Wynne Hsu
Unveiling the Cognitive Compass: Theory-of-Mind-Guided Multimodal Emotion Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Despite rapid progress in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), their capability for deep emotional understanding remains limited. We argue that genuine affective intelligence requires explicit modeling of Theory of Mind (ToM), the cognitive substrate from which emotions arise. To this end, we introduce HitEmotion, a ToM-grounded hierarchical benchmark that diagnoses capability breakpoints across increasing levels of cognitive depth. Second, we propose a ToM-guided reasoning chain that tracks mental states and calibrates cross-modal evidence to achieve faithful emotional reasoning. We further introduce TMPO, a reinforcement learning method that uses intermediate mental states as process-level supervision to guide and strengthen model reasoning. Extensive experiments show that HitEmotion exposes deep emotional reasoning deficits in state-of-the-art models, especially on cognitively demanding tasks. In evaluation, the ToM-guided reasoning chain and TMPO improve end-task accuracy and yield more faithful, more coherent rationales. In conclusion, our work provides the research community with a practical toolkit for evaluating and enhancing the cognition-based emotional understanding capabilities of MLLMs. Our dataset and code are available at: https://HitEmotion.github.io/.
Training LLMs with LogicReward for Faithful and Rigorous Reasoning
Dec 20, 2025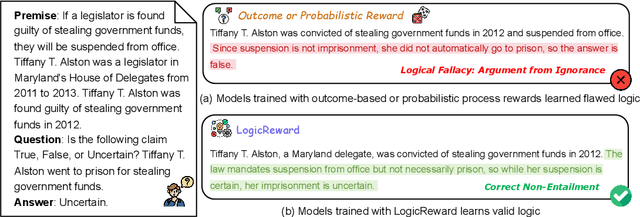
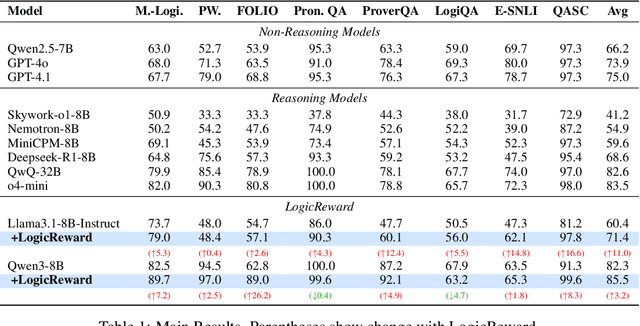
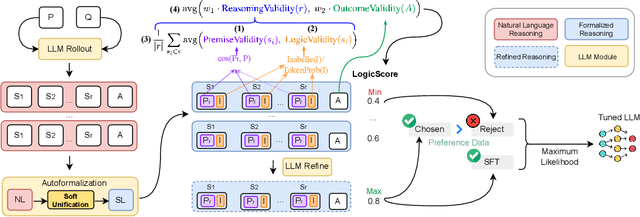
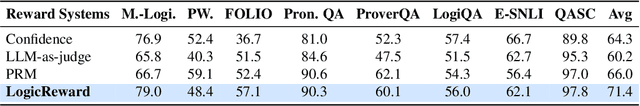
Abstract:Although LLMs exhibit strong reasoning capabilities, existing training methods largely depend on outcome-based feedback, which can produce correct answers with flawed reasoning. Prior work introduces supervision on intermediate steps but still lacks guarantees of logical soundness, which is crucial in high-stakes scenarios where logical consistency is paramount. To address this, we propose LogicReward, a novel reward system that guides model training by enforcing step-level logical correctness with a theorem prover. We further introduce Autoformalization with Soft Unification, which reduces natural language ambiguity and improves formalization quality, enabling more effective use of the theorem prover. An 8B model trained on data constructed with LogicReward surpasses GPT-4o and o4-mini by 11.6\% and 2\% on natural language inference and logical reasoning tasks with simple training procedures. Further analysis shows that LogicReward enhances reasoning faithfulness, improves generalizability to unseen tasks such as math and commonsense reasoning, and provides a reliable reward signal even without ground-truth labels. We will release all data and code at https://llm-symbol.github.io/LogicReward.
Multi-Part Object Representations via Graph Structures and Co-Part Discovery
Dec 20, 2025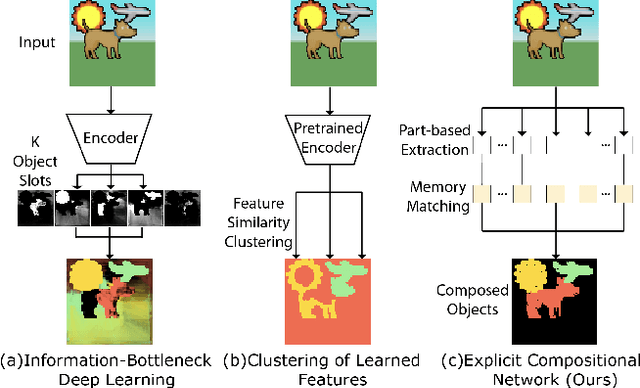
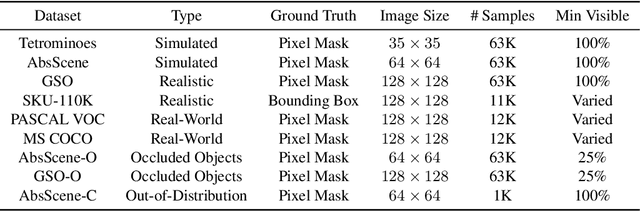
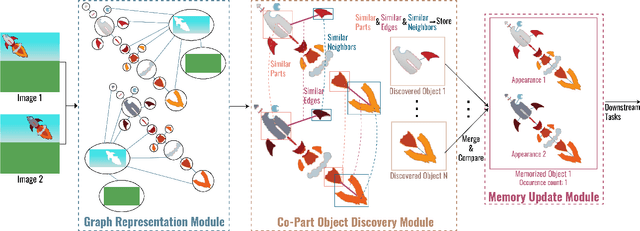
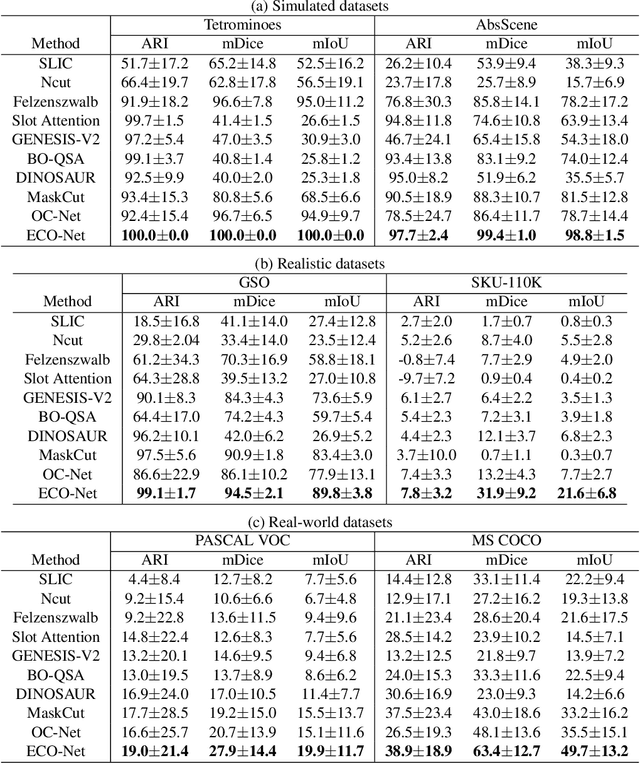
Abstract:Discovering object-centric representations from images can significantly enhance the robustness, sample efficiency and generalizability of vision models. Works on images with multi-part objects typically follow an implicit object representation approach, which fail to recognize these learned objects in occluded or out-of-distribution contexts. This is due to the assumption that object part-whole relations are implicitly encoded into the representations through indirect training objectives. We address this limitation by proposing a novel method that leverages on explicit graph representations for parts and present a co-part object discovery algorithm. We then introduce three benchmarks to evaluate the robustness of object-centric methods in recognizing multi-part objects within occluded and out-of-distribution settings. Experimental results on simulated, realistic, and real-world images show marked improvements in the quality of discovered objects compared to state-of-the-art methods, as well as the accurate recognition of multi-part objects in occluded and out-of-distribution contexts. We also show that the discovered object-centric representations can more accurately predict key object properties in a downstream task, highlighting the potential of our method to advance the field of object-centric representations.
Multi-Modal Continual Learning via Cross-Modality Adapters and Representation Alignment with Knowledge Preservation
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Continual learning is essential for adapting models to new tasks while retaining previously acquired knowledge. While existing approaches predominantly focus on uni-modal data, multi-modal learning offers substantial benefits by utilizing diverse sensory inputs, akin to human perception. However, multi-modal continual learning presents additional challenges, as the model must effectively integrate new information from various modalities while preventing catastrophic forgetting. In this work, we propose a pre-trained model-based framework for multi-modal continual learning. Our framework includes a novel cross-modality adapter with a mixture-of-experts structure to facilitate effective integration of multi-modal information across tasks. We also introduce a representation alignment loss that fosters learning of robust multi-modal representations, and regularize relationships between learned representations to preserve knowledge from previous tasks. Experiments on several multi-modal datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baselines in both class-incremental and domain-incremental learning, achieving higher accuracy and reduced forgetting.
* Accepted to ECAI 2025
TRUST-VL: An Explainable News Assistant for General Multimodal Misinformation Detection
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal misinformation, encompassing textual, visual, and cross-modal distortions, poses an increasing societal threat that is amplified by generative AI. Existing methods typically focus on a single type of distortion and struggle to generalize to unseen scenarios. In this work, we observe that different distortion types share common reasoning capabilities while also requiring task-specific skills. We hypothesize that joint training across distortion types facilitates knowledge sharing and enhances the model's ability to generalize. To this end, we introduce TRUST-VL, a unified and explainable vision-language model for general multimodal misinformation detection. TRUST-VL incorporates a novel Question-Aware Visual Amplifier module, designed to extract task-specific visual features. To support training, we also construct TRUST-Instruct, a large-scale instruction dataset containing 198K samples featuring structured reasoning chains aligned with human fact-checking workflows. Extensive experiments on both in-domain and zero-shot benchmarks demonstrate that TRUST-VL achieves state-of-the-art performance, while also offering strong generalization and interpretability.
On the Adaptive Psychological Persuasion of Large Language Models
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Previous work has showcased the intriguing capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in instruction-following and rhetorical fluency. However, systematic exploration of their dual capabilities to autonomously persuade and resist persuasion, particularly in contexts involving psychological rhetoric, remains unexplored. In this paper, we first evaluate four commonly adopted LLMs by tasking them to alternately act as persuaders and listeners in adversarial dialogues. Empirical results show that persuader LLMs predominantly employ repetitive strategies, leading to low success rates. Then we introduce eleven comprehensive psychological persuasion strategies, finding that explicitly instructing LLMs to adopt specific strategies such as Fluency Effect and Repetition Effect significantly improves persuasion success rates. However, no ``one-size-fits-all'' strategy proves universally effective, with performance heavily dependent on contextual counterfactuals. Motivated by these observations, we propose an adaptive framework based on direct preference optimization that trains LLMs to autonomously select optimal strategies by leveraging persuasion results from strategy-specific responses as preference pairs. Experiments on three open-source LLMs confirm that the proposed adaptive psychological persuasion method effectively enables persuader LLMs to select optimal strategies, significantly enhancing their success rates while maintaining general capabilities. Our code is available at https://github.com/KalinaEine/PsychologicalPersuasion.
Probing then Editing Response Personality of Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities to generate responses that exhibit consistent personality traits. Despite the major attempts to analyze personality expression through output-based evaluations, little is known about how such traits are internally encoded within LLM parameters. In this paper, we introduce a layer-wise probing framework to systematically investigate the layer-wise capability of LLMs in encoding personality for responding. We conduct probing experiments on 11 open-source LLMs over the PersonalityEdit benchmark and find that LLMs predominantly encode personality for responding in their middle and upper layers, with instruction-tuned models demonstrating a slightly clearer separation of personality traits. Furthermore, by interpreting the trained probing hyperplane as a layer-wise boundary for each personality category, we propose a layer-wise perturbation method to edit the personality expressed by LLMs during inference. Our results show that even when the prompt explicitly specifies a particular personality, our method can still successfully alter the response personality of LLMs. Interestingly, the difficulty of converting between certain personality traits varies substantially, which aligns with the representational distances in our probing experiments. Finally, we conduct a comprehensive MMLU benchmark evaluation and time overhead analysis, demonstrating that our proposed personality editing method incurs only minimal degradation in general capabilities while maintaining low training costs and acceptable inference latency. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/universe-sky/probing-then-editing-personality.
Watch Out Your Album! On the Inadvertent Privacy Memorization in Multi-Modal Large Language Models
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Multi-Modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have exhibited remarkable performance on various vision-language tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). Despite accumulating evidence of privacy concerns associated with task-relevant content, it remains unclear whether MLLMs inadvertently memorize private content that is entirely irrelevant to the training tasks. In this paper, we investigate how randomly generated task-irrelevant private content can become spuriously correlated with downstream objectives due to partial mini-batch training dynamics, thus causing inadvertent memorization. Concretely, we randomly generate task-irrelevant watermarks into VQA fine-tuning images at varying probabilities and propose a novel probing framework to determine whether MLLMs have inadvertently encoded such content. Our experiments reveal that MLLMs exhibit notably different training behaviors in partial mini-batch settings with task-irrelevant watermarks embedded. Furthermore, through layer-wise probing, we demonstrate that MLLMs trigger distinct representational patterns when encountering previously seen task-irrelevant knowledge, even if this knowledge does not influence their output during prompting. Our code is available at https://github.com/illusionhi/ProbingPrivacy.
Investigating the Adaptive Robustness with Knowledge Conflicts in LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Feb 21, 2025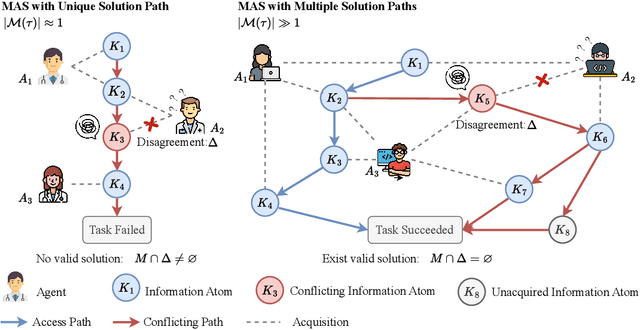

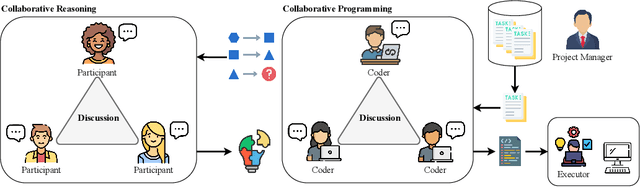
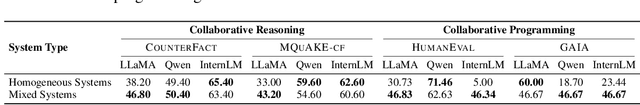
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have upgraded them from sophisticated text generators to autonomous agents capable of corporation and tool use in multi-agent systems (MASs). However, the robustness of these LLM-based MASs, especially under knowledge conflicts, remains unclear. In this paper, we design four comprehensive metrics to investigate the robustness of MASs when facing mild or task-critical knowledge conflicts. We first analyze mild knowledge conflicts introduced by heterogeneous agents and find that they do not harm system robustness but instead improve collaborative decision-making. Next, we investigate task-critical knowledge conflicts by synthesizing knowledge conflicts and embedding them into one of the agents. Our results show that these conflicts have surprisingly little to no impact on MAS robustness. Furthermore, we observe that MASs demonstrate certain self-repairing capabilities by reducing their reliance on knowledge conflicts and adopting alternative solution paths to maintain stability. Finally, we conduct ablation studies on the knowledge conflict number, agent number, and interaction rounds, finding that the self-repairing capability of MASs has intrinsic limits, and all findings hold consistently across various factors. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/wbw625/MultiAgentRobustness.
From Personas to Talks: Revisiting the Impact of Personas on LLM-Synthesized Emotional Support Conversations
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized the generation of emotional support conversations (ESC), offering scalable solutions with reduced costs and enhanced data privacy. This paper explores the role of personas in the creation of ESC by LLMs. Our research utilizes established psychological frameworks to measure and infuse persona traits into LLMs, which then generate dialogues in the emotional support scenario. We conduct extensive evaluations to understand the stability of persona traits in dialogues, examining shifts in traits post-generation and their impact on dialogue quality and strategy distribution. Experimental results reveal several notable findings: 1) LLMs can infer core persona traits, 2) subtle shifts in emotionality and extraversion occur, influencing the dialogue dynamics, and 3) the application of persona traits modifies the distribution of emotional support strategies, enhancing the relevance and empathetic quality of the responses. These findings highlight the potential of persona-driven LLMs in crafting more personalized, empathetic, and effective emotional support dialogues, which has significant implications for the future design of AI-driven emotional support systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge