Yuxin Zhang
Tony
SIDeR: Semantic Identity Decoupling for Unrestricted Face Privacy
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:With the deep integration of facial recognition into online banking, identity verification, and other networked services, achieving effective decoupling of identity information from visual representations during image storage and transmission has become a critical challenge for privacy protection. To address this issue, we propose SIDeR, a Semantic decoupling-driven framework for unrestricted face privacy protection. SIDeR decomposes a facial image into a machine-recognizable identity feature vector and a visually perceptible semantic appearance component. By leveraging semantic-guided recomposition in the latent space of a diffusion model, it generates visually anonymous adversarial faces while maintaining machine-level identity consistency. The framework incorporates momentum-driven unrestricted perturbation optimization and a semantic-visual balancing factor to synthesize multiple visually diverse, highly natural adversarial samples. Furthermore, for authorized access, the protected image can be restored to its original form when the correct password is provided. Extensive experiments on the CelebA-HQ and FFHQ datasets demonstrate that SIDeR achieves a 99% attack success rate in black-box scenarios and outperforms baseline methods by 41.28% in PSNR-based restoration quality.
KTV: Keyframes and Key Tokens Selection for Efficient Training-Free Video LLMs
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Training-free video understanding leverages the strong image comprehension capabilities of pre-trained vision language models (VLMs) by treating a video as a sequence of static frames, thus obviating the need for costly video-specific training. However, this paradigm often suffers from severe visual redundancy and high computational overhead, especially when processing long videos. Crucially, existing keyframe selection strategies, especially those based on CLIP similarity, are prone to biases and may inadvertently overlook critical frames, resulting in suboptimal video comprehension. To address these significant challenges, we propose \textbf{KTV}, a novel two-stage framework for efficient and effective training-free video understanding. In the first stage, KTV performs question-agnostic keyframe selection by clustering frame-level visual features, yielding a compact, diverse, and representative subset of frames that mitigates temporal redundancy. In the second stage, KTV applies key visual token selection, pruning redundant or less informative tokens from each selected keyframe based on token importance and redundancy, which significantly reduces the number of tokens fed into the LLM. Extensive experiments on the Multiple-Choice VideoQA task demonstrate that KTV outperforms state-of-the-art training-free baselines while using significantly fewer visual tokens, \emph{e.g.}, only 504 visual tokens for a 60-min video with 10800 frames, achieving $44.8\%$ accuracy on the MLVU-Test benchmark. In particular, KTV also exceeds several training-based approaches on certain benchmarks.
Out of the Memory Barrier: A Highly Memory Efficient Training System for LLMs with Million-Token Contexts
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) on long contexts is severely constrained by prohibitive GPU memory overhead, not training time. The primary culprits are the activations, whose memory footprints scale linearly with sequence length. We introduce OOMB, a highly memory-efficient training system that directly confronts this barrier. Our approach employs a chunk-recurrent training framework with on-the-fly activation recomputation, which maintains a constant activation memory footprint (O(1)) and shifts the primary bottleneck to the growing KV cache. To manage the KV cache, OOMB integrates a suite of synergistic optimizations: a paged memory manager for both the KV cache and its gradients to eliminate fragmentation, asynchronous CPU offloading to hide data transfer latency, and page-level sparse attention to reduce both computational complexity and communication overhead. The synergy of these techniques yields exceptional efficiency. Our empirical results show that for every additional 10K tokens of context, the end-to-end training memory overhead increases by a mere 10MB for Qwen2.5-7B. This allows training Qwen2.5-7B with a 4M-token context on a single H200 GPU, a feat that would otherwise require a large cluster using context parallelism. This work represents a substantial advance in resource efficiency for long-context LLM training. The source code is available at https://github.com/wenhaoli-xmu/OOMB.
FSVideo: Fast Speed Video Diffusion Model in a Highly-Compressed Latent Space
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce FSVideo, a fast speed transformer-based image-to-video (I2V) diffusion framework. We build our framework on the following key components: 1.) a new video autoencoder with highly-compressed latent space ($64\times64\times4$ spatial-temporal downsampling ratio), achieving competitive reconstruction quality; 2.) a diffusion transformer (DIT) architecture with a new layer memory design to enhance inter-layer information flow and context reuse within DIT, and 3.) a multi-resolution generation strategy via a few-step DIT upsampler to increase video fidelity. Our final model, which contains a 14B DIT base model and a 14B DIT upsampler, achieves competitive performance against other popular open-source models, while being an order of magnitude faster. We discuss our model design as well as training strategies in this report.
Beyond Pixels: Visual Metaphor Transfer via Schema-Driven Agentic Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:A visual metaphor constitutes a high-order form of human creativity, employing cross-domain semantic fusion to transform abstract concepts into impactful visual rhetoric. Despite the remarkable progress of generative AI, existing models remain largely confined to pixel-level instruction alignment and surface-level appearance preservation, failing to capture the underlying abstract logic necessary for genuine metaphorical generation. To bridge this gap, we introduce the task of Visual Metaphor Transfer (VMT), which challenges models to autonomously decouple the "creative essence" from a reference image and re-materialize that abstract logic onto a user-specified target subject. We propose a cognitive-inspired, multi-agent framework that operationalizes Conceptual Blending Theory (CBT) through a novel Schema Grammar ("G"). This structured representation decouples relational invariants from specific visual entities, providing a rigorous foundation for cross-domain logic re-instantiation. Our pipeline executes VMT through a collaborative system of specialized agents: a perception agent that distills the reference into a schema, a transfer agent that maintains generic space invariance to discover apt carriers, a generation agent for high-fidelity synthesis and a hierarchical diagnostic agent that mimics a professional critic, performing closed-loop backtracking to identify and rectify errors across abstract logic, component selection, and prompt encoding. Extensive experiments and human evaluations demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms SOTA baselines in metaphor consistency, analogy appropriateness, and visual creativity, paving the way for automated high-impact creative applications in advertising and media. Source code will be made publicly available.
TAG-MoE: Task-Aware Gating for Unified Generative Mixture-of-Experts
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Unified image generation and editing models suffer from severe task interference in dense diffusion transformers architectures, where a shared parameter space must compromise between conflicting objectives (e.g., local editing v.s. subject-driven generation). While the sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) paradigm is a promising solution, its gating networks remain task-agnostic, operating based on local features, unaware of global task intent. This task-agnostic nature prevents meaningful specialization and fails to resolve the underlying task interference. In this paper, we propose a novel framework to inject semantic intent into MoE routing. We introduce a Hierarchical Task Semantic Annotation scheme to create structured task descriptors (e.g., scope, type, preservation). We then design Predictive Alignment Regularization to align internal routing decisions with the task's high-level semantics. This regularization evolves the gating network from a task-agnostic executor to a dispatch center. Our model effectively mitigates task interference, outperforming dense baselines in fidelity and quality, and our analysis shows that experts naturally develop clear and semantically correlated specializations.
GEN3D: Generating Domain-Free 3D Scenes from a Single Image
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Despite recent advancements in neural 3D reconstruction, the dependence on dense multi-view captures restricts their broader applicability. Additionally, 3D scene generation is vital for advancing embodied AI and world models, which depend on diverse, high-quality scenes for learning and evaluation. In this work, we propose Gen3d, a novel method for generation of high-quality, wide-scope, and generic 3D scenes from a single image. After the initial point cloud is created by lifting the RGBD image, Gen3d maintains and expands its world model. The 3D scene is finalized through optimizing a Gaussian splatting representation. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets demonstrate the strong generalization capability and superior performance of our method in generating a world model and Synthesizing high-fidelity and consistent novel views.
Test-Time Iterative Error Correction for Efficient Diffusion Models
Nov 09, 2025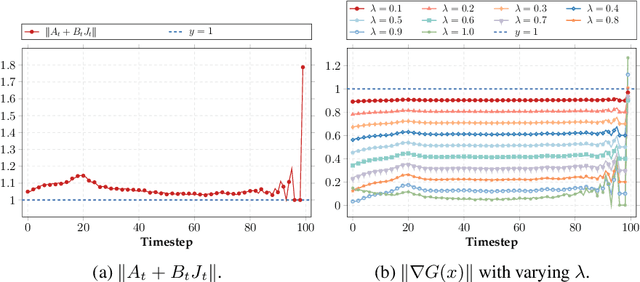

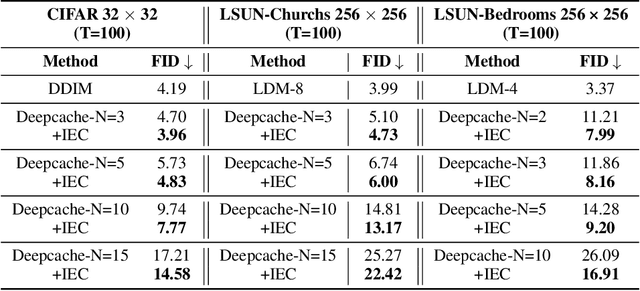
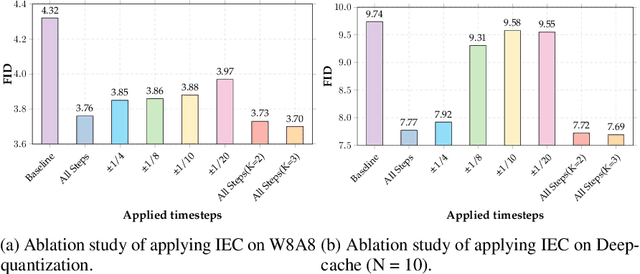
Abstract:With the growing demand for high-quality image generation on resource-constrained devices, efficient diffusion models have received increasing attention. However, such models suffer from approximation errors introduced by efficiency techniques, which significantly degrade generation quality. Once deployed, these errors are difficult to correct, as modifying the model is typically infeasible in deployment environments. Through an analysis of error propagation across diffusion timesteps, we reveal that these approximation errors can accumulate exponentially, severely impairing output quality. Motivated by this insight, we propose Iterative Error Correction (IEC), a novel test-time method that mitigates inference-time errors by iteratively refining the model's output. IEC is theoretically proven to reduce error propagation from exponential to linear growth, without requiring any retraining or architectural changes. IEC can seamlessly integrate into the inference process of existing diffusion models, enabling a flexible trade-off between performance and efficiency. Extensive experiments show that IEC consistently improves generation quality across various datasets, efficiency techniques, and model architectures, establishing it as a practical and generalizable solution for test-time enhancement of efficient diffusion models.
Step-Audio-EditX Technical Report
Nov 05, 2025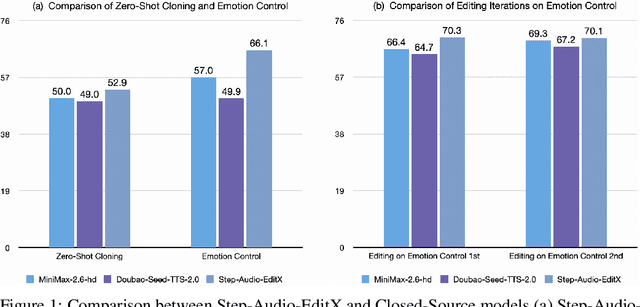
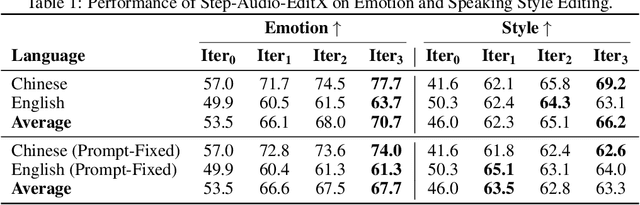
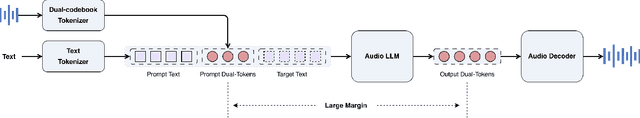
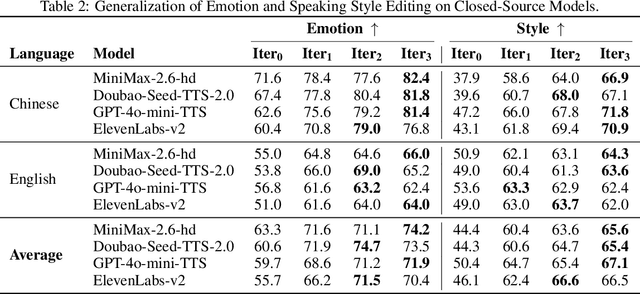
Abstract:We present Step-Audio-EditX, the first open-source LLM-based audio model excelling at expressive and iterative audio editing encompassing emotion, speaking style, and paralinguistics alongside robust zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) capabilities.Our core innovation lies in leveraging only large-margin synthetic data, which circumvents the need for embedding-based priors or auxiliary modules. This large-margin learning approach enables both iterative control and high expressivity across voices, and represents a fundamental pivot from the conventional focus on representation-level disentanglement. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio-EditX surpasses both MiniMax-2.6-hd and Doubao-Seed-TTS-2.0 in emotion editing and other fine-grained control tasks.
Spotlight Attention: Towards Efficient LLM Generation via Non-linear Hashing-based KV Cache Retrieval
Aug 27, 2025

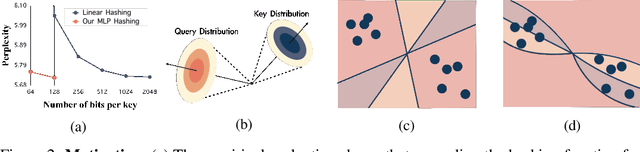

Abstract:Reducing the key-value (KV) cache burden in Large Language Models (LLMs) significantly accelerates inference. Dynamically selecting critical KV caches during decoding helps maintain performance. Existing methods use random linear hashing to identify important tokens, but this approach is inefficient due to the orthogonal distribution of queries and keys within two narrow cones in LLMs. We introduce Spotlight Attention, a novel method that employs non-linear hashing functions to optimize the embedding distribution of queries and keys, enhancing coding efficiency and robustness. We also developed a lightweight, stable training framework using a Bradley-Terry ranking-based loss, enabling optimization of the non-linear hashing module on GPUs with 16GB memory in 8 hours. Experimental results show that Spotlight Attention drastically improves retrieval precision while shortening the length of the hash code at least 5$\times$ compared to traditional linear hashing. Finally, we exploit the computational advantages of bitwise operations by implementing specialized CUDA kernels, achieving hashing retrieval for 512K tokens in under 100$\mu$s on a single A100 GPU, with end-to-end throughput up to 3$\times$ higher than vanilla decoding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge