Junyang Wang
Mobile-Agent-v3: Foundamental Agents for GUI Automation
Aug 21, 2025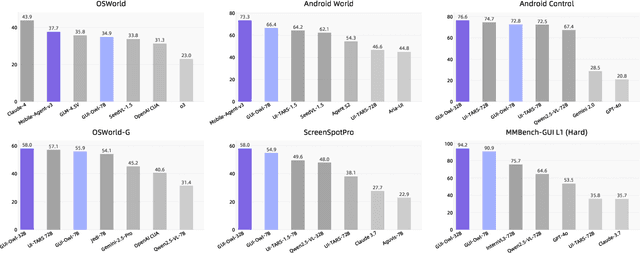
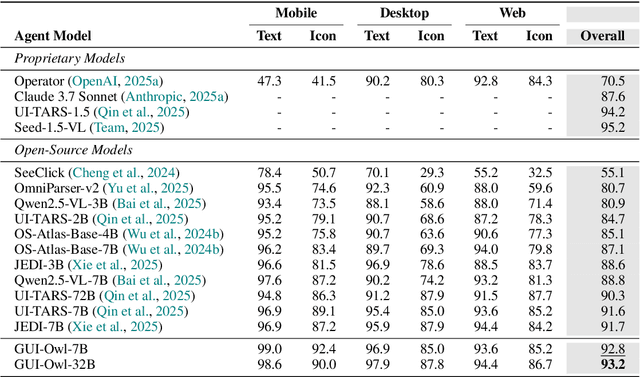
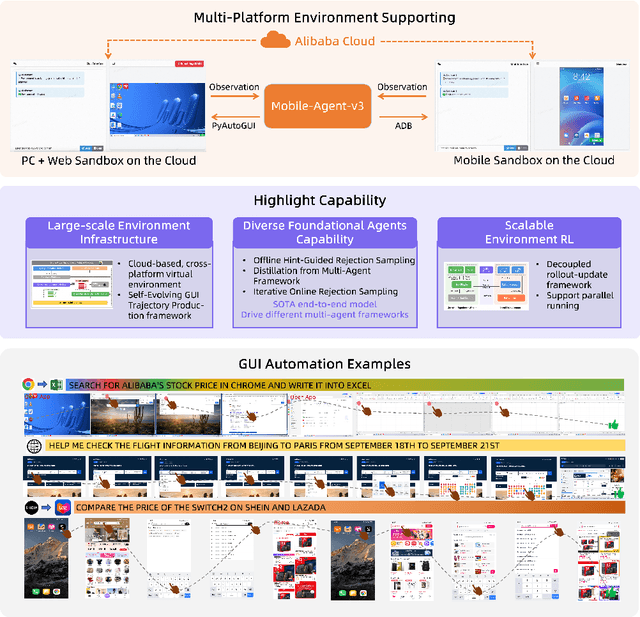
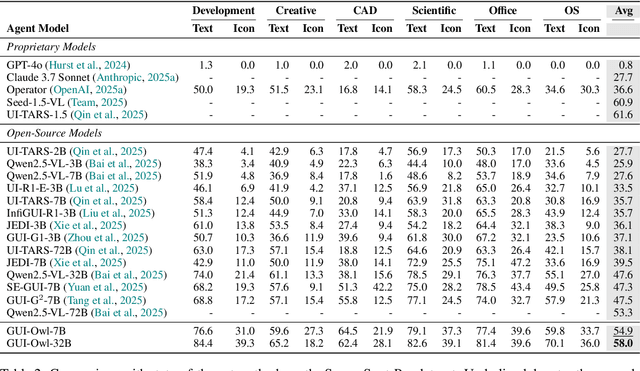
Abstract:This paper introduces GUI-Owl, a foundational GUI agent model that achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source end-to-end models on ten GUI benchmarks across desktop and mobile environments, covering grounding, question answering, planning, decision-making, and procedural knowledge. GUI-Owl-7B achieves 66.4 on AndroidWorld and 29.4 on OSWorld. Building on this, we propose Mobile-Agent-v3, a general-purpose GUI agent framework that further improves performance to 73.3 on AndroidWorld and 37.7 on OSWorld, setting a new state-of-the-art for open-source GUI agent frameworks. GUI-Owl incorporates three key innovations: (1) Large-scale Environment Infrastructure: a cloud-based virtual environment spanning Android, Ubuntu, macOS, and Windows, enabling our Self-Evolving GUI Trajectory Production framework. This generates high-quality interaction data via automated query generation and correctness validation, leveraging GUI-Owl to refine trajectories iteratively, forming a self-improving loop. It supports diverse data pipelines and reduces manual annotation. (2) Diverse Foundational Agent Capabilities: by integrating UI grounding, planning, action semantics, and reasoning patterns, GUI-Owl supports end-to-end decision-making and can act as a modular component in multi-agent systems. (3) Scalable Environment RL: we develop a scalable reinforcement learning framework with fully asynchronous training for real-world alignment. We also introduce Trajectory-aware Relative Policy Optimization (TRPO) for online RL, achieving 34.9 on OSWorld. GUI-Owl and Mobile-Agent-v3 are open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
Look Before You Leap: A GUI-Critic-R1 Model for Pre-Operative Error Diagnosis in GUI Automation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been extensively utilized for multimodal reasoning tasks, including Graphical User Interface (GUI) automation. Unlike general offline multimodal tasks, GUI automation is executed in online interactive environments, necessitating step-by-step decision-making based on real-time status of the environment. This task has a lower tolerance for decision-making errors at each step, as any mistakes may cumulatively disrupt the process and potentially lead to irreversible outcomes like deletions or payments. To address these issues, we introduce a pre-operative critic mechanism that provides effective feedback prior to the actual execution, by reasoning about the potential outcome and correctness of actions. Specifically, we propose a Suggestion-aware Gradient Relative Policy Optimization (S-GRPO) strategy to construct our pre-operative critic model GUI-Critic-R1, incorporating a novel suggestion reward to enhance the reliability of the model's feedback. Furthermore, we develop a reasoning-bootstrapping based data collection pipeline to create a GUI-Critic-Train and a GUI-Critic-Test, filling existing gaps in GUI critic data. Static experiments on the GUI-Critic-Test across both mobile and web domains reveal that our GUI-Critic-R1 offers significant advantages in critic accuracy compared to current MLLMs. Dynamic evaluation on GUI automation benchmark further highlights the effectiveness and superiority of our model, as evidenced by improved success rates and operational efficiency.
Mobile-Agent-V: A Video-Guided Approach for Effortless and Efficient Operational Knowledge Injection in Mobile Automation
May 21, 2025Abstract:The exponential rise in mobile device usage necessitates streamlined automation for effective task management, yet many AI frameworks fall short due to inadequate operational expertise. While manually written knowledge can bridge this gap, it is often burdensome and inefficient. We introduce Mobile-Agent-V, an innovative framework that utilizes video as a guiding tool to effortlessly and efficiently inject operational knowledge into mobile automation processes. By deriving knowledge directly from video content, Mobile-Agent-V eliminates manual intervention, significantly reducing the effort and time required for knowledge acquisition. To rigorously evaluate this approach, we propose Mobile-Knowledge, a benchmark tailored to assess the impact of external knowledge on mobile agent performance. Our experimental findings demonstrate that Mobile-Agent-V enhances performance by 36% compared to existing methods, underscoring its effortless and efficient advantages in mobile automation.
Mobile-Agent-V: Learning Mobile Device Operation Through Video-Guided Multi-Agent Collaboration
Feb 25, 2025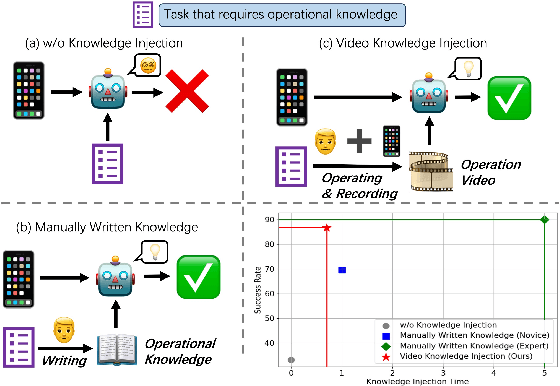
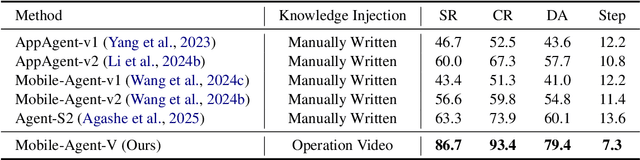
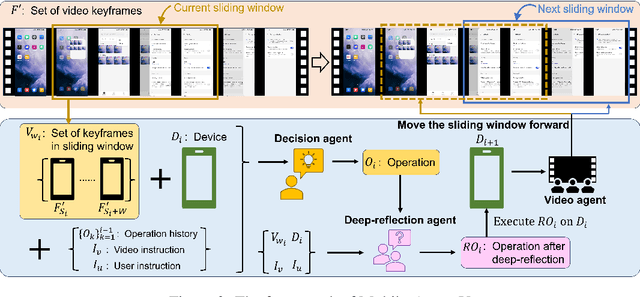
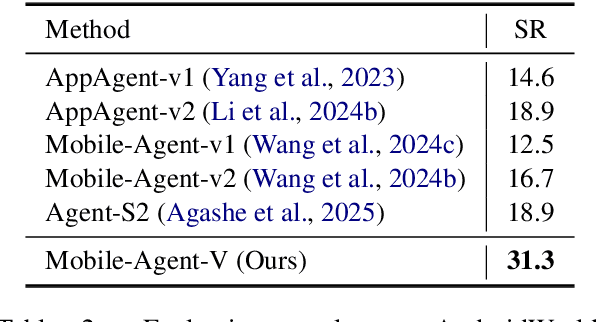
Abstract:The rapid increase in mobile device usage necessitates improved automation for seamless task management. However, many AI-driven frameworks struggle due to insufficient operational knowledge. Manually written knowledge helps but is labor-intensive and inefficient. To address these challenges, we introduce Mobile-Agent-V, a framework that leverages video guidance to provide rich and cost-effective operational knowledge for mobile automation. Mobile-Agent-V enhances task execution capabilities by leveraging video inputs without requiring specialized sampling or preprocessing. Mobile-Agent-V integrates a sliding window strategy and incorporates a video agent and deep-reflection agent to ensure that actions align with user instructions. Through this innovative approach, users can record task processes with guidance, enabling the system to autonomously learn and execute tasks efficiently. Experimental results show that Mobile-Agent-V achieves a 30% performance improvement compared to existing frameworks. The code will be open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
PC-Agent: A Hierarchical Multi-Agent Collaboration Framework for Complex Task Automation on PC
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:In the field of MLLM-based GUI agents, compared to smartphones, the PC scenario not only features a more complex interactive environment, but also involves more intricate intra- and inter-app workflows. To address these issues, we propose a hierarchical agent framework named PC-Agent. Specifically, from the perception perspective, we devise an Active Perception Module (APM) to overcome the inadequate abilities of current MLLMs in perceiving screenshot content. From the decision-making perspective, to handle complex user instructions and interdependent subtasks more effectively, we propose a hierarchical multi-agent collaboration architecture that decomposes decision-making processes into Instruction-Subtask-Action levels. Within this architecture, three agents (i.e., Manager, Progress and Decision) are set up for instruction decomposition, progress tracking and step-by-step decision-making respectively. Additionally, a Reflection agent is adopted to enable timely bottom-up error feedback and adjustment. We also introduce a new benchmark PC-Eval with 25 real-world complex instructions. Empirical results on PC-Eval show that our PC-Agent achieves a 32% absolute improvement of task success rate over previous state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent/tree/main/PC-Agent.
Mobile-Agent-E: Self-Evolving Mobile Assistant for Complex Tasks
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:Smartphones have become indispensable in modern life, yet navigating complex tasks on mobile devices often remains frustrating. Recent advancements in large multimodal model (LMM)-based mobile agents have demonstrated the ability to perceive and act in mobile environments. However, current approaches face significant limitations: they fall short in addressing real-world human needs, struggle with reasoning-intensive and long-horizon tasks, and lack mechanisms to learn and improve from prior experiences. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Mobile-Agent-E, a hierarchical multi-agent framework capable of self-evolution through past experience. By hierarchical, we mean an explicit separation of high-level planning and low-level action execution. The framework comprises a Manager, responsible for devising overall plans by breaking down complex tasks into subgoals, and four subordinate agents--Perceptor, Operator, Action Reflector, and Notetaker--which handle fine-grained visual perception, immediate action execution, error verification, and information aggregation, respectively. Mobile-Agent-E also features a novel self-evolution module which maintains a persistent long-term memory comprising Tips and Shortcuts. Tips are general guidance and lessons learned from prior tasks on how to effectively interact with the environment. Shortcuts are reusable, executable sequences of atomic operations tailored for specific subroutines. The inclusion of Tips and Shortcuts facilitates continuous refinement in performance and efficiency. Alongside this framework, we introduce Mobile-Eval-E, a new benchmark featuring complex mobile tasks requiring long-horizon, multi-app interactions. Empirical results show that Mobile-Agent-E achieves a 22% absolute improvement over previous state-of-the-art approaches across three foundation model backbones. Project page: https://x-plug.github.io/MobileAgent.
RemoteRAG: A Privacy-Preserving LLM Cloud RAG Service
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) improves the service quality of large language models by retrieving relevant documents from credible literature and integrating them into the context of the user query. Recently, the rise of the cloud RAG service has made it possible for users to query relevant documents conveniently. However, directly sending queries to the cloud brings potential privacy leakage. In this paper, we are the first to formally define the privacy-preserving cloud RAG service to protect the user query and propose RemoteRAG as a solution regarding privacy, efficiency, and accuracy. For privacy, we introduce $(n,\epsilon)$-DistanceDP to characterize privacy leakage of the user query and the leakage inferred from relevant documents. For efficiency, we limit the search range from the total documents to a small number of selected documents related to a perturbed embedding generated from $(n,\epsilon)$-DistanceDP, so that computation and communication costs required for privacy protection significantly decrease. For accuracy, we ensure that the small range includes target documents related to the user query with detailed theoretical analysis. Experimental results also demonstrate that RemoteRAG can resist existing embedding inversion attack methods while achieving no loss in retrieval under various settings. Moreover, RemoteRAG is efficient, incurring only $0.67$ seconds and $46.66$KB of data transmission ($2.72$ hours and $1.43$ GB with the non-optimized privacy-preserving scheme) when retrieving from a total of $10^6$ documents.
Mobile-Agent-v2: Mobile Device Operation Assistant with Effective Navigation via Multi-Agent Collaboration
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Mobile device operation tasks are increasingly becoming a popular multi-modal AI application scenario. Current Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), constrained by their training data, lack the capability to function effectively as operation assistants. Instead, MLLM-based agents, which enhance capabilities through tool invocation, are gradually being applied to this scenario. However, the two major navigation challenges in mobile device operation tasks, task progress navigation and focus content navigation, are significantly complicated under the single-agent architecture of existing work. This is due to the overly long token sequences and the interleaved text-image data format, which limit performance. To address these navigation challenges effectively, we propose Mobile-Agent-v2, a multi-agent architecture for mobile device operation assistance. The architecture comprises three agents: planning agent, decision agent, and reflection agent. The planning agent generates task progress, making the navigation of history operations more efficient. To retain focus content, we design a memory unit that updates with task progress. Additionally, to correct erroneous operations, the reflection agent observes the outcomes of each operation and handles any mistakes accordingly. Experimental results indicate that Mobile-Agent-v2 achieves over a 30% improvement in task completion compared to the single-agent architecture of Mobile-Agent. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
Mobile-Agent: Autonomous Multi-Modal Mobile Device Agent with Visual Perception
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Mobile device agent based on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) is becoming a popular application. In this paper, we introduce Mobile-Agent, an autonomous multi-modal mobile device agent. Mobile-Agent first leverages visual perception tools to accurately identify and locate both the visual and textual elements within the app's front-end interface. Based on the perceived vision context, it then autonomously plans and decomposes the complex operation task, and navigates the mobile Apps through operations step by step. Different from previous solutions that rely on XML files of Apps or mobile system metadata, Mobile-Agent allows for greater adaptability across diverse mobile operating environments in a vision-centric way, thereby eliminating the necessity for system-specific customizations. To assess the performance of Mobile-Agent, we introduced Mobile-Eval, a benchmark for evaluating mobile device operations. Based on Mobile-Eval, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation of Mobile-Agent. The experimental results indicate that Mobile-Agent achieved remarkable accuracy and completion rates. Even with challenging instructions, such as multi-app operations, Mobile-Agent can still complete the requirements. Code and model will be open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
An LLM-free Multi-dimensional Benchmark for MLLMs Hallucination Evaluation
Nov 13, 2023Abstract:Despite making significant progress in multi-modal tasks, current Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) encounter the significant challenge of hallucination, which may lead to harmful consequences. Therefore, evaluating MLLMs' hallucinations is becoming increasingly important in model improvement and practical application deployment. Previous works are limited in high evaluation costs (e.g., relying on humans or advanced LLMs) and insufficient evaluation dimensions (e.g., types of hallucination and task). In this paper, we propose an LLM-free multi-dimensional benchmark AMBER, which can be used to evaluate both generative task and discriminative task including object existence, object attribute and object relation hallucination. Based on AMBER, we design a low-cost and efficient evaluation pipeline. Additionally, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation and detailed analysis of mainstream MLLMs including GPT-4V(ision), and also give guideline suggestions for mitigating hallucinations. The data and code of AMBER are available at https://github.com/junyangwang0410/AMBER.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge