Zhuokai Zhao
Token-Level LLM Collaboration via FusionRoute
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit strengths across diverse domains. However, achieving strong performance across these domains with a single general-purpose model typically requires scaling to sizes that are prohibitively expensive to train and deploy. On the other hand, while smaller domain-specialized models are much more efficient, they struggle to generalize beyond their training distributions. To address this dilemma, we propose FusionRoute, a robust and effective token-level multi-LLM collaboration framework in which a lightweight router simultaneously (i) selects the most suitable expert at each decoding step and (ii) contributes a complementary logit that refines or corrects the selected expert's next-token distribution via logit addition. Unlike existing token-level collaboration methods that rely solely on fixed expert outputs, we provide a theoretical analysis showing that pure expert-only routing is fundamentally limited: unless strong global coverage assumptions hold, it cannot in general realize the optimal decoding policy. By augmenting expert selection with a trainable complementary generator, FusionRoute expands the effective policy class and enables recovery of optimal value functions under mild conditions. Empirically, across both Llama-3 and Gemma-2 families and diverse benchmarks spanning mathematical reasoning, code generation, and instruction following, FusionRoute outperforms both sequence- and token-level collaboration, model merging, and direct fine-tuning, while remaining competitive with domain experts on their respective tasks.
Scaling Agent Learning via Experience Synthesis
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:While reinforcement learning (RL) can empower autonomous agents by enabling self-improvement through interaction, its practical adoption remains challenging due to costly rollouts, limited task diversity, unreliable reward signals, and infrastructure complexity, all of which obstruct the collection of scalable experience data. To address these challenges, we introduce DreamGym, the first unified framework designed to synthesize diverse experiences with scalability in mind to enable effective online RL training for autonomous agents. Rather than relying on expensive real-environment rollouts, DreamGym distills environment dynamics into a reasoning-based experience model that derives consistent state transitions and feedback signals through step-by-step reasoning, enabling scalable agent rollout collection for RL. To improve the stability and quality of transitions, DreamGym leverages an experience replay buffer initialized with offline real-world data and continuously enriched with fresh interactions to actively support agent training. To improve knowledge acquisition, DreamGym adaptively generates new tasks that challenge the current agent policy, enabling more effective online curriculum learning. Experiments across diverse environments and agent backbones demonstrate that DreamGym substantially improves RL training, both in fully synthetic settings and in sim-to-real transfer scenarios. On non-RL-ready tasks like WebArena, DreamGym outperforms all baselines by over 30%. And in RL-ready but costly settings, it matches GRPO and PPO performance using only synthetic interactions. When transferring a policy trained purely on synthetic experiences to real-environment RL, DreamGym yields significant additional performance gains while requiring far fewer real-world interactions, providing a scalable warm-start strategy for general-purpose RL.
Thought Communication in Multiagent Collaboration
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Natural language has long enabled human cooperation, but its lossy, ambiguous, and indirect nature limits the potential of collective intelligence. While machines are not subject to these constraints, most LLM-based multi-agent systems still rely solely on natural language, exchanging tokens or their embeddings. To go beyond language, we introduce a new paradigm, thought communication, which enables agents to interact directly mind-to-mind, akin to telepathy. To uncover these latent thoughts in a principled way, we formalize the process as a general latent variable model, where agent states are generated by an unknown function of underlying thoughts. We prove that, in a nonparametric setting without auxiliary information, both shared and private latent thoughts between any pair of agents can be identified. Moreover, the global structure of thought sharing, including which agents share which thoughts and how these relationships are structured, can also be recovered with theoretical guarantees. Guided by the established theory, we develop a framework that extracts latent thoughts from all agents prior to communication and assigns each agent the relevant thoughts, along with their sharing patterns. This paradigm naturally extends beyond LLMs to all modalities, as most observational data arise from hidden generative processes. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks validate the theory and demonstrate the collaborative advantages of thought communication. We hope this work illuminates the potential of leveraging the hidden world, as many challenges remain unsolvable through surface-level observation alone, regardless of compute or data scale.
Exploring System 1 and 2 communication for latent reasoning in LLMs
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Should LLM reasoning live in a separate module, or within a single model's forward pass and representational space? We study dual-architecture latent reasoning, where a fluent Base exchanges latent messages with a Coprocessor, and test two hypotheses aimed at improving latent communication over Liu et al. (2024): (H1) increase channel capacity; (H2) learn communication via joint finetuning. Under matched latent-token budgets on GPT-2 and Qwen-3, H2 is consistently strongest while H1 yields modest gains. A unified soft-embedding baseline, a single model with the same forward pass and shared representations, using the same latent-token budget, nearly matches H2 and surpasses H1, suggesting current dual designs mostly add compute rather than qualitatively improving reasoning. Across GSM8K, ProsQA, and a Countdown stress test with increasing branching factor, scaling the latent-token budget beyond small values fails to improve robustness. Latent analyses show overlapping subspaces with limited specialization, consistent with weak reasoning gains. We conclude dual-model latent reasoning remains promising in principle, but likely requires objectives and communication mechanisms that explicitly shape latent spaces for algorithmic planning.
Boosting LLM Reasoning via Spontaneous Self-Correction
Jun 07, 2025



Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success on a broad range of tasks, math reasoning remains a challenging one. One of the approaches for improving math reasoning is self-correction, which designs self-improving loops to let the model correct its own mistakes. However, existing self-correction approaches treat corrections as standalone post-generation refinements, relying on extra prompt and system designs to elicit self-corrections, instead of performing real-time, spontaneous self-corrections in a single pass. To address this, we propose SPOC, a spontaneous self-correction approach that enables LLMs to generate interleaved solutions and verifications in a single inference pass, with generation dynamically terminated based on verification outcomes, thereby effectively scaling inference time compute. SPOC considers a multi-agent perspective by assigning dual roles -- solution proposer and verifier -- to the same model. We adopt a simple yet effective approach to generate synthetic data for fine-tuning, enabling the model to develop capabilities for self-verification and multi-agent collaboration. We further improve its solution proposal and verification accuracy through online reinforcement learning. Experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks show that SPOC significantly improves performance. Notably, SPOC boosts the accuracy of Llama-3.1-8B and 70B Instruct models, achieving gains of 8.8% and 11.6% on MATH500, 10.0% and 20.0% on AMC23, and 3.3% and 6.7% on AIME24, respectively.
DISCO Balances the Scales: Adaptive Domain- and Difficulty-Aware Reinforcement Learning on Imbalanced Data
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly aligned with human preferences through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Among RLHF methods, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) has gained attention for its simplicity and strong performance, notably eliminating the need for a learned value function. However, GRPO implicitly assumes a balanced domain distribution and uniform semantic alignment across groups - assumptions that rarely hold in real-world datasets. When applied to multi-domain, imbalanced data, GRPO disproportionately optimizes for dominant domains, neglecting underrepresented ones and resulting in poor generalization and fairness. We propose Domain-Informed Self-Consistency Policy Optimization (DISCO), a principled extension to GRPO that addresses inter-group imbalance with two key innovations. Domain-aware reward scaling counteracts frequency bias by reweighting optimization based on domain prevalence. Difficulty-aware reward scaling leverages prompt-level self-consistency to identify and prioritize uncertain prompts that offer greater learning value. Together, these strategies promote more equitable and effective policy learning across domains. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and skewed training distributions show that DISCO improves generalization, outperforms existing GRPO variants by 5% on Qwen3 models, and sets new state-of-the-art results on multi-domain alignment benchmarks.
S'MoRE: Structural Mixture of Residual Experts for LLM Fine-tuning
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning pre-trained large language models (LLMs) presents a dual challenge of balancing parameter efficiency and model capacity. Existing methods like low-rank adaptations (LoRA) are efficient but lack flexibility, while Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures enhance model capacity at the cost of more & under-utilized parameters. To address these limitations, we propose Structural Mixture of Residual Experts (S'MoRE), a novel framework that seamlessly integrates the efficiency of LoRA with the flexibility of MoE. Specifically, S'MoRE employs hierarchical low-rank decomposition of expert weights, yielding residuals of varying orders interconnected in a multi-layer structure. By routing input tokens through sub-trees of residuals, S'MoRE emulates the capacity of many experts by instantiating and assembling just a few low-rank matrices. We craft the inter-layer propagation of S'MoRE's residuals as a special type of Graph Neural Network (GNN), and prove that under similar parameter budget, S'MoRE improves "structural flexibility" of traditional MoE (or Mixture-of-LoRA) by exponential order. Comprehensive theoretical analysis and empirical results demonstrate that S'MoRE achieves superior fine-tuning performance, offering a transformative approach for efficient LLM adaptation.
Transfer between Modalities with MetaQueries
Apr 08, 2025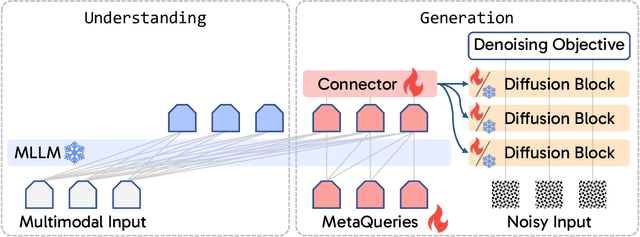
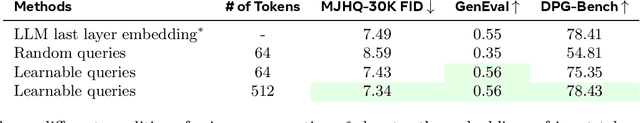
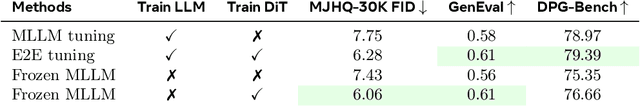
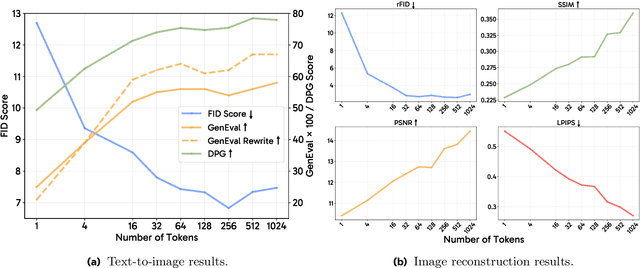
Abstract:Unified multimodal models aim to integrate understanding (text output) and generation (pixel output), but aligning these different modalities within a single architecture often demands complex training recipes and careful data balancing. We introduce MetaQueries, a set of learnable queries that act as an efficient interface between autoregressive multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) and diffusion models. MetaQueries connects the MLLM's latents to the diffusion decoder, enabling knowledge-augmented image generation by leveraging the MLLM's deep understanding and reasoning capabilities. Our method simplifies training, requiring only paired image-caption data and standard diffusion objectives. Notably, this transfer is effective even when the MLLM backbone remains frozen, thereby preserving its state-of-the-art multimodal understanding capabilities while achieving strong generative performance. Additionally, our method is flexible and can be easily instruction-tuned for advanced applications such as image editing and subject-driven generation.
CAFe: Unifying Representation and Generation with Contrastive-Autoregressive Finetuning
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large vision-language models (LVLMs) has driven significant progress in multimodal tasks, enabling models to interpret, reason, and generate outputs across both visual and textual domains. While excelling in generative tasks, existing LVLMs often face limitations in tasks requiring high-fidelity representation learning, such as generating image or text embeddings for retrieval. Recent work has proposed finetuning LVLMs for representational learning, but the fine-tuned model often loses its generative capabilities due to the representational learning training paradigm. To address this trade-off, we introduce CAFe, a contrastive-autoregressive fine-tuning framework that enhances LVLMs for both representation and generative tasks. By integrating a contrastive objective with autoregressive language modeling, our approach unifies these traditionally separate tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results in both multimodal retrieval and multimodal generative benchmarks, including object hallucination (OH) mitigation. CAFe establishes a novel framework that synergizes embedding and generative functionalities in a single model, setting a foundation for future multimodal models that excel in both retrieval precision and coherent output generation.
HumanMM: Global Human Motion Recovery from Multi-shot Videos
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel framework designed to reconstruct long-sequence 3D human motion in the world coordinates from in-the-wild videos with multiple shot transitions. Such long-sequence in-the-wild motions are highly valuable to applications such as motion generation and motion understanding, but are of great challenge to be recovered due to abrupt shot transitions, partial occlusions, and dynamic backgrounds presented in such videos. Existing methods primarily focus on single-shot videos, where continuity is maintained within a single camera view, or simplify multi-shot alignment in camera space only. In this work, we tackle the challenges by integrating an enhanced camera pose estimation with Human Motion Recovery (HMR) by incorporating a shot transition detector and a robust alignment module for accurate pose and orientation continuity across shots. By leveraging a custom motion integrator, we effectively mitigate the problem of foot sliding and ensure temporal consistency in human pose. Extensive evaluations on our created multi-shot dataset from public 3D human datasets demonstrate the robustness of our method in reconstructing realistic human motion in world coordinates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge