Changsheng Xu
Replacing Parameters with Preferences: Federated Alignment of Heterogeneous Vision-Language Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:VLMs have broad potential in privacy-sensitive domains such as healthcare and finance, yet strict data-sharing constraints render centralized training infeasible. FL mitigates this issue by enabling decentralized training, but practical deployments face challenges due to client heterogeneity in computational resources, application requirements, and model architectures. We argue that while replacing data with model parameters characterizes the present of FL, replacing parameters with preferences represents a more scalable and privacy-preserving future. Motivated by this perspective, we propose MoR, a federated alignment framework based on GRPO with Mixture-of-Rewards for heterogeneous VLMs. MoR initializes a visual foundation model as a KL-regularized reference, while each client locally trains a reward model from local preference annotations, capturing specific evaluation signals without exposing raw data. To reconcile heterogeneous rewards, we introduce a routing-based fusion mechanism that adaptively aggregates client reward signals. Finally, the server performs GRPO with this mixed reward to optimize the base VLM. Experiments on three public VQA benchmarks demonstrate that MoR consistently outperforms federated alignment baselines in generalization, robustness, and cross-client adaptability. Our approach provides a scalable solution for privacy-preserving alignment of heterogeneous VLMs under federated settings.
SoMe: A Realistic Benchmark for LLM-based Social Media Agents
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Intelligent agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated impressive capabilities and gained increasing popularity on social media platforms. While LLM agents are reshaping the ecology of social media, there exists a current gap in conducting a comprehensive evaluation of their ability to comprehend media content, understand user behaviors, and make intricate decisions. To address this challenge, we introduce SoMe, a pioneering benchmark designed to evaluate social media agents equipped with various agent tools for accessing and analyzing social media data. SoMe comprises a diverse collection of 8 social media agent tasks, 9,164,284 posts, 6,591 user profiles, and 25,686 reports from various social media platforms and external websites, with 17,869 meticulously annotated task queries. Compared with the existing datasets and benchmarks for social media tasks, SoMe is the first to provide a versatile and realistic platform for LLM-based social media agents to handle diverse social media tasks. By extensive quantitative and qualitative analysis, we provide the first overview insight into the performance of mainstream agentic LLMs in realistic social media environments and identify several limitations. Our evaluation reveals that both the current closed-source and open-source LLMs cannot handle social media agent tasks satisfactorily. SoMe provides a challenging yet meaningful testbed for future social media agents. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/LivXue/SoMe
LiveStar: Live Streaming Assistant for Real-World Online Video Understanding
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Despite significant progress in Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) for offline video understanding, existing online Video-LLMs typically struggle to simultaneously process continuous frame-by-frame inputs and determine optimal response timing, often compromising real-time responsiveness and narrative coherence. To address these limitations, we introduce LiveStar, a pioneering live streaming assistant that achieves always-on proactive responses through adaptive streaming decoding. Specifically, LiveStar incorporates: (1) a training strategy enabling incremental video-language alignment for variable-length video streams, preserving temporal consistency across dynamically evolving frame sequences; (2) a response-silence decoding framework that determines optimal proactive response timing via a single forward pass verification; (3) memory-aware acceleration via peak-end memory compression for online inference on 10+ minute videos, combined with streaming key-value cache to achieve 1.53x faster inference. We also construct an OmniStar dataset, a comprehensive dataset for training and benchmarking that encompasses 15 diverse real-world scenarios and 5 evaluation tasks for online video understanding. Extensive experiments across three benchmarks demonstrate LiveStar's state-of-the-art performance, achieving an average 19.5% improvement in semantic correctness with 18.1% reduced timing difference compared to existing online Video-LLMs, while improving FPS by 12.0% across all five OmniStar tasks. Our model and dataset can be accessed at https://github.com/yzy-bupt/LiveStar.
Look Before You Leap: A GUI-Critic-R1 Model for Pre-Operative Error Diagnosis in GUI Automation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been extensively utilized for multimodal reasoning tasks, including Graphical User Interface (GUI) automation. Unlike general offline multimodal tasks, GUI automation is executed in online interactive environments, necessitating step-by-step decision-making based on real-time status of the environment. This task has a lower tolerance for decision-making errors at each step, as any mistakes may cumulatively disrupt the process and potentially lead to irreversible outcomes like deletions or payments. To address these issues, we introduce a pre-operative critic mechanism that provides effective feedback prior to the actual execution, by reasoning about the potential outcome and correctness of actions. Specifically, we propose a Suggestion-aware Gradient Relative Policy Optimization (S-GRPO) strategy to construct our pre-operative critic model GUI-Critic-R1, incorporating a novel suggestion reward to enhance the reliability of the model's feedback. Furthermore, we develop a reasoning-bootstrapping based data collection pipeline to create a GUI-Critic-Train and a GUI-Critic-Test, filling existing gaps in GUI critic data. Static experiments on the GUI-Critic-Test across both mobile and web domains reveal that our GUI-Critic-R1 offers significant advantages in critic accuracy compared to current MLLMs. Dynamic evaluation on GUI automation benchmark further highlights the effectiveness and superiority of our model, as evidenced by improved success rates and operational efficiency.
Locality Preserving Markovian Transition for Instance Retrieval
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-based re-ranking methods are effective in modeling the data manifolds through similarity propagation in affinity graphs. However, positive signals tend to diminish over several steps away from the source, reducing discriminative power beyond local regions. To address this issue, we introduce the Locality Preserving Markovian Transition (LPMT) framework, which employs a long-term thermodynamic transition process with multiple states for accurate manifold distance measurement. The proposed LPMT first integrates diffusion processes across separate graphs using Bidirectional Collaborative Diffusion (BCD) to establish strong similarity relationships. Afterwards, Locality State Embedding (LSE) encodes each instance into a distribution for enhanced local consistency. These distributions are interconnected via the Thermodynamic Markovian Transition (TMT) process, enabling efficient global retrieval while maintaining local effectiveness. Experimental results across diverse tasks confirm the effectiveness of LPMT for instance retrieval.
Harmony: A Unified Framework for Modality Incremental Learning
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Incremental learning aims to enable models to continuously acquire knowledge from evolving data streams while preserving previously learned capabilities. While current research predominantly focuses on unimodal incremental learning and multimodal incremental learning where the modalities are consistent, real-world scenarios often present data from entirely new modalities, posing additional challenges. This paper investigates the feasibility of developing a unified model capable of incremental learning across continuously evolving modal sequences. To this end, we introduce a novel paradigm called Modality Incremental Learning (MIL), where each learning stage involves data from distinct modalities. To address this task, we propose a novel framework named Harmony, designed to achieve modal alignment and knowledge retention, enabling the model to reduce the modal discrepancy and learn from a sequence of distinct modalities, ultimately completing tasks across multiple modalities within a unified framework. Our approach introduces the adaptive compatible feature modulation and cumulative modal bridging. Through constructing historical modal features and performing modal knowledge accumulation and alignment, the proposed components collaboratively bridge modal differences and maintain knowledge retention, even with solely unimodal data available at each learning phase.These components work in concert to establish effective modality connections and maintain knowledge retention, even when only unimodal data is available at each learning stage. Extensive experiments on the MIL task demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing incremental learning methods, validating its effectiveness in MIL scenarios.
A Survey on Cross-Modal Interaction Between Music and Multimodal Data
Apr 17, 2025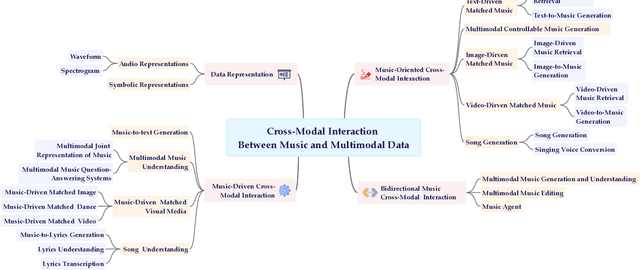
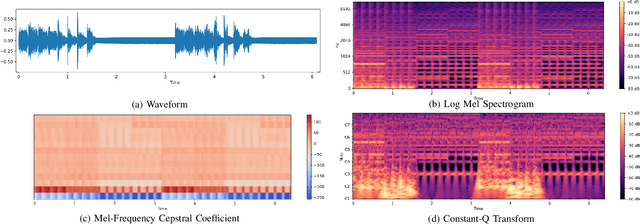

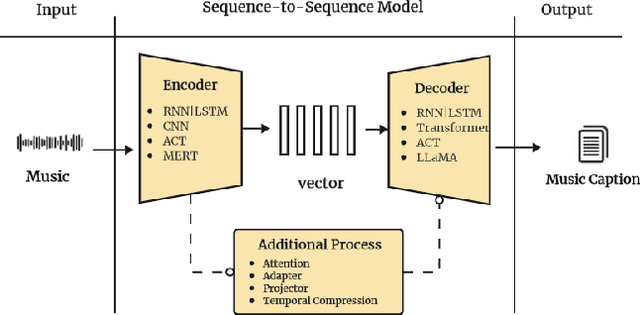
Abstract:Multimodal learning has driven innovation across various industries, particularly in the field of music. By enabling more intuitive interaction experiences and enhancing immersion, it not only lowers the entry barriers to the music but also increases its overall appeal. This survey aims to provide a comprehensive review of multimodal tasks related to music, outlining how music contributes to multimodal learning and offering insights for researchers seeking to expand the boundaries of computational music. Unlike text and images, which are often semantically or visually intuitive, music primarily interacts with humans through auditory perception, making its data representation inherently less intuitive. Therefore, this paper first introduces the representations of music and provides an overview of music datasets. Subsequently, we categorize cross-modal interactions between music and multimodal data into three types: music-driven cross-modal interactions, music-oriented cross-modal interactions, and bidirectional music cross-modal interactions. For each category, we systematically trace the development of relevant sub-tasks, analyze existing limitations, and discuss emerging trends. Furthermore, we provide a comprehensive summary of datasets and evaluation metrics used in multimodal tasks related to music, offering benchmark references for future research. Finally, we discuss the current challenges in cross-modal interactions involving music and propose potential directions for future research.
Short-video Propagation Influence Rating: A New Real-world Dataset and A New Large Graph Model
Mar 31, 2025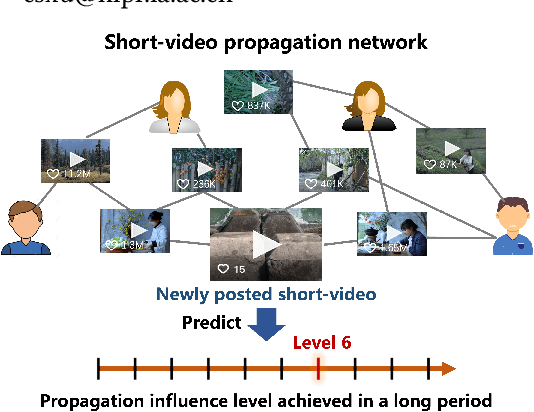
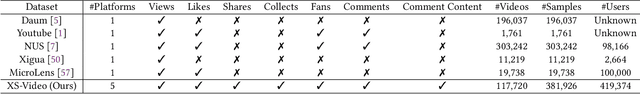

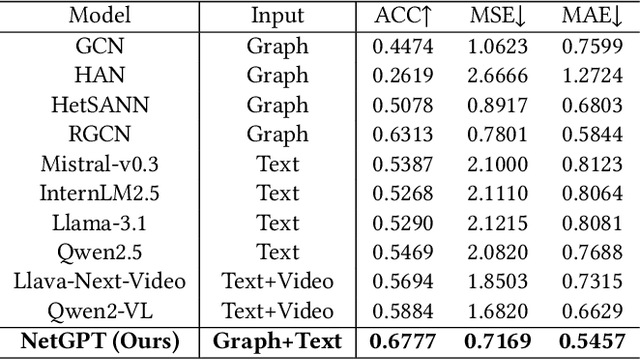
Abstract:Short-video platforms have gained immense popularity, captivating the interest of millions, if not billions, of users globally. Recently, researchers have highlighted the significance of analyzing the propagation of short-videos, which typically involves discovering commercial values, public opinions, user behaviors, etc. This paper proposes a new Short-video Propagation Influence Rating (SPIR) task and aims to promote SPIR from both the dataset and method perspectives. First, we propose a new Cross-platform Short-Video (XS-Video) dataset, which aims to provide a large-scale and real-world short-video propagation network across various platforms to facilitate the research on short-video propagation. Our XS-Video dataset includes 117,720 videos, 381,926 samples, and 535 topics across 5 biggest Chinese platforms, annotated with the propagation influence from level 0 to 9. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first large-scale short-video dataset that contains cross-platform data or provides all of the views, likes, shares, collects, fans, comments, and comment content. Second, we propose a Large Graph Model (LGM) named NetGPT, based on a novel three-stage training mechanism, to bridge heterogeneous graph-structured data with the powerful reasoning ability and knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs). Our NetGPT can comprehend and analyze the short-video propagation graph, enabling it to predict the long-term propagation influence of short-videos. Comprehensive experimental results evaluated by both classification and regression metrics on our XS-Video dataset indicate the superiority of our method for SPIR.
Language Guided Concept Bottleneck Models for Interpretable Continual Learning
Mar 30, 2025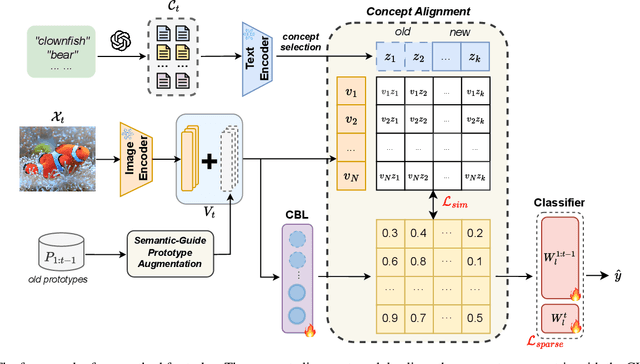
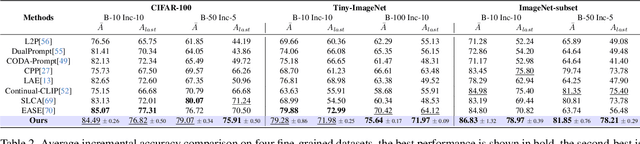
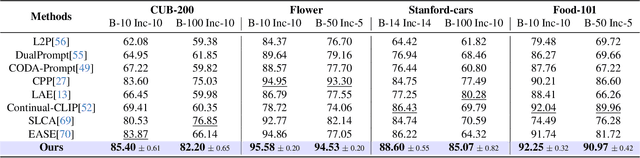
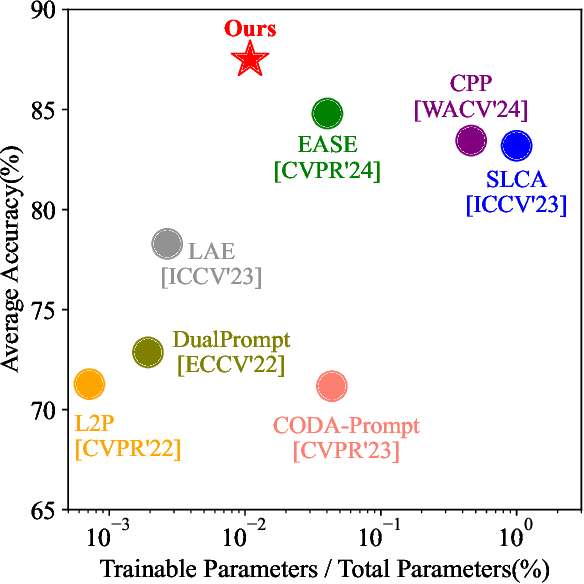
Abstract:Continual learning (CL) aims to enable learning systems to acquire new knowledge constantly without forgetting previously learned information. CL faces the challenge of mitigating catastrophic forgetting while maintaining interpretability across tasks. Most existing CL methods focus primarily on preserving learned knowledge to improve model performance. However, as new information is introduced, the interpretability of the learning process becomes crucial for understanding the evolving decision-making process, yet it is rarely explored. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework that integrates language-guided Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) to address both challenges. Our approach leverages the Concept Bottleneck Layer, aligning semantic consistency with CLIP models to learn human-understandable concepts that can generalize across tasks. By focusing on interpretable concepts, our method not only enhances the models ability to retain knowledge over time but also provides transparent decision-making insights. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by achieving superior performance on several datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods with an improvement of up to 3.06% in final average accuracy on ImageNet-subset. Additionally, we offer concept visualizations for model predictions, further advancing the understanding of interpretable continual learning.
Efficient Multi-Instance Generation with Janus-Pro-Dirven Prompt Parsing
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-guided diffusion models have revolutionized conditional image generation, yet they struggle to synthesize complex scenes with multiple objects due to imprecise spatial grounding and limited scalability. We address these challenges through two key modules: 1) Janus-Pro-driven Prompt Parsing, a prompt-layout parsing module that bridges text understanding and layout generation via a compact 1B-parameter architecture, and 2) MIGLoRA, a parameter-efficient plug-in integrating Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) into UNet (SD1.5) and DiT (SD3) backbones. MIGLoRA is capable of preserving the base model's parameters and ensuring plug-and-play adaptability, minimizing architectural intrusion while enabling efficient fine-tuning. To support a comprehensive evaluation, we create DescripBox and DescripBox-1024, benchmarks that span diverse scenes and resolutions. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on COCO and LVIS benchmarks while maintaining parameter efficiency, demonstrating superior layout fidelity and scalability for open-world synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge