Yulin Hu
TEA-Bench: A Systematic Benchmarking of Tool-enhanced Emotional Support Dialogue Agent
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Emotional Support Conversation requires not only affective expression but also grounded instrumental support to provide trustworthy guidance. However, existing ESC systems and benchmarks largely focus on affective support in text-only settings, overlooking how external tools can enable factual grounding and reduce hallucination in multi-turn emotional support. We introduce TEA-Bench, the first interactive benchmark for evaluating tool-augmented agents in ESC, featuring realistic emotional scenarios, an MCP-style tool environment, and process-level metrics that jointly assess the quality and factual grounding of emotional support. Experiments on nine LLMs show that tool augmentation generally improves emotional support quality and reduces hallucination, but the gains are strongly capacity-dependent: stronger models use tools more selectively and effectively, while weaker models benefit only marginally. We further release TEA-Dialog, a dataset of tool-enhanced ESC dialogues, and find that supervised fine-tuning improves in-distribution support but generalizes poorly. Our results underscore the importance of tool use in building reliable emotional support agents.
When Personalization Legitimizes Risks: Uncovering Safety Vulnerabilities in Personalized Dialogue Agents
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Long-term memory enables large language model (LLM) agents to support personalized and sustained interactions. However, most work on personalized agents prioritizes utility and user experience, treating memory as a neutral component and largely overlooking its safety implications. In this paper, we reveal intent legitimation, a previously underexplored safety failure in personalized agents, where benign personal memories bias intent inference and cause models to legitimize inherently harmful queries. To study this phenomenon, we introduce PS-Bench, a benchmark designed to identify and quantify intent legitimation in personalized interactions. Across multiple memory-augmented agent frameworks and base LLMs, personalization increases attack success rates by 15.8%-243.7% relative to stateless baselines. We further provide mechanistic evidence for intent legitimation from internal representations space, and propose a lightweight detection-reflection method that effectively reduces safety degradation. Overall, our work provides the first systematic exploration and evaluation of intent legitimation as a safety failure mode that naturally arises from benign, real-world personalization, highlighting the importance of assessing safety under long-term personal context. WARNING: This paper may contain harmful content.
OP-Bench: Benchmarking Over-Personalization for Memory-Augmented Personalized Conversational Agents
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Memory-augmented conversational agents enable personalized interactions using long-term user memory and have gained substantial traction. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on whether agents can recall and apply user information, while overlooking whether such personalization is used appropriately. In fact, agents may overuse personal information, producing responses that feel forced, intrusive, or socially inappropriate to users. We refer to this issue as \emph{over-personalization}. In this work, we formalize over-personalization into three types: Irrelevance, Repetition, and Sycophancy, and introduce \textbf{OP-Bench} a benchmark of 1,700 verified instances constructed from long-horizon dialogue histories. Using \textbf{OP-Bench}, we evaluate multiple large language models and memory-augmentation methods, and find that over-personalization is widespread when memory is introduced. Further analysis reveals that agents tend to retrieve and over-attend to user memories even when unnecessary. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{Self-ReCheck}, a lightweight, model-agnostic memory filtering mechanism that mitigates over-personalization while preserving personalization performance. Our work takes an initial step toward more controllable and appropriate personalization in memory-augmented dialogue systems.
On Signal Peak Power Constraint of Over-the-Air Federated Learning
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has been considered a promising privacy preserving distributed edge learning framework. Over-the-air computation (AirComp) technique leveraging analog transmission enables the aggregation of local updates directly over-the-air by exploiting the superposition properties of wireless multiple-access channel, thereby drastically reducing the communication bottleneck issues of FL compared with digital transmission schemes. This work points out that existing AirComp-FL overlooks a key practical constraint, the instantaneous peak-power constraints imposed by the non-linearity of radiofrequency power amplifiers. We present and analyze the effect of the classic method to deal with this issue, amplitude clipping combined with filtering. We investigate the effect of instantaneous peak-power constraints in AirComp-FL for both single-carrier and multi-carrier orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. We highlight the specificity of AirComp-FL: the samples depend on the gradient value distribution, leading to a higher peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) than that observed for uniformly distributed signals. Simulation results demonstrate that, in practical settings, the instantaneous transmit power regularly exceeds the power-amplifier limit; however, by applying clipping and filtering, the FL performance can be degraded. The degradation becomes pronounced especially in multi-carrier OFDM systems due to the in-band distortions caused by clipping and filtering.
Joint Link Adaptation and Device Scheduling Approach for URLLC Industrial IoT Network: A DRL-based Method with Bayesian Optimization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:In this article, we consider an industrial internet of things (IIoT) network supporting multi-device dynamic ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) while the channel state information (CSI) is imperfect. A joint link adaptation (LA) and device scheduling (including the order) design is provided, aiming at maximizing the total transmission rate under strict block error rate (BLER) constraints. In particular, a Bayesian optimization (BO) driven Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) method is proposed, which determines the device served order sequence and the corresponding modulation and coding scheme (MCS) adaptively based on the imperfect CSI. Note that the imperfection of CSI, error sample imbalance in URLLC networks, as well as the parameter sensitivity nature of the TD3 algorithm likely diminish the algorithm's convergence speed and reliability. To address such an issue, we proposed a BO based training mechanism for the convergence speed improvement, which provides a more reliable learning direction and sample selection method to track the imbalance sample problem. Via extensive simulations, we show that the proposed algorithm achieves faster convergence and higher sum-rate performance compared to existing solutions.
HGC-Herd: Efficient Heterogeneous Graph Condensation via Representative Node Herding
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) have demonstrated strong capability in modeling complex semantics across multi-type nodes and relations. However, their scalability to large-scale graphs remains challenging due to structural redundancy and high-dimensional node features. Existing graph condensation approaches, such as GCond, are primarily developed for homogeneous graphs and rely on gradient matching, resulting in considerable computational, memory, and optimization overhead. We propose HGC-Herd, a training-free condensation framework that generates compact yet informative heterogeneous graphs while maintaining both semantic and structural fidelity. HGC-Herd integrates lightweight feature propagation to encode multi-hop relational context and employs a class-wise herding mechanism to identify representative nodes per class, producing balanced and discriminative subsets for downstream learning tasks. Extensive experiments on ACM, DBLP, and Freebase validate that HGC-Herd attains comparable or superior accuracy to full-graph training while markedly reducing both runtime and memory consumption. These results underscore its practical value for efficient and scalable heterogeneous graph representation learning.
Exploring and Exploiting the Inherent Efficiency within Large Reasoning Models for Self-Guided Efficiency Enhancement
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large reasoning models (LRMs) have significantly enhanced language models' capabilities in complex problem-solving by emulating human-like deliberative thinking. However, these models often exhibit overthinking (i.e., the generation of unnecessarily verbose and redundant content), which hinders efficiency and inflates inference cost. In this work, we explore the representational and behavioral origins of this inefficiency, revealing that LRMs inherently possess the capacity for more concise reasoning. Empirical analyses show that correct reasoning paths vary significantly in length, and the shortest correct responses often suffice, indicating untapped efficiency potential. Exploiting these findings, we propose two lightweight methods to enhance LRM efficiency. First, we introduce Efficiency Steering, a training-free activation steering technique that modulates reasoning behavior via a single direction in the model's representation space. Second, we develop Self-Rewarded Efficiency RL, a reinforcement learning framework that dynamically balances task accuracy and brevity by rewarding concise correct solutions. Extensive experiments on seven LRM backbones across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our methods significantly reduce reasoning length while preserving or improving task performance. Our results highlight that reasoning efficiency can be improved by leveraging and guiding the intrinsic capabilities of existing models in a self-guided manner.
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025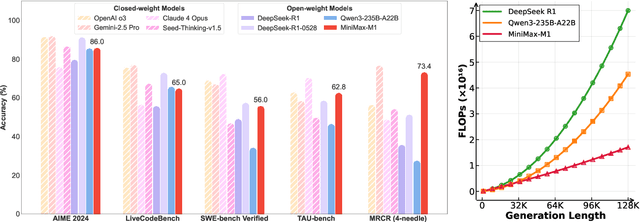
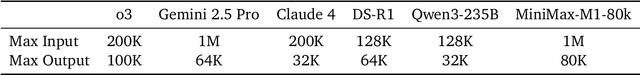
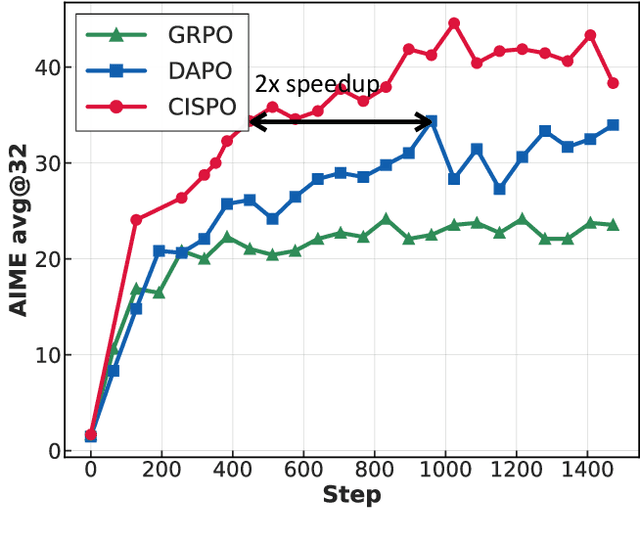
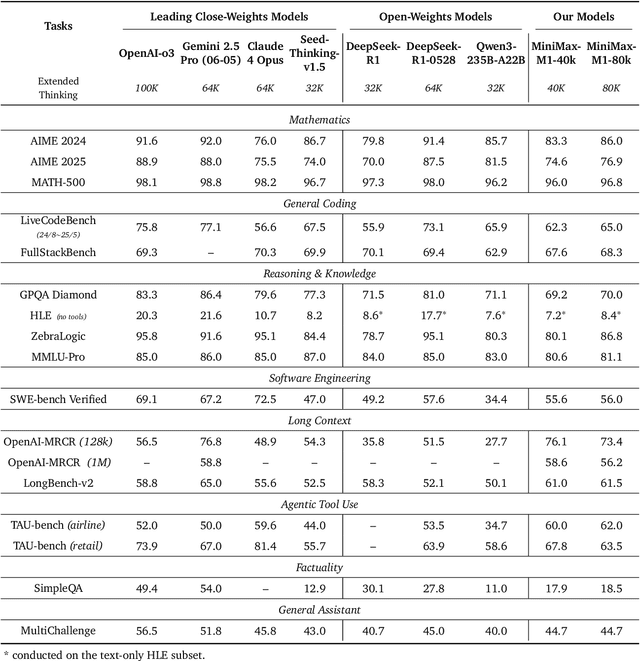
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
MPO: Multilingual Safety Alignment via Reward Gap Optimization
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly central to AI applications worldwide, necessitating robust multilingual safety alignment to ensure secure deployment across diverse linguistic contexts. Existing preference learning methods for safety alignment, such as RLHF and DPO, are primarily monolingual and struggle with noisy multilingual data. To address these limitations, we introduce Multilingual reward gaP Optimization (MPO), a novel approach that leverages the well-aligned safety capabilities of the dominant language (English) to improve safety alignment across multiple languages. MPO directly minimizes the reward gap difference between the dominant language and target languages, effectively transferring safety capabilities while preserving the original strengths of the dominant language. Extensive experiments on three LLMs, LLaMA-3.1, Gemma-2 and Qwen2.5, validate MPO's efficacy in multilingual safety alignment without degrading general multilingual utility.
When Less Language is More: Language-Reasoning Disentanglement Makes LLMs Better Multilingual Reasoners
May 21, 2025Abstract:Multilingual reasoning remains a significant challenge for large language models (LLMs), with performance disproportionately favoring high-resource languages. Drawing inspiration from cognitive neuroscience, which suggests that human reasoning functions largely independently of language processing, we hypothesize that LLMs similarly encode reasoning and language as separable components that can be disentangled to enhance multilingual reasoning. To evaluate this, we perform a causal intervention by ablating language-specific representations at inference time. Experiments on 10 open-source LLMs spanning 11 typologically diverse languages show that this language-specific ablation consistently boosts multilingual reasoning performance. Layer-wise analyses further confirm that language and reasoning representations can be effectively decoupled throughout the model, yielding improved multilingual reasoning capabilities, while preserving top-layer language features remains essential for maintaining linguistic fidelity. Compared to post-training such as supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning, our training-free ablation achieves comparable or superior results with minimal computational overhead. These findings shed light on the internal mechanisms underlying multilingual reasoning in LLMs and suggest a lightweight and interpretable strategy for improving cross-lingual generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge