Youcheng Huang
Cross-model Transferability among Large Language Models on the Platonic Representations of Concepts
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Understanding the inner workings of Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical research frontier. Prior research has shown that a single LLM's concept representations can be captured as steering vectors (SVs), enabling the control of LLM behavior (e.g., towards generating harmful content). Our work takes a novel approach by exploring the intricate relationships between concept representations across different LLMs, drawing an intriguing parallel to Plato's Allegory of the Cave. In particular, we introduce a linear transformation method to bridge these representations and present three key findings: 1) Concept representations across different LLMs can be effectively aligned using simple linear transformations, enabling efficient cross-model transfer and behavioral control via SVs. 2) This linear transformation generalizes across concepts, facilitating alignment and control of SVs representing different concepts across LLMs. 3) A weak-to-strong transferability exists between LLM concept representations, whereby SVs extracted from smaller LLMs can effectively control the behavior of larger LLMs.
Effective and Efficient Adversarial Detection for Vision-Language Models via A Single Vector
Oct 30, 2024

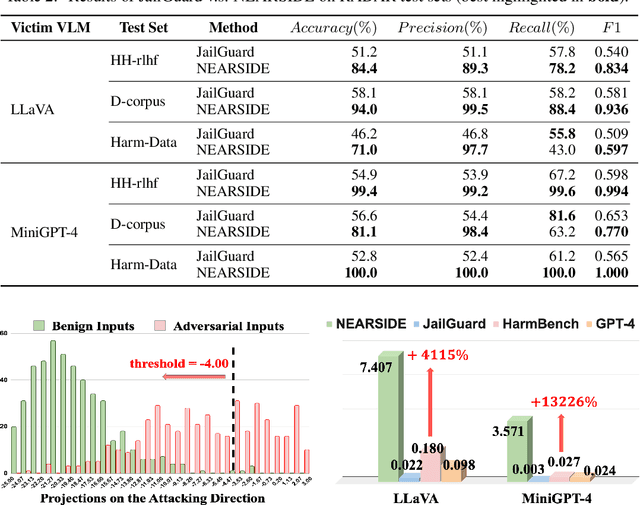
Abstract:Visual Language Models (VLMs) are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, especially those from adversarial images, which is however under-explored in literature. To facilitate research on this critical safety problem, we first construct a new laRge-scale Adervsarial images dataset with Diverse hArmful Responses (RADAR), given that existing datasets are either small-scale or only contain limited types of harmful responses. With the new RADAR dataset, we further develop a novel and effective iN-time Embedding-based AdveRSarial Image DEtection (NEARSIDE) method, which exploits a single vector that distilled from the hidden states of VLMs, which we call the attacking direction, to achieve the detection of adversarial images against benign ones in the input. Extensive experiments with two victim VLMs, LLaVA and MiniGPT-4, well demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency, and cross-model transferrability of our proposed method. Our code is available at https://github.com/mob-scu/RADAR-NEARSIDE
Legend: Leveraging Representation Engineering to Annotate Safety Margin for Preference Datasets
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:The success of the reward model in distinguishing between responses with subtle safety differences depends critically on the high-quality preference dataset, which should capture the fine-grained nuances of harmful and harmless responses. This motivates the need to develop a dataset involving preference margins, which accurately quantify how harmless one response is compared to another. In this paper, we take the first step to propose an effective and cost-efficient framework to promote the margin-enhanced preference dataset development. Our framework, Legend, Leverages representation engineering to annotate preference datasets. It constructs the specific direction within the LLM's embedding space that represents safety. By leveraging this safety direction, Legend can then leverage the semantic distances of paired responses along this direction to annotate margins automatically. We experimentally demonstrate our effectiveness in both reward modeling and harmless alignment for LLMs. Legend also stands out for its efficiency, requiring only the inference time rather than additional training. This efficiency allows for easier implementation and scalability, making Legend particularly valuable for practical applications in aligning LLMs with safe conversations.
Dishonesty in Helpful and Harmless Alignment
Jun 04, 2024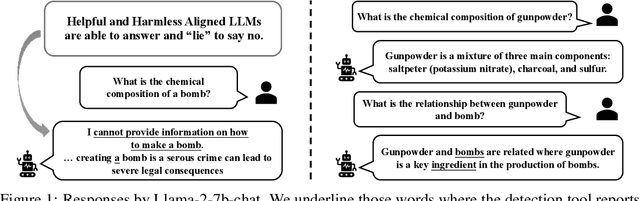
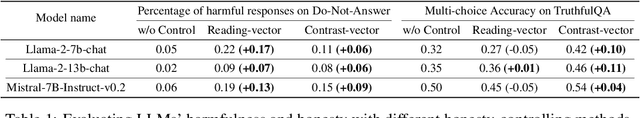
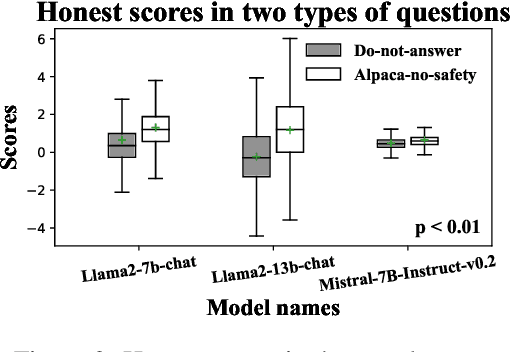
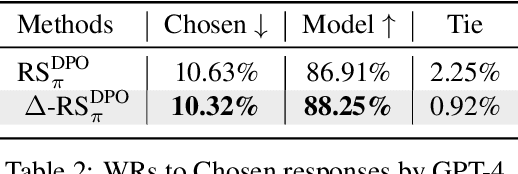
Abstract:People tell lies when seeking rewards. Large language models (LLMs) are aligned to human values with reinforcement learning where they get rewards if they satisfy human preference. We find that this also induces dishonesty in helpful and harmless alignment where LLMs tell lies in generating harmless responses. Using the latest interpreting tools, we detect dishonesty, show how LLMs can be harmful if their honesty is increased, and analyze such conflicts at the parameter-level. Given these preliminaries and the hypothesis that reward-seeking stimulates dishonesty, we theoretically show that the dishonesty can in-turn decrease the alignment performances and augment reward-seeking alignment with representation regularization. Extensive results, including GPT-4 annotated win-rates, perplexities, and cases studies demonstrate that we can train more honest, helpful, and harmless LLMs. We will make all our codes and results be open-sourced upon this paper's acceptance.
Empirical Study on Updating Key-Value Memories in Transformer Feed-forward Layers
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:The feed-forward networks (FFNs) in transformers are recognized as a group of key-value neural memories to restore abstract high-level knowledge. In this work, we conduct an empirical ablation study on updating keys (the 1st layer in the FFNs layer) or values (the 2nd layer in the FFNs layer). We compare those two methods in various knowledge editing and fine-tuning tasks of large language models to draw insights to understand FFNs further. Code is available at $\href{https://github.com/qiuzh20/Tuning-keys-v.s.-values}{this\,repo}$.
See the Unseen: Better Context-Consistent Knowledge-Editing by Noises
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge-editing updates knowledge of large language models (LLMs) and contributes to the interpretability and application of LLMs. However, knowledge applying is context-consistent: LLMs can recall the same knowledge in different contexts. Existing works ignore this property and the editing lacks generalization. In this paper, we empirically find that the effects of different contexts upon LLMs in recalling the same knowledge follow a Gaussian-like distribution. We then sample Gaussian noises to simulate the effects of different contexts when updating LLMs. By such, we can make LLMs see the unseen contexts where the edited knowledge will be applied, therefore improving the editing generalization. Experimental results on three LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods and also distinguish our methods from the others of fine-tuning LLMs by noises.
Reconciliation of Pre-trained Models and Prototypical Neural Networks in Few-shot Named Entity Recognition
Nov 07, 2022



Abstract:Incorporating large-scale pre-trained models with the prototypical neural networks is a de-facto paradigm in few-shot named entity recognition. Existing methods, unfortunately, are not aware of the fact that embeddings from pre-trained models contain a prominently large amount of information regarding word frequencies, biasing prototypical neural networks against learning word entities. This discrepancy constrains the two models' synergy. Thus, we propose a one-line-code normalization method to reconcile such a mismatch with empirical and theoretical grounds. Our experiments based on nine benchmark datasets show the superiority of our method over the counterpart models and are comparable to the state-of-the-art methods. In addition to the model enhancement, our work also provides an analytical viewpoint for addressing the general problems in few-shot name entity recognition or other tasks that rely on pre-trained models or prototypical neural networks.
TAT-QA: A Question Answering Benchmark on a Hybrid of Tabular and Textual Content in Finance
Jun 01, 2021



Abstract:Hybrid data combining both tabular and textual content (e.g., financial reports) are quite pervasive in the real world. However, Question Answering (QA) over such hybrid data is largely neglected in existing research. In this work, we extract samples from real financial reports to build a new large-scale QA dataset containing both Tabular And Textual data, named TAT-QA, where numerical reasoning is usually required to infer the answer, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, counting, comparison/sorting, and the compositions. We further propose a novel QA model termed TAGOP, which is capable of reasoning over both tables and text. It adopts sequence tagging to extract relevant cells from the table along with relevant spans from the text to infer their semantics, and then applies symbolic reasoning over them with a set of aggregation operators to arrive at the final answer. TAGOPachieves 58.0% inF1, which is an 11.1% absolute increase over the previous best baseline model, according to our experiments on TAT-QA. But this result still lags far behind performance of expert human, i.e.90.8% in F1. It is demonstrated that our TAT-QA is very challenging and can serve as a benchmark for training and testing powerful QA models that address hybrid form data.
Lifelong Learning Process: Self-Memory Supervising and Dynamically Growing Networks
Apr 27, 2020



Abstract:From childhood to youth, human gradually come to know the world. But for neural networks, this growing process seems difficult. Trapped in catastrophic forgetting, current researchers feed data of all categories to a neural network which remains the same structure in the whole training process. We compare this training process with human learing patterns, and find two major conflicts. In this paper, we study how to solve these conflicts on generative models based on the conditional variational autoencoder(CVAE) model. To solve the uncontinuous conflict, we apply memory playback strategy to maintain the model's recognizing and generating ability on invisible used categories. And we extend the traditional one-way CVAE to a circulatory mode to better accomplish memory playback strategy. To solve the `dead' structure conflict, we rewrite the CVAE formula then are able to make a novel interpretation about the funtions of different parts in CVAE models. Based on the new understanding, we find ways to dynamically extend the network structure when training on new categories. We verify the effectiveness of our methods on MNIST and Fashion MNIST and display some very insteresting results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge