Amirreza Mirzaei
ComAlign: Compositional Alignment in Vision-Language Models
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have showcased a remarkable ability to extract transferable features for downstream tasks. Nonetheless, the training process of these models is usually based on a coarse-grained contrastive loss between the global embedding of images and texts which may lose the compositional structure of these modalities. Many recent studies have shown VLMs lack compositional understandings like attribute binding and identifying object relationships. Although some recent methods have tried to achieve finer-level alignments, they either are not based on extracting meaningful components of proper granularity or don't properly utilize the modalities' correspondence (especially in image-text pairs with more ingredients). Addressing these limitations, we introduce Compositional Alignment (ComAlign), a fine-grained approach to discover more exact correspondence of text and image components using only the weak supervision in the form of image-text pairs. Our methodology emphasizes that the compositional structure (including entities and relations) extracted from the text modality must also be retained in the image modality. To enforce correspondence of fine-grained concepts in image and text modalities, we train a lightweight network lying on top of existing visual and language encoders using a small dataset. The network is trained to align nodes and edges of the structure across the modalities. Experimental results on various VLMs and datasets demonstrate significant improvements in retrieval and compositional benchmarks, affirming the effectiveness of our plugin model.
Benchmarking Generalization via In-Context Instructions on 1,600+ Language Tasks
Apr 16, 2022
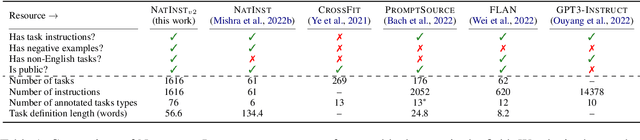
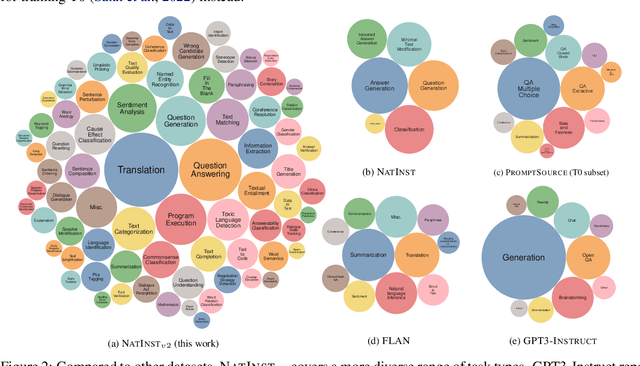
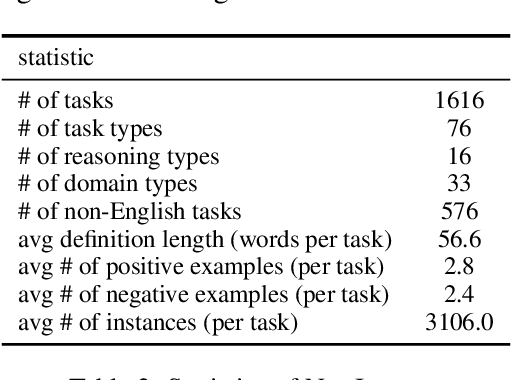
Abstract:How can we measure the generalization of models to a variety of unseen tasks when provided with their language instructions? To facilitate progress in this goal, we introduce Natural-Instructions v2, a collection of 1,600+ diverse language tasks and their expert written instructions. More importantly, the benchmark covers 70+ distinct task types, such as tagging, in-filling, and rewriting. This benchmark is collected with contributions of NLP practitioners in the community and through an iterative peer review process to ensure their quality. This benchmark enables large-scale evaluation of cross-task generalization of the models -- training on a subset of tasks and evaluating on the remaining unseen ones. For instance, we are able to rigorously quantify generalization as a function of various scaling parameters, such as the number of observed tasks, the number of instances, and model sizes. As a by-product of these experiments. we introduce Tk-Instruct, an encoder-decoder Transformer that is trained to follow a variety of in-context instructions (plain language task definitions or k-shot examples) which outperforms existing larger models on our benchmark. We hope this benchmark facilitates future progress toward more general-purpose language understanding models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge