Yun Li
CoViPAL: Layer-wise Contextualized Visual Token Pruning for Large Vision-Language Models
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) process multimodal inputs consisting of text tokens and vision tokens extracted from images or videos. Due to the rich visual information, a single image can generate thousands of vision tokens, leading to high computational costs during the prefilling stage and significant memory overhead during decoding. Existing methods attempt to prune redundant vision tokens, revealing substantial redundancy in visual representations. However, these methods often struggle in shallow layers due to the lack of sufficient contextual information. We argue that many visual tokens are inherently redundant even in shallow layers and can be safely and effectively pruned with appropriate contextual signals. In this work, we propose CoViPAL, a layer-wise contextualized visual token pruning method that employs a Plug-and-Play Pruning Module (PPM) to predict and remove redundant vision tokens before they are processed by the LVLM. The PPM is lightweight, model-agnostic, and operates independently of the LVLM architecture, ensuring seamless integration with various models. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that CoViPAL outperforms training-free pruning methods under equal token budgets and surpasses training-based methods with comparable supervision. CoViPAL offers a scalable and efficient solution to improve inference efficiency in LVLMs without compromising accuracy.
Multimodal Medical Endoscopic Image Analysis via Progressive Disentangle-aware Contrastive Learning
Aug 23, 2025

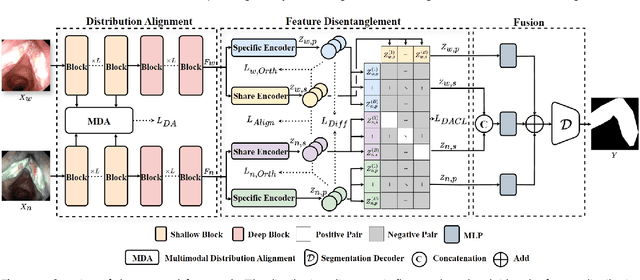

Abstract:Accurate segmentation of laryngo-pharyngeal tumors is crucial for precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning. However, traditional single-modality imaging methods often fall short of capturing the complex anatomical and pathological features of these tumors. In this study, we present an innovative multi-modality representation learning framework based on the `Align-Disentangle-Fusion' mechanism that seamlessly integrates 2D White Light Imaging (WLI) and Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) pairs to enhance segmentation performance. A cornerstone of our approach is multi-scale distribution alignment, which mitigates modality discrepancies by aligning features across multiple transformer layers. Furthermore, a progressive feature disentanglement strategy is developed with the designed preliminary disentanglement and disentangle-aware contrastive learning to effectively separate modality-specific and shared features, enabling robust multimodal contrastive learning and efficient semantic fusion. Comprehensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior accuracy across diverse real clinical scenarios.
Automated CAD Modeling Sequence Generation from Text Descriptions via Transformer-Based Large Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Designing complex computer-aided design (CAD) models is often time-consuming due to challenges such as computational inefficiency and the difficulty of generating precise models. We propose a novel language-guided framework for industrial design automation to address these issues, integrating large language models (LLMs) with computer-automated design (CAutoD).Through this framework, CAD models are automatically generated from parameters and appearance descriptions, supporting the automation of design tasks during the detailed CAD design phase. Our approach introduces three key innovations: (1) a semi-automated data annotation pipeline that leverages LLMs and vision-language large models (VLLMs) to generate high-quality parameters and appearance descriptions; (2) a Transformer-based CAD generator (TCADGen) that predicts modeling sequences via dual-channel feature aggregation; (3) an enhanced CAD modeling generation model, called CADLLM, that is designed to refine the generated sequences by incorporating the confidence scores from TCADGen. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms traditional methods in both accuracy and efficiency, providing a powerful tool for automating industrial workflows and generating complex CAD models from textual prompts. The code is available at https://jianxliao.github.io/cadllm-page/
CellTypeAgent: Trustworthy cell type annotation with Large Language Models
May 13, 2025Abstract:Cell type annotation is a critical yet laborious step in single-cell RNA sequencing analysis. We present a trustworthy large language model (LLM)-agent, CellTypeAgent, which integrates LLMs with verification from relevant databases. CellTypeAgent achieves higher accuracy than existing methods while mitigating hallucinations. We evaluated CellTypeAgent across nine real datasets involving 303 cell types from 36 tissues. This combined approach holds promise for more efficient and reliable cell type annotation.
STI-Bench: Are MLLMs Ready for Precise Spatial-Temporal World Understanding?
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The use of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) as an end-to-end solution for Embodied AI and Autonomous Driving has become a prevailing trend. While MLLMs have been extensively studied for visual semantic understanding tasks, their ability to perform precise and quantitative spatial-temporal understanding in real-world applications remains largely unexamined, leading to uncertain prospects. To evaluate models' Spatial-Temporal Intelligence, we introduce STI-Bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate MLLMs' spatial-temporal understanding through challenging tasks such as estimating and predicting the appearance, pose, displacement, and motion of objects. Our benchmark encompasses a wide range of robot and vehicle operations across desktop, indoor, and outdoor scenarios. The extensive experiments reveals that the state-of-the-art MLLMs still struggle in real-world spatial-temporal understanding, especially in tasks requiring precise distance estimation and motion analysis.
MDocAgent: A Multi-Modal Multi-Agent Framework for Document Understanding
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Document Question Answering (DocQA) is a very common task. Existing methods using Large Language Models (LLMs) or Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) often prioritize information from a single modal, failing to effectively integrate textual and visual cues. These approaches struggle with complex multi-modal reasoning, limiting their performance on real-world documents. We present MDocAgent (A Multi-Modal Multi-Agent Framework for Document Understanding), a novel RAG and multi-agent framework that leverages both text and image. Our system employs five specialized agents: a general agent, a critical agent, a text agent, an image agent and a summarizing agent. These agents engage in multi-modal context retrieval, combining their individual insights to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the document's content. This collaborative approach enables the system to synthesize information from both textual and visual components, leading to improved accuracy in question answering. Preliminary experiments on five benchmarks like MMLongBench, LongDocURL demonstrate the effectiveness of our MDocAgent, achieve an average improvement of 12.1% compared to current state-of-the-art method. This work contributes to the development of more robust and comprehensive DocQA systems capable of handling the complexities of real-world documents containing rich textual and visual information. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/MDocAgent.
Is LLMs Hallucination Usable? LLM-based Negative Reasoning for Fake News Detection
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:The questionable responses caused by knowledge hallucination may lead to LLMs' unstable ability in decision-making. However, it has never been investigated whether the LLMs' hallucination is possibly usable to generate negative reasoning for facilitating the detection of fake news. This study proposes a novel supervised self-reinforced reasoning rectification approach - SR$^3$ that yields both common reasonable reasoning and wrong understandings (negative reasoning) for news via LLMs reflection for semantic consistency learning. Upon that, we construct a negative reasoning-based news learning model called - \emph{NRFE}, which leverages positive or negative news-reasoning pairs for learning the semantic consistency between them. To avoid the impact of label-implicated reasoning, we deploy a student model - \emph{NRFE-D} that only takes news content as input to inspect the performance of our method by distilling the knowledge from \emph{NRFE}. The experimental results verified on three popular fake news datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method compared with three kinds of baselines including prompting on LLMs, fine-tuning on pre-trained SLMs, and other representative fake news detection methods.
Better Process Supervision with Bi-directional Rewarding Signals
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Process supervision, i.e., evaluating each step, is critical for complex large language model (LLM) reasoning and test-time searching with increased inference compute. Existing approaches, represented by process reward models (PRMs), primarily focus on rewarding signals up to the current step, exhibiting a one-directional nature and lacking a mechanism to model the distance to the final target. To address this problem, we draw inspiration from the A* algorithm, which states that an effective supervisory signal should simultaneously consider the incurred cost and the estimated cost for reaching the target. Building on this key insight, we introduce BiRM, a novel process supervision model that not only evaluates the correctness of previous steps but also models the probability of future success. We conduct extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning tasks and demonstrate that BiRM provides more precise evaluations of LLM reasoning steps, achieving an improvement of 3.1% on Gaokao2023 over PRM under the Best-of-N sampling method. Besides, in search-based strategies, BiRM provides more comprehensive guidance and outperforms ORM by 5.0% and PRM by 3.8% respectively on MATH-500.
Investigating the Adaptive Robustness with Knowledge Conflicts in LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Feb 21, 2025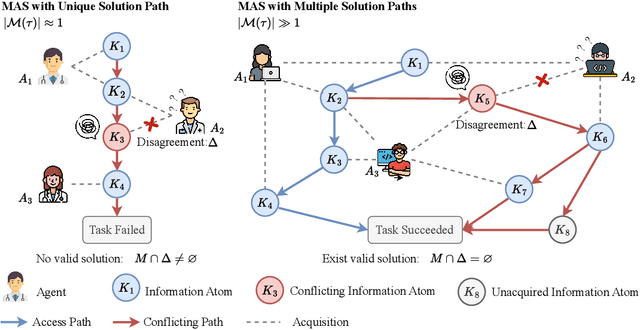

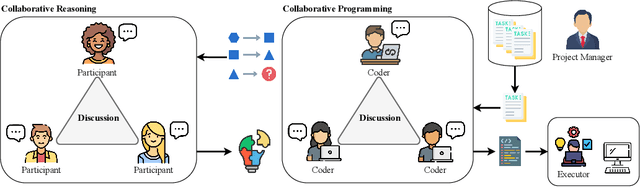
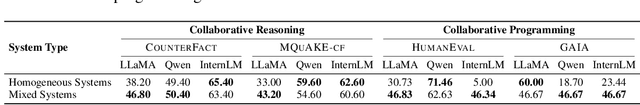
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have upgraded them from sophisticated text generators to autonomous agents capable of corporation and tool use in multi-agent systems (MASs). However, the robustness of these LLM-based MASs, especially under knowledge conflicts, remains unclear. In this paper, we design four comprehensive metrics to investigate the robustness of MASs when facing mild or task-critical knowledge conflicts. We first analyze mild knowledge conflicts introduced by heterogeneous agents and find that they do not harm system robustness but instead improve collaborative decision-making. Next, we investigate task-critical knowledge conflicts by synthesizing knowledge conflicts and embedding them into one of the agents. Our results show that these conflicts have surprisingly little to no impact on MAS robustness. Furthermore, we observe that MASs demonstrate certain self-repairing capabilities by reducing their reliance on knowledge conflicts and adopting alternative solution paths to maintain stability. Finally, we conduct ablation studies on the knowledge conflict number, agent number, and interaction rounds, finding that the self-repairing capability of MASs has intrinsic limits, and all findings hold consistently across various factors. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/wbw625/MultiAgentRobustness.
Sce2DriveX: A Generalized MLLM Framework for Scene-to-Drive Learning
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving, which directly maps raw sensor inputs to low-level vehicle controls, is an important part of Embodied AI. Despite successes in applying Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for high-level traffic scene semantic understanding, it remains challenging to effectively translate these conceptual semantics understandings into low-level motion control commands and achieve generalization and consensus in cross-scene driving. We introduce Sce2DriveX, a human-like driving chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning MLLM framework. Sce2DriveX utilizes multimodal joint learning from local scene videos and global BEV maps to deeply understand long-range spatiotemporal relationships and road topology, enhancing its comprehensive perception and reasoning capabilities in 3D dynamic/static scenes and achieving driving generalization across scenes. Building on this, it reconstructs the implicit cognitive chain inherent in human driving, covering scene understanding, meta-action reasoning, behavior interpretation analysis, motion planning and control, thereby further bridging the gap between autonomous driving and human thought processes. To elevate model performance, we have developed the first extensive Visual Question Answering (VQA) driving instruction dataset tailored for 3D spatial understanding and long-axis task reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Sce2DriveX achieves state-of-the-art performance from scene understanding to end-to-end driving, as well as robust generalization on the CARLA Bench2Drive benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge