Xiyao Wang
University of Toronto
Lemon: A Unified and Scalable 3D Multimodal Model for Universal Spatial Understanding
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Scaling large multimodal models (LMMs) to 3D understanding poses unique challenges: point cloud data is sparse and irregular, existing models rely on fragmented architectures with modality-specific encoders, and training pipelines often suffer from instability and poor scalability. We introduce Lemon, a unified transformer architecture that addresses these challenges by jointly processing 3D point cloud patches and language tokens as a single sequence. Unlike prior work that relies on modality-specific encoders and cross-modal alignment modules, this design enables early spatial-linguistic fusion, eliminates redundant encoders, improves parameter efficiency, and supports more effective model scaling. To handle the complexity of 3D data, we develop a structured patchification and tokenization scheme that preserves spatial context, and a three-stage training curriculum that progressively builds capabilities from object-level recognition to scene-level spatial reasoning. Lemon establishes new state-of-the-art performance across comprehensive 3D understanding and reasoning tasks, from object recognition and captioning to spatial reasoning in 3D scenes, while demonstrating robust scaling properties as model size and training data increase. Our work provides a unified foundation for advancing 3D spatial intelligence in real-world applications.
Multi-Preference Lambda-weighted Listwise DPO for Dynamic Preference Alignment
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:While large-scale unsupervised language models (LMs) capture broad world knowledge and reasoning capabilities, steering their behavior toward desired objectives remains challenging due to the lack of explicit supervision. Existing alignment techniques, such as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), rely on training a reward model and performing reinforcement learning to align with human preferences. However, RLHF is often computationally intensive, unstable, and sensitive to hyperparameters. To address these limitations, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) was introduced as a lightweight and stable alternative, enabling direct alignment of language models with pairwise preference data via classification loss. However, DPO and its extensions generally assume a single static preference distribution, limiting flexibility in multi-objective or dynamic alignment settings. In this paper, we propose a novel framework: Multi-Preference Lambda-weighted Listwise DPO, which extends DPO to incorporate multiple human preference dimensions (e.g., helpfulness, harmlessness, informativeness) and enables dynamic interpolation through a controllable simplex-weighted formulation. Our method supports both listwise preference feedback and flexible alignment across varying user intents without re-training. Empirical and theoretical analysis demonstrates that our method is as effective as traditional DPO on static objectives while offering greater generality and adaptability for real-world deployment.
ViCrit: A Verifiable Reinforcement Learning Proxy Task for Visual Perception in VLMs
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown great effectiveness for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) using tasks that are challenging yet easily verifiable, such as math reasoning or code generation. However, extending this success to visual perception in vision-language models (VLMs) has been impeded by the scarcity of vision-centric tasks that are simultaneously challenging and unambiguously verifiable. To this end, we introduce ViCrit (Visual Caption Hallucination Critic), an RL proxy task that trains VLMs to localize a subtle, synthetic visual hallucination injected into paragraphs of human-written image captions. Starting from a 200-word captions, we inject a single, subtle visual description error-altering a few words on objects, attributes, counts, or spatial relations-and task the model to pinpoint the corrupted span given the image and the modified caption. This formulation preserves the full perceptual difficulty while providing a binary, exact-match reward that is easy to compute and unambiguous. Models trained with the ViCrit Task exhibit substantial gains across a variety of VL benchmarks. Crucially, the improvements transfer beyond natural-image training data to abstract image reasoning and visual math, showing promises of learning to perceive rather than barely memorizing seen objects. To facilitate evaluation, we further introduce ViCrit-Bench, a category-balanced diagnostic benchmark that systematically probes perception errors across diverse image domains and error types. Together, our results demonstrate that fine-grained hallucination criticism is an effective and generalizable objective for enhancing visual perception in VLMs.
What makes Reasoning Models Different? Follow the Reasoning Leader for Efficient Decoding
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve strong reasoning performance by emitting long chains of thought. Yet, these verbose traces slow down inference and often drift into unnecessary detail, known as the overthinking phenomenon. To better understand LRMs' behavior, we systematically analyze the token-level misalignment between reasoning and non-reasoning models. While it is expected that their primary difference lies in the stylistic "thinking cues", LRMs uniquely exhibit two pivotal, previously under-explored phenomena: a Global Misalignment Rebound, where their divergence from non-reasoning models persists or even grows as response length increases, and more critically, a Local Misalignment Diminish, where the misalignment concentrates at the "thinking cues" each sentence starts with but rapidly declines in the remaining of the sentence. Motivated by the Local Misalignment Diminish, we propose FoReaL-Decoding, a collaborative fast-slow thinking decoding method for cost-quality trade-off. In FoReaL-Decoding, a Leading model leads the first few tokens for each sentence, and then a weaker draft model completes the following tokens to the end of each sentence. FoReaL-Decoding adopts a stochastic gate to smoothly interpolate between the small and the large model. On four popular math-reasoning benchmarks (AIME24, GPQA-Diamond, MATH500, AMC23), FoReaL-Decoding reduces theoretical FLOPs by 30 to 50% and trims CoT length by up to 40%, while preserving 86 to 100% of model performance. These results establish FoReaL-Decoding as a simple, plug-and-play route to controllable cost-quality trade-offs in reasoning-centric tasks.
MORSE-500: A Programmatically Controllable Video Benchmark to Stress-Test Multimodal Reasoning
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Despite rapid advances in vision-language models (VLMs), current benchmarks for multimodal reasoning fall short in three key dimensions. First, they overwhelmingly rely on static images, failing to capture the temporal complexity of real-world environments. Second, they narrowly focus on mathematical problem-solving, neglecting the broader spectrum of reasoning skills -- including abstract, physical, planning, spatial, and temporal capabilities -- required for robust multimodal intelligence. Third, many benchmarks quickly saturate, offering limited headroom for diagnosing failure modes or measuring continued progress. We introduce MORSE-500 (Multimodal Reasoning Stress-test Environment), a video benchmark composed of 500 fully scripted clips with embedded questions spanning six complementary reasoning categories. Each instance is programmatically generated using deterministic Python scripts (via Manim, Matplotlib, MoviePy), generative video models, and curated real footage. This script-driven design allows fine-grained control over visual complexity, distractor density, and temporal dynamics -- enabling difficulty to be scaled systematically as models improve. Unlike static benchmarks that become obsolete once saturated, MORSE-500 is built to evolve: its controllable generation pipeline supports the creation of arbitrarily challenging new instances, making it ideally suited for stress-testing next-generation models. Initial experiments with state-of-the-art systems -- including various Gemini 2.5 Pro and OpenAI o3 which represent the strongest available at the time, alongside strong open-source models -- reveal substantial performance gaps across all categories, with particularly large deficits in abstract and planning tasks. We release the full dataset, generation scripts, and evaluation harness to support transparent, reproducible, and forward-looking multimodal reasoning research.
DISCO Balances the Scales: Adaptive Domain- and Difficulty-Aware Reinforcement Learning on Imbalanced Data
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly aligned with human preferences through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Among RLHF methods, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) has gained attention for its simplicity and strong performance, notably eliminating the need for a learned value function. However, GRPO implicitly assumes a balanced domain distribution and uniform semantic alignment across groups - assumptions that rarely hold in real-world datasets. When applied to multi-domain, imbalanced data, GRPO disproportionately optimizes for dominant domains, neglecting underrepresented ones and resulting in poor generalization and fairness. We propose Domain-Informed Self-Consistency Policy Optimization (DISCO), a principled extension to GRPO that addresses inter-group imbalance with two key innovations. Domain-aware reward scaling counteracts frequency bias by reweighting optimization based on domain prevalence. Difficulty-aware reward scaling leverages prompt-level self-consistency to identify and prioritize uncertain prompts that offer greater learning value. Together, these strategies promote more equitable and effective policy learning across domains. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and skewed training distributions show that DISCO improves generalization, outperforms existing GRPO variants by 5% on Qwen3 models, and sets new state-of-the-art results on multi-domain alignment benchmarks.
SoTA with Less: MCTS-Guided Sample Selection for Data-Efficient Visual Reasoning Self-Improvement
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we present an effective method to enhance visual reasoning with significantly fewer training samples, relying purely on self-improvement with no knowledge distillation. Our key insight is that the difficulty of training data during reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) is critical. Appropriately challenging samples can substantially boost reasoning capabilities even when the dataset is small. Despite being intuitive, the main challenge remains in accurately quantifying sample difficulty to enable effective data filtering. To this end, we propose a novel way of repurposing Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to achieve that. Starting from our curated 70k open-source training samples, we introduce an MCTS-based selection method that quantifies sample difficulty based on the number of iterations required by the VLMs to solve each problem. This explicit step-by-step reasoning in MCTS enforces the model to think longer and better identifies samples that are genuinely challenging. We filter and retain 11k samples to perform RFT on Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct, resulting in our final model, ThinkLite-VL. Evaluation results on eight benchmarks show that ThinkLite-VL improves the average performance of Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct by 7%, using only 11k training samples with no knowledge distillation. This significantly outperforms all existing 7B-level reasoning VLMs, and our fairly comparable baselines that use classic selection methods such as accuracy-based filtering. Notably, on MathVista, ThinkLite-VL-7B achieves the SoTA accuracy of 75.1, surpassing Qwen2.5-VL-72B, GPT-4o, and O1. Our code, data, and model are available at https://github.com/si0wang/ThinkLite-VL.
Towards Self-Improvement of LLMs via MCTS: Leveraging Stepwise Knowledge with Curriculum Preference Learning
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) has recently emerged as a powerful technique for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Techniques such as SFT or DPO have enabled LLMs to distill high-quality behaviors from MCTS, improving their reasoning performance. However, existing distillation methods underutilize the rich trajectory information generated by MCTS, limiting the potential for improvements in LLM reasoning. In this paper, we propose AlphaLLM-CPL, a novel pairwise training framework that enables LLMs to self-improve through MCTS behavior distillation. AlphaLLM-CPL efficiently leverages MCTS trajectories via two key innovations: (1) AlphaLLM-CPL constructs stepwise trajectory pairs from child nodes sharing the same parent in the search tree, providing step-level information for more effective MCTS behavior distillation. (2) AlphaLLM-CPL introduces curriculum preference learning, dynamically adjusting the training sequence of trajectory pairs in each offline training epoch to prioritize critical learning steps and mitigate overfitting. Experimental results on mathematical reasoning tasks demonstrate that AlphaLLM-CPL significantly outperforms previous MCTS behavior distillation methods, substantially boosting the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
LLaVA-Critic: Learning to Evaluate Multimodal Models
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:We introduce LLaVA-Critic, the first open-source large multimodal model (LMM) designed as a generalist evaluator to assess performance across a wide range of multimodal tasks. LLaVA-Critic is trained using a high-quality critic instruction-following dataset that incorporates diverse evaluation criteria and scenarios. Our experiments demonstrate the model's effectiveness in two key areas: (1) LMM-as-a-Judge, where LLaVA-Critic provides reliable evaluation scores, performing on par with or surpassing GPT models on multiple evaluation benchmarks; and (2) Preference Learning, where it generates reward signals for preference learning, enhancing model alignment capabilities. This work underscores the potential of open-source LMMs in self-critique and evaluation, setting the stage for future research into scalable, superhuman alignment feedback mechanisms for LMMs.
Multi-Stage Balanced Distillation: Addressing Long-Tail Challenges in Sequence-Level Knowledge Distillation
Jun 19, 2024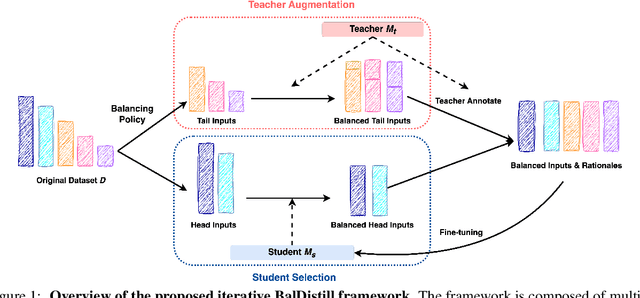
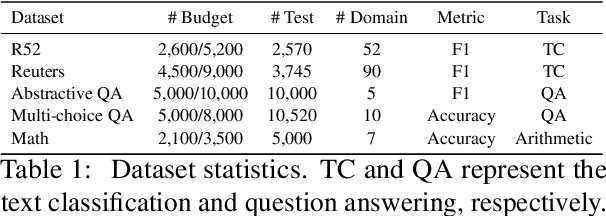
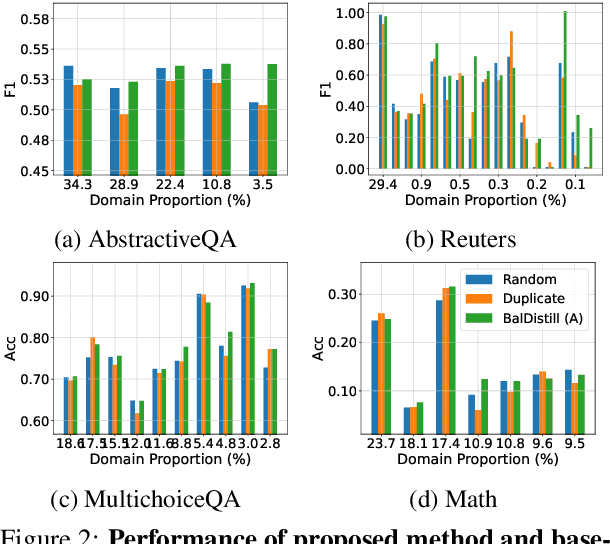
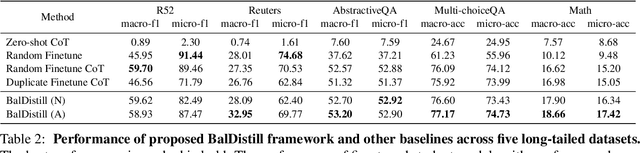
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced various natural language processing tasks, but deploying them remains computationally expensive. Knowledge distillation (KD) is a promising solution, enabling the transfer of capabilities from larger teacher LLMs to more compact student models. Particularly, sequence-level KD, which distills rationale-based reasoning processes instead of merely final outcomes, shows great potential in enhancing students' reasoning capabilities. However, current methods struggle with sequence level KD under long-tailed data distributions, adversely affecting generalization on sparsely represented domains. We introduce the Multi-Stage Balanced Distillation (BalDistill) framework, which iteratively balances training data within a fixed computational budget. By dynamically selecting representative head domain examples and synthesizing tail domain examples, BalDistill achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse long-tailed datasets, enhancing both the efficiency and efficacy of the distilled models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge