Giannis Karamanolakis
MergeME: Model Merging Techniques for Homogeneous and Heterogeneous MoEs
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:The recent success of specialized Large Language Models (LLMs) in domains such as mathematical reasoning and coding has led to growing interest in methods for merging these expert LLMs into a unified Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model, with the goal of enhancing performance in each domain while retaining effectiveness on general tasks. However, the effective merging of expert models remains an open challenge, especially for models with highly divergent weight parameters or different architectures. State-of-the-art MoE merging methods only work with homogeneous model architectures and rely on simple unweighted averaging to merge expert layers, which does not address parameter interference and requires extensive fine-tuning of the merged MoE to restore performance. To address these limitations, this paper introduces new MoE merging techniques, including strategies to mitigate parameter interference, routing heuristics to reduce the need for MoE fine-tuning, and a novel method for merging experts with different architectures. Extensive experiments across multiple domains demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods, reducing fine-tuning costs, improving performance over state-of-the-art methods, and expanding the applicability of MoE merging.
Interactive Machine Teaching by Labeling Rules and Instances
Sep 08, 2024Abstract:Weakly supervised learning aims to reduce the cost of labeling data by using expert-designed labeling rules. However, existing methods require experts to design effective rules in a single shot, which is difficult in the absence of proper guidance and tooling. Therefore, it is still an open question whether experts should spend their limited time writing rules or instead providing instance labels via active learning. In this paper, we investigate how to exploit an expert's limited time to create effective supervision. First, to develop practical guidelines for rule creation, we conduct an exploratory analysis of diverse collections of existing expert-designed rules and find that rule precision is more important than coverage across datasets. Second, we compare rule creation to individual instance labeling via active learning and demonstrate the importance of both across 6 datasets. Third, we propose an interactive learning framework, INTERVAL, that achieves efficiency by automatically extracting candidate rules based on rich patterns (e.g., by prompting a language model), and effectiveness by soliciting expert feedback on both candidate rules and individual instances. Across 6 datasets, INTERVAL outperforms state-of-the-art weakly supervised approaches by 7% in F1. Furthermore, it requires as few as 10 queries for expert feedback to reach F1 values that existing active learning methods cannot match even with 100 queries.
Flood Event Extraction from News Media to Support Satellite-Based Flood Insurance
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Floods cause large losses to property, life, and livelihoods across the world every year, hindering sustainable development. Safety nets to help absorb financial shocks in disasters, such as insurance, are often unavailable in regions of the world most vulnerable to floods, like Bangladesh. Index-based insurance has emerged as an affordable solution, which considers weather data or information from satellites to create a "flood index" that should correlate with the damage insured. However, existing flood event databases are often incomplete, and satellite sensors are not reliable under extreme weather conditions (e.g., because of clouds), which limits the spatial and temporal resolution of current approaches for index-based insurance. In this work, we explore a novel approach for supporting satellite-based flood index insurance by extracting high-resolution spatio-temporal information from news media. First, we publish a dataset consisting of 40,000 news articles covering flood events in Bangladesh by 10 prominent news sources, and inundated area estimates for each division in Bangladesh collected from a satellite radar sensor. Second, we show that keyword-based models are not adequate for this novel application, while context-based classifiers cover complex and implicit flood related patterns. Third, we show that time series extracted from news media have substantial correlation Spearman's rho$=0.70 with satellite estimates of inundated area. Our work demonstrates that news media is a promising source for improving the temporal resolution and expanding the spatial coverage of the available flood damage data.
Benchmarking Generalization via In-Context Instructions on 1,600+ Language Tasks
Apr 16, 2022
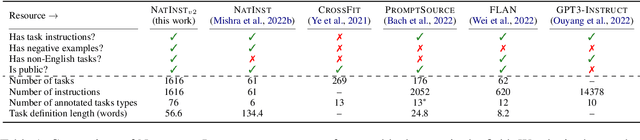
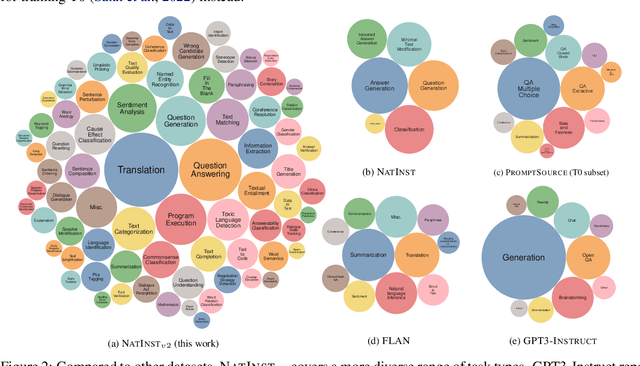
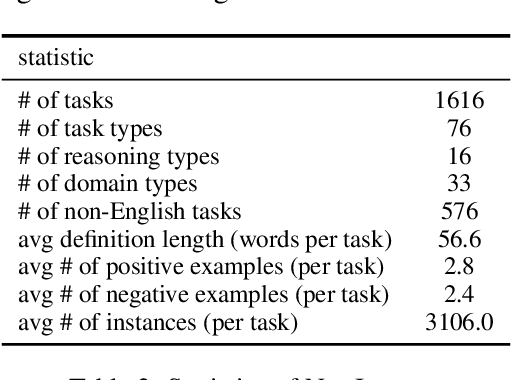
Abstract:How can we measure the generalization of models to a variety of unseen tasks when provided with their language instructions? To facilitate progress in this goal, we introduce Natural-Instructions v2, a collection of 1,600+ diverse language tasks and their expert written instructions. More importantly, the benchmark covers 70+ distinct task types, such as tagging, in-filling, and rewriting. This benchmark is collected with contributions of NLP practitioners in the community and through an iterative peer review process to ensure their quality. This benchmark enables large-scale evaluation of cross-task generalization of the models -- training on a subset of tasks and evaluating on the remaining unseen ones. For instance, we are able to rigorously quantify generalization as a function of various scaling parameters, such as the number of observed tasks, the number of instances, and model sizes. As a by-product of these experiments. we introduce Tk-Instruct, an encoder-decoder Transformer that is trained to follow a variety of in-context instructions (plain language task definitions or k-shot examples) which outperforms existing larger models on our benchmark. We hope this benchmark facilitates future progress toward more general-purpose language understanding models.
WALNUT: A Benchmark on Weakly Supervised Learning for Natural Language Understanding
Aug 28, 2021



Abstract:Building quality machine learning models for natural language understanding (NLU) tasks relies heavily on labeled data. Weak supervision has been shown to provide valuable supervision when large amount of labeled data is unavailable or expensive to obtain. Existing works studying weak supervision for NLU either mostly focus on a specific task or simulate weak supervision signals from ground-truth labels. To date a benchmark for NLU with real world weak supervision signals for a collection of NLU tasks is still not available. In this paper, we propose such a benchmark, named WALNUT, to advocate and facilitate research on weak supervision for NLU. WALNUT consists of NLU tasks with different types, including both document-level prediction tasks and token-level prediction tasks and for each task contains weak labels generated by multiple real-world weak sources. We conduct baseline evaluations on the benchmark to systematically test the value of weak supervision for NLU tasks, with various weak supervision methods and model architectures. We demonstrate the benefits of weak supervision for low-resource NLU tasks and expect WALNUT to stimulate further research on methodologies to best leverage weak supervision. The benchmark and code for baselines will be publicly available at aka.ms/walnut_benchmark.
Self-Training with Weak Supervision
Apr 12, 2021



Abstract:State-of-the-art deep neural networks require large-scale labeled training data that is often expensive to obtain or not available for many tasks. Weak supervision in the form of domain-specific rules has been shown to be useful in such settings to automatically generate weakly labeled training data. However, learning with weak rules is challenging due to their inherent heuristic and noisy nature. An additional challenge is rule coverage and overlap, where prior work on weak supervision only considers instances that are covered by weak rules, thus leaving valuable unlabeled data behind. In this work, we develop a weak supervision framework (ASTRA) that leverages all the available data for a given task. To this end, we leverage task-specific unlabeled data through self-training with a model (student) that considers contextualized representations and predicts pseudo-labels for instances that may not be covered by weak rules. We further develop a rule attention network (teacher) that learns how to aggregate student pseudo-labels with weak rule labels, conditioned on their fidelity and the underlying context of an instance. Finally, we construct a semi-supervised learning objective for end-to-end training with unlabeled data, domain-specific rules, and a small amount of labeled data. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets for text classification demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach with significant improvements over state-of-the-art baselines.
Detecting Foodborne Illness Complaints in Multiple Languages Using English Annotations Only
Oct 11, 2020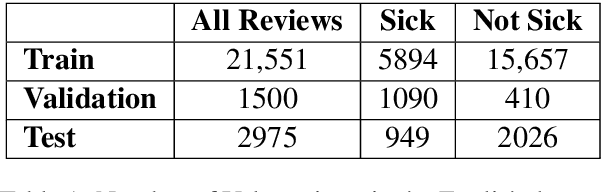
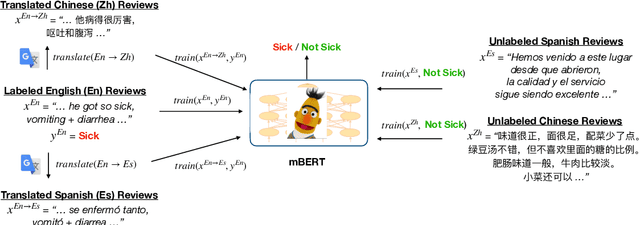
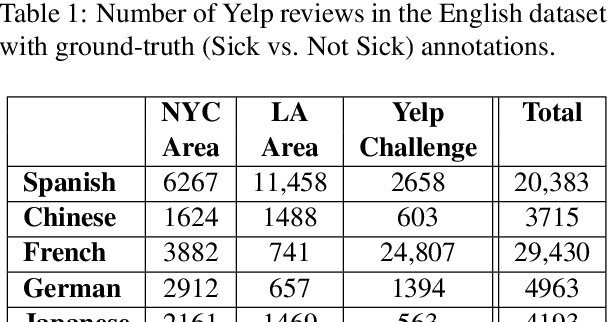
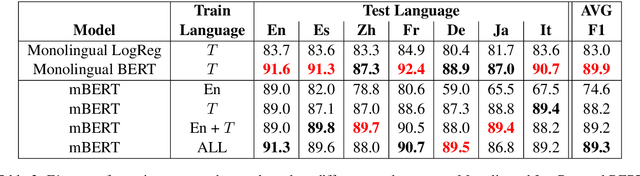
Abstract:Health departments have been deploying text classification systems for the early detection of foodborne illness complaints in social media documents such as Yelp restaurant reviews. Current systems have been successfully applied for documents in English and, as a result, a promising direction is to increase coverage and recall by considering documents in additional languages, such as Spanish or Chinese. Training previous systems for more languages, however, would be expensive, as it would require the manual annotation of many documents for each new target language. To address this challenge, we consider cross-lingual learning and train multilingual classifiers using only the annotations for English-language reviews. Recent zero-shot approaches based on pre-trained multi-lingual BERT (mBERT) have been shown to effectively align languages for aspects such as sentiment. Interestingly, we show that those approaches are less effective for capturing the nuances of foodborne illness, our public health application of interest. To improve performance without extra annotations, we create artificial training documents in the target language through machine translation and train mBERT jointly for the source (English) and target language. Furthermore, we show that translating labeled documents to multiple languages leads to additional performance improvements for some target languages. We demonstrate the benefits of our approach through extensive experiments with Yelp restaurant reviews in seven languages. Our classifiers identify foodborne illness complaints in multilingual reviews from the Yelp Challenge dataset, which highlights the potential of our general approach for deployment in health departments.
Cross-Lingual Text Classification with Minimal Resources by Transferring a Sparse Teacher
Oct 06, 2020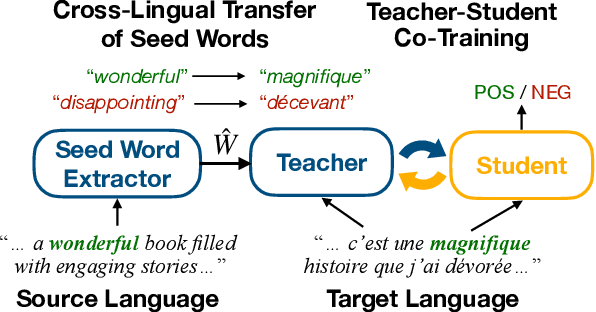
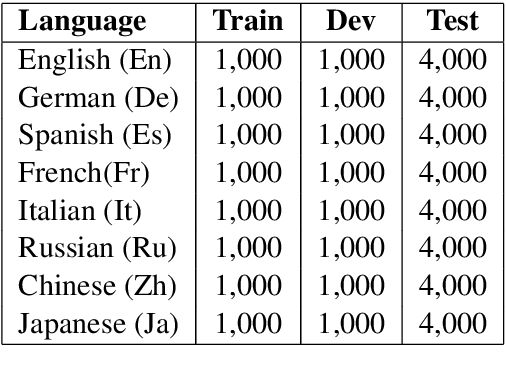
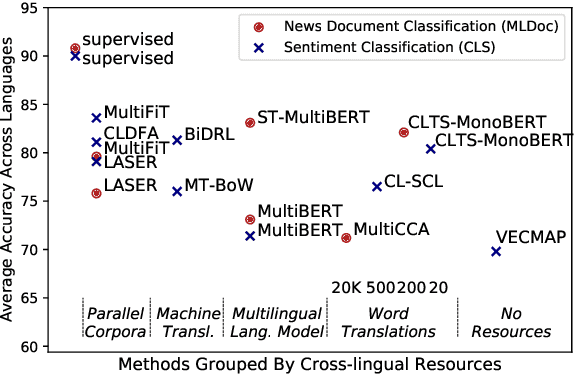
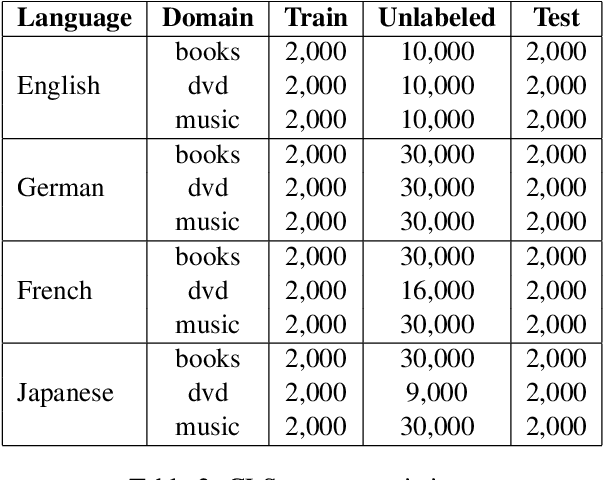
Abstract:Cross-lingual text classification alleviates the need for manually labeled documents in a target language by leveraging labeled documents from other languages. Existing approaches for transferring supervision across languages require expensive cross-lingual resources, such as parallel corpora, while less expensive cross-lingual representation learning approaches train classifiers without target labeled documents. In this work, we propose a cross-lingual teacher-student method, CLTS, that generates "weak" supervision in the target language using minimal cross-lingual resources, in the form of a small number of word translations. Given a limited translation budget, CLTS extracts and transfers only the most important task-specific seed words across languages and initializes a teacher classifier based on the translated seed words. Then, CLTS iteratively trains a more powerful student that also exploits the context of the seed words in unlabeled target documents and outperforms the teacher. CLTS is simple and surprisingly effective in 18 diverse languages: by transferring just 20 seed words, even a bag-of-words logistic regression student outperforms state-of-the-art cross-lingual methods (e.g., based on multilingual BERT). Moreover, CLTS can accommodate any type of student classifier: leveraging a monolingual BERT student leads to further improvements and outperforms even more expensive approaches by up to 12% in accuracy. Finally, CLTS addresses emerging tasks in low-resource languages using just a small number of word translations.
AutoKnow: Self-Driving Knowledge Collection for Products of Thousands of Types
Jun 24, 2020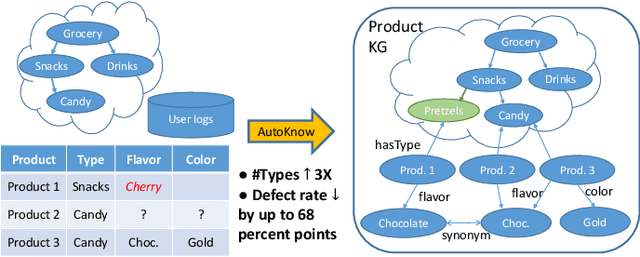
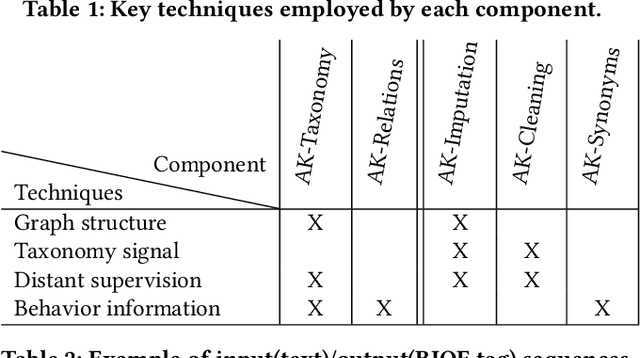
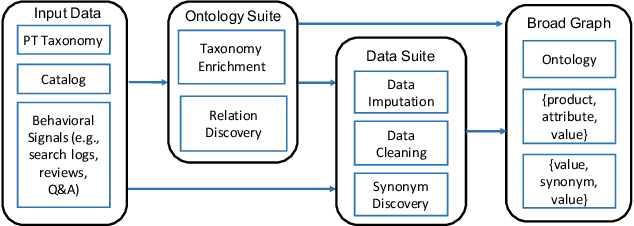
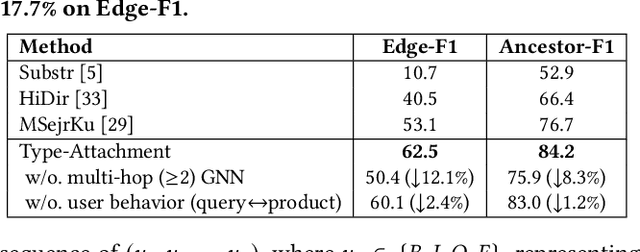
Abstract:Can one build a knowledge graph (KG) for all products in the world? Knowledge graphs have firmly established themselves as valuable sources of information for search and question answering, and it is natural to wonder if a KG can contain information about products offered at online retail sites. There have been several successful examples of generic KGs, but organizing information about products poses many additional challenges, including sparsity and noise of structured data for products, complexity of the domain with millions of product types and thousands of attributes, heterogeneity across large number of categories, as well as large and constantly growing number of products. We describe AutoKnow, our automatic (self-driving) system that addresses these challenges. The system includes a suite of novel techniques for taxonomy construction, product property identification, knowledge extraction, anomaly detection, and synonym discovery. AutoKnow is (a) automatic, requiring little human intervention, (b) multi-scalable, scalable in multiple dimensions (many domains, many products, and many attributes), and (c) integrative, exploiting rich customer behavior logs. AutoKnow has been operational in collecting product knowledge for over 11K product types.
TXtract: Taxonomy-Aware Knowledge Extraction for Thousands of Product Categories
May 01, 2020



Abstract:Extracting structured knowledge from product profiles is crucial for various applications in e-Commerce. State-of-the-art approaches for knowledge extraction were each designed for a single category of product, and thus do not apply to real-life e-Commerce scenarios, which often contain thousands of diverse categories. This paper proposes TXtract, a taxonomy-aware knowledge extraction model that applies to thousands of product categories organized in a hierarchical taxonomy. Through category conditional self-attention and multi-task learning, our approach is both scalable, as it trains a single model for thousands of categories, and effective, as it extracts category-specific attribute values. Experiments on products from a taxonomy with 4,000 categories show that TXtract outperforms state-of-the-art approaches by up to 10% in F1 and 15% in coverage across all categories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge