Meiyu Li
Extracting Research Instruments from Educational Literature Using LLMs
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming information extraction from academic literature, offering new possibilities for knowledge management. This study presents an LLM-based system designed to extract detailed information about research instruments used in the education field, including their names, types, target respondents, measured constructs, and outcomes. Using multi-step prompting and a domain-specific data schema, it generates structured outputs optimized for educational research. Our evaluation shows that this system significantly outperforms other approaches, particularly in identifying instrument names and detailed information. This demonstrates the potential of LLM-powered information extraction in educational contexts, offering a systematic way to organize research instrument information. The ability to aggregate such information at scale enhances accessibility for researchers and education leaders, facilitating informed decision-making in educational research and policy.
DC-Al GAN: Pseudoprogression and True Tumor Progression of Glioblastoma multiform Image Classification Based On DCGAN and Alexnet
Feb 26, 2019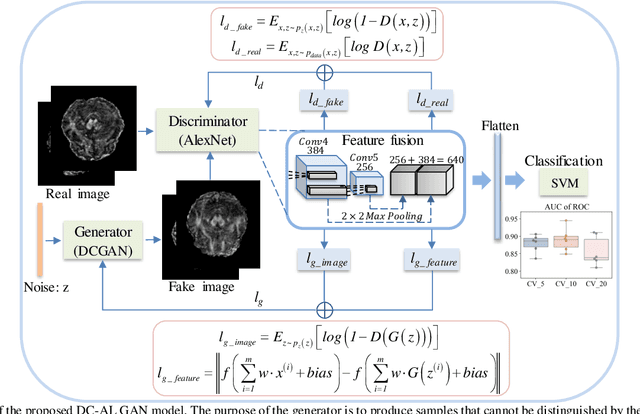
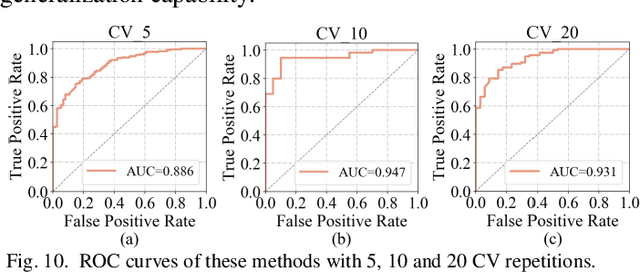
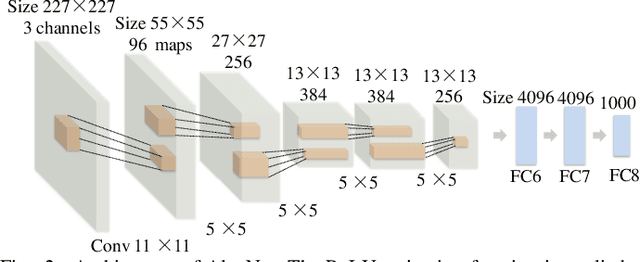
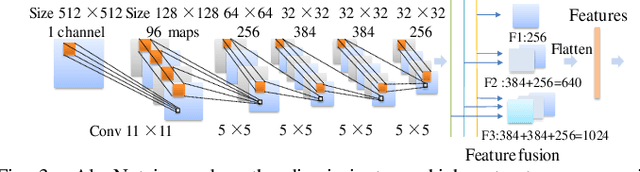
Abstract:Glioblastoma multiform (GBM) is a kind of head tumor with an extraordinarily complex treatment process. The survival period is typically 14-16 months, and the 2 year survival rate is approximately 26%-33%. The clinical treatment strategies for the pseudoprogression (PsP) and true tumor progression (TTP) of GBM are different, so accurately distinguishing these two conditions is particularly significant.As PsP and TTP of GBM are similar in shape and other characteristics, it is hard to distinguish these two forms with precision. In order to differentiate them accurately, this paper introduces a feature learning method based on a generative adversarial network: DC-Al GAN. GAN consists of two architectures: generator and discriminator. Alexnet is used as the discriminator in this work. Owing to the adversarial and competitive relationship between generator and discriminator, the latter extracts highly concise features during training. In DC-Al GAN, features are extracted from Alexnet in the final classification phase, and the highly nature of them contributes positively to the classification accuracy.The generator in DC-Al GAN is modified by the deep convolutional generative adversarial network (DCGAN) by adding three convolutional layers. This effectively generates higher resolution sample images. Feature fusion is used to combine high layer features with low layer features, allowing for the creation and use of more precise features for classification. The experimental results confirm that DC-Al GAN achieves high accuracy on GBM datasets for PsP and TTP image classification, which is superior to other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge