. Existing research utilizes entity embeddings obtained by aggregating single structural information to identify potential seed pairs, thus reducing the reliance on pre-aligned seed pairs. However, due to the structural heterogeneity of KGs, the quality of potential seed pairs obtained using only a single structural information is not ideal. In addition, although existing research improves the quality of potential seed pairs through semi-supervised iteration, they underestimate the impact of embedding distortion produced by noisy seed pairs on the alignment effect. In order to solve the above problems, we propose a seed expanded-aware graph neural network with iterative optimization for semi-supervised entity alignment, named SE-GNN. First, we utilize the semantic attributes and structural features of entities, combined with a conditional filtering mechanism, to obtain high-quality initial potential seed pairs. Next, we designed a local and global awareness mechanism. It introduces initial potential seed pairs and combines local and global information to obtain a more comprehensive entity embedding representation, which alleviates the impact of KGs structural heterogeneity and lays the foundation for the optimization of initial potential seed pairs. Then, we designed the threshold nearest neighbor embedding correction strategy. It combines the similarity threshold and the bidirectional nearest neighbor method as a filtering mechanism to select iterative potential seed pairs and also uses an embedding correction strategy to eliminate the embedding distortion.
LRA-GNN: Latent Relation-Aware Graph Neural Network with Initial and Dynamic Residual for Facial Age Estimation
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Face information is mainly concentrated among facial key points, and frontier research has begun to use graph neural networks to segment faces into patches as nodes to model complex face representations. However, these methods construct node-to-node relations based on similarity thresholds, so there is a problem that some latent relations are missing. These latent relations are crucial for deep semantic representation of face aging. In this novel, we propose a new Latent Relation-Aware Graph Neural Network with Initial and Dynamic Residual (LRA-GNN) to achieve robust and comprehensive facial representation. Specifically, we first construct an initial graph utilizing facial key points as prior knowledge, and then a random walk strategy is employed to the initial graph for obtaining the global structure, both of which together guide the subsequent effective exploration and comprehensive representation. Then LRA-GNN leverages the multi-attention mechanism to capture the latent relations and generates a set of fully connected graphs containing rich facial information and complete structure based on the aforementioned guidance. To avoid over-smoothing issues for deep feature extraction on the fully connected graphs, the deep residual graph convolutional networks are carefully designed, which fuse adaptive initial residuals and dynamic developmental residuals to ensure the consistency and diversity of information. Finally, to improve the estimation accuracy and generalization ability, progressive reinforcement learning is proposed to optimize the ensemble classification regressor. Our proposed framework surpasses the state-of-the-art baselines on several age estimation benchmarks, demonstrating its strength and effectiveness.
MergeME: Model Merging Techniques for Homogeneous and Heterogeneous MoEs
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:The recent success of specialized Large Language Models (LLMs) in domains such as mathematical reasoning and coding has led to growing interest in methods for merging these expert LLMs into a unified Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model, with the goal of enhancing performance in each domain while retaining effectiveness on general tasks. However, the effective merging of expert models remains an open challenge, especially for models with highly divergent weight parameters or different architectures. State-of-the-art MoE merging methods only work with homogeneous model architectures and rely on simple unweighted averaging to merge expert layers, which does not address parameter interference and requires extensive fine-tuning of the merged MoE to restore performance. To address these limitations, this paper introduces new MoE merging techniques, including strategies to mitigate parameter interference, routing heuristics to reduce the need for MoE fine-tuning, and a novel method for merging experts with different architectures. Extensive experiments across multiple domains demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods, reducing fine-tuning costs, improving performance over state-of-the-art methods, and expanding the applicability of MoE merging.
Large Language Models Meet Graph Neural Networks: A Perspective of Graph Mining
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Graph mining is an important area in data mining and machine learning that involves extracting valuable information from graph-structured data. In recent years, significant progress has been made in this field through the development of graph neural networks (GNNs). However, GNNs are still deficient in generalizing to diverse graph data. Aiming to this issue, Large Language Models (LLMs) could provide new solutions for graph mining tasks with their superior semantic understanding. In this review, we systematically review the combination and application techniques of LLMs and GNNs and present a novel taxonomy for research in this interdisciplinary field, which involves three main categories: GNN-driving-LLM, LLM-driving-GNN, and GNN-LLM-co-driving. Within this framework, we reveal the capabilities of LLMs in enhancing graph feature extraction as well as improving the effectiveness of downstream tasks such as node classification, link prediction, and community detection. Although LLMs have demonstrated their great potential in handling graph-structured data, their high computational requirements and complexity remain challenges. Future research needs to continue to explore how to efficiently fuse LLMs and GNNs to achieve more powerful graph learning and reasoning capabilities and provide new impetus for the development of graph mining techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge