Ziwei Zheng
Systematic Characterization of Minimal Deep Learning Architectures: A Unified Analysis of Convergence, Pruning, and Quantization
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Deep learning networks excel at classification, yet identifying minimal architectures that reliably solve a task remains challenging. We present a computational methodology for systematically exploring and analyzing the relationships among convergence, pruning, and quantization. The workflow first performs a structured design sweep across a large set of architectures, then evaluates convergence behavior, pruning sensitivity, and quantization robustness on representative models. Focusing on well-known image classification of increasing complexity, and across Deep Neural Networks, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Vision Transformers, our initial results show that, despite architectural diversity, performance is largely invariant and learning dynamics consistently exhibit three regimes: unstable, learning, and overfitting. We further characterize the minimal learnable parameters required for stable learning, uncover distinct convergence and pruning phases, and quantify the effect of reduced numeric precision on trainable parameters. Aligning with intuition, the results confirm that deeper architectures are more resilient to pruning than shallower ones, with parameter redundancy as high as 60%, and quantization impacts models with fewer learnable parameters more severely and has a larger effect on harder image datasets. These findings provide actionable guidance for selecting compact, stable models under pruning and low-precision constraints in image classification.
HeadHunt-VAD: Hunting Robust Anomaly-Sensitive Heads in MLLM for Tuning-Free Video Anomaly Detection
Dec 23, 2025
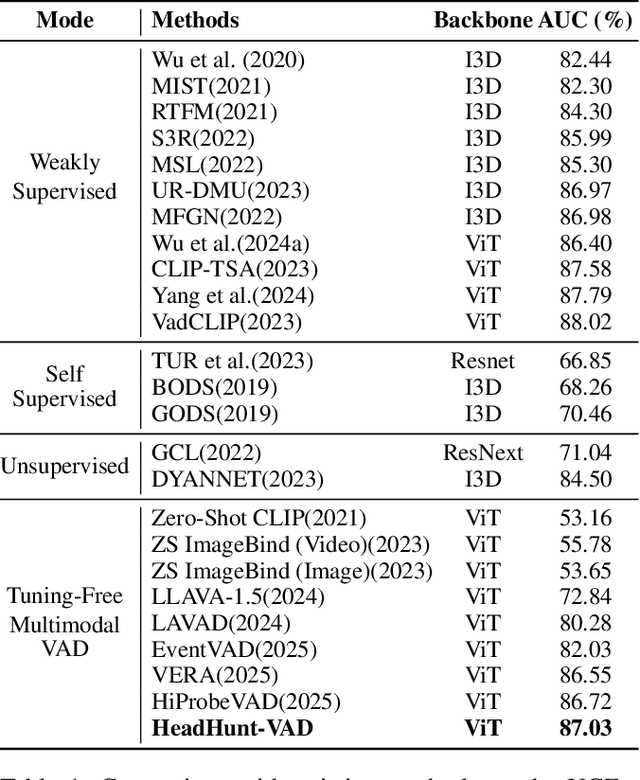
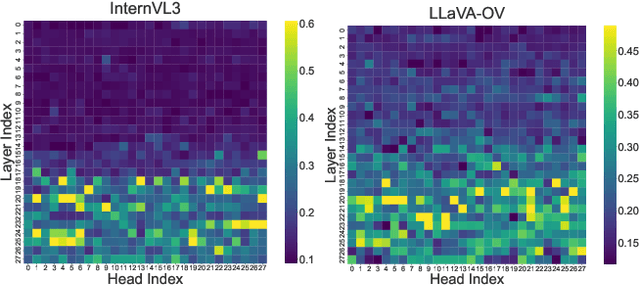
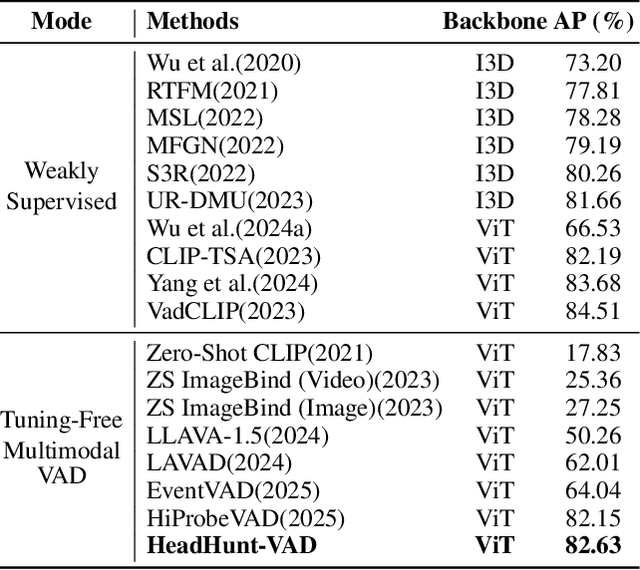
Abstract:Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) aims to locate events that deviate from normal patterns in videos. Traditional approaches often rely on extensive labeled data and incur high computational costs. Recent tuning-free methods based on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offer a promising alternative by leveraging their rich world knowledge. However, these methods typically rely on textual outputs, which introduces information loss, exhibits normalcy bias, and suffers from prompt sensitivity, making them insufficient for capturing subtle anomalous cues. To address these constraints, we propose HeadHunt-VAD, a novel tuning-free VAD paradigm that bypasses textual generation by directly hunting robust anomaly-sensitive internal attention heads within the frozen MLLM. Central to our method is a Robust Head Identification module that systematically evaluates all attention heads using a multi-criteria analysis of saliency and stability, identifying a sparse subset of heads that are consistently discriminative across diverse prompts. Features from these expert heads are then fed into a lightweight anomaly scorer and a temporal locator, enabling efficient and accurate anomaly detection with interpretable outputs. Extensive experiments show that HeadHunt-VAD achieves state-of-the-art performance among tuning-free methods on two major VAD benchmarks while maintaining high efficiency, validating head-level probing in MLLMs as a powerful and practical solution for real-world anomaly detection.
Mobile-Agent-v3: Foundamental Agents for GUI Automation
Aug 21, 2025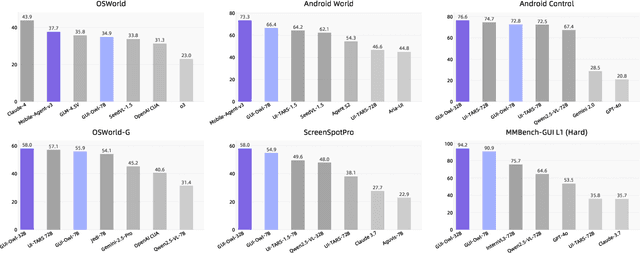
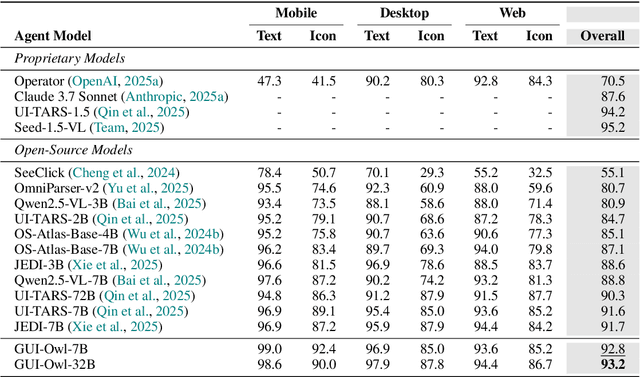
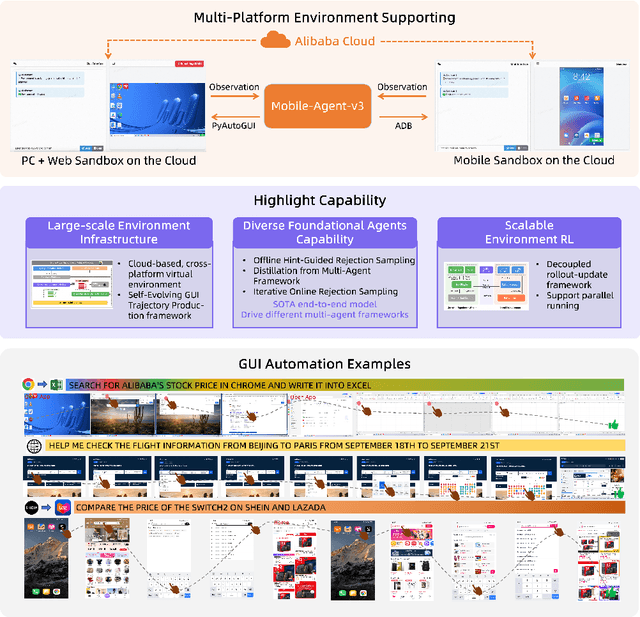
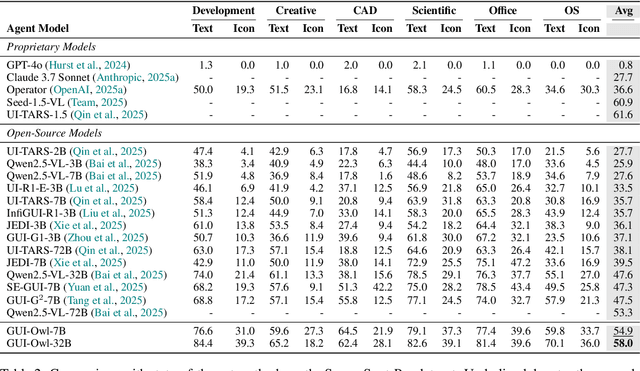
Abstract:This paper introduces GUI-Owl, a foundational GUI agent model that achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source end-to-end models on ten GUI benchmarks across desktop and mobile environments, covering grounding, question answering, planning, decision-making, and procedural knowledge. GUI-Owl-7B achieves 66.4 on AndroidWorld and 29.4 on OSWorld. Building on this, we propose Mobile-Agent-v3, a general-purpose GUI agent framework that further improves performance to 73.3 on AndroidWorld and 37.7 on OSWorld, setting a new state-of-the-art for open-source GUI agent frameworks. GUI-Owl incorporates three key innovations: (1) Large-scale Environment Infrastructure: a cloud-based virtual environment spanning Android, Ubuntu, macOS, and Windows, enabling our Self-Evolving GUI Trajectory Production framework. This generates high-quality interaction data via automated query generation and correctness validation, leveraging GUI-Owl to refine trajectories iteratively, forming a self-improving loop. It supports diverse data pipelines and reduces manual annotation. (2) Diverse Foundational Agent Capabilities: by integrating UI grounding, planning, action semantics, and reasoning patterns, GUI-Owl supports end-to-end decision-making and can act as a modular component in multi-agent systems. (3) Scalable Environment RL: we develop a scalable reinforcement learning framework with fully asynchronous training for real-world alignment. We also introduce Trajectory-aware Relative Policy Optimization (TRPO) for online RL, achieving 34.9 on OSWorld. GUI-Owl and Mobile-Agent-v3 are open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
HiProbe-VAD: Video Anomaly Detection via Hidden States Probing in Tuning-Free Multimodal LLMs
Jul 23, 2025



Abstract:Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) aims to identify and locate deviations from normal patterns in video sequences. Traditional methods often struggle with substantial computational demands and a reliance on extensive labeled datasets, thereby restricting their practical applicability. To address these constraints, we propose HiProbe-VAD, a novel framework that leverages pre-trained Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for VAD without requiring fine-tuning. In this paper, we discover that the intermediate hidden states of MLLMs contain information-rich representations, exhibiting higher sensitivity and linear separability for anomalies compared to the output layer. To capitalize on this, we propose a Dynamic Layer Saliency Probing (DLSP) mechanism that intelligently identifies and extracts the most informative hidden states from the optimal intermediate layer during the MLLMs reasoning. Then a lightweight anomaly scorer and temporal localization module efficiently detects anomalies using these extracted hidden states and finally generate explanations. Experiments on the UCF-Crime and XD-Violence datasets demonstrate that HiProbe-VAD outperforms existing training-free and most traditional approaches. Furthermore, our framework exhibits remarkable cross-model generalization capabilities in different MLLMs without any tuning, unlocking the potential of pre-trained MLLMs for video anomaly detection and paving the way for more practical and scalable solutions.
Seeing It or Not? Interpretable Vision-aware Latent Steering to Mitigate Object Hallucinations
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable success but continue to struggle with object hallucination (OH), generating outputs inconsistent with visual inputs. While previous work has proposed methods to reduce OH, the visual decision-making mechanisms that lead to hallucinations remain poorly understood. In this paper, we propose VaLSe, a Vision-aware Latent Steering framework that adopts an interpretation-then-mitigation strategy to address OH in LVLMs. By tackling dual challenges of modeling complex vision-language interactions and eliminating spurious activation artifacts, VaLSe can generate visual contribution maps that trace how specific visual inputs influence individual output tokens. These maps reveal the model's vision-aware focus regions, which are then used to perform latent space steering, realigning internal representations toward semantically relevant content and reducing hallucinated outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VaLSe is a powerful interpretability tool and an effective method for enhancing model robustness against OH across multiple benchmarks. Furthermore, our analysis uncovers limitations in existing OH evaluation metrics, underscoring the need for more nuanced, interpretable, and visually grounded OH benchmarks in future work. Code is available at: https://github.com/Ziwei-Zheng/VaLSe.
DeepEyes: Incentivizing "Thinking with Images" via Reinforcement Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown strong capabilities in multimodal understanding and reasoning, yet they are primarily constrained by text-based reasoning processes. However, achieving seamless integration of visual and textual reasoning which mirrors human cognitive processes remains a significant challenge. In particular, effectively incorporating advanced visual input processing into reasoning mechanisms is still an open question. Thus, in this paper, we explore the interleaved multimodal reasoning paradigm and introduce DeepEyes, a model with "thinking with images" capabilities incentivized through end-to-end reinforcement learning without the need for cold-start SFT. Notably, this ability emerges natively within the model itself, leveraging its inherent grounding ability as a tool instead of depending on separate specialized models. Specifically, we propose a tool-use-oriented data selection mechanism and a reward strategy to encourage successful tool-assisted reasoning trajectories. DeepEyes achieves significant performance gains on fine-grained perception and reasoning benchmarks and also demonstrates improvement in grounding, hallucination, and mathematical reasoning tasks. Interestingly, we observe the distinct evolution of tool-calling behavior from initial exploration to efficient and accurate exploitation, and diverse thinking patterns that closely mirror human visual reasoning processes. Code is available at https://github.com/Visual-Agent/DeepEyes.
Spot Risks Before Speaking! Unraveling Safety Attention Heads in Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:With the integration of an additional modality, large vision-language models (LVLMs) exhibit greater vulnerability to safety risks (e.g., jailbreaking) compared to their language-only predecessors. Although recent studies have devoted considerable effort to the post-hoc alignment of LVLMs, the inner safety mechanisms remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we discover that internal activations of LVLMs during the first token generation can effectively identify malicious prompts across different attacks. This inherent safety perception is governed by sparse attention heads, which we term ``safety heads." Further analysis reveals that these heads act as specialized shields against malicious prompts; ablating them leads to higher attack success rates, while the model's utility remains unaffected. By locating these safety heads and concatenating their activations, we construct a straightforward but powerful malicious prompt detector that integrates seamlessly into the generation process with minimal extra inference overhead. Despite its simple structure of a logistic regression model, the detector surprisingly exhibits strong zero-shot generalization capabilities. Experiments across various prompt-based attacks confirm the effectiveness of leveraging safety heads to protect LVLMs. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/Ziwei-Zheng/SAHs}.
Nullu: Mitigating Object Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models via HalluSpace Projection
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Recent studies have shown that large vision-language models (LVLMs) often suffer from the issue of object hallucinations (OH). To mitigate this issue, we introduce an efficient method that edits the model weights based on an unsafe subspace, which we call HalluSpace in this paper. With truthful and hallucinated text prompts accompanying the visual content as inputs, the HalluSpace can be identified by extracting the hallucinated embedding features and removing the truthful representations in LVLMs. By orthogonalizing the model weights, input features will be projected into the Null space of the HalluSpace to reduce OH, based on which we name our method Nullu. We reveal that HalluSpaces generally contain statistical bias and unimodal priors of the large language models (LLMs) applied to build LVLMs, which have been shown as essential causes of OH in previous studies. Therefore, null space projection suppresses the LLMs' priors to filter out the hallucinated features, resulting in contextually accurate outputs. Experiments show that our method can effectively mitigate OH across different LVLM families without extra inference costs and also show strong performance in general LVLM benchmarks. Code is released at \url{https://github.com/Ziwei-Zheng/Nullu}.
OStr-DARTS: Differentiable Neural Architecture Search based on Operation Strength
Sep 22, 2024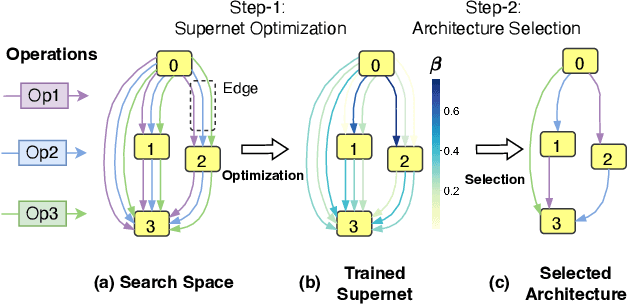
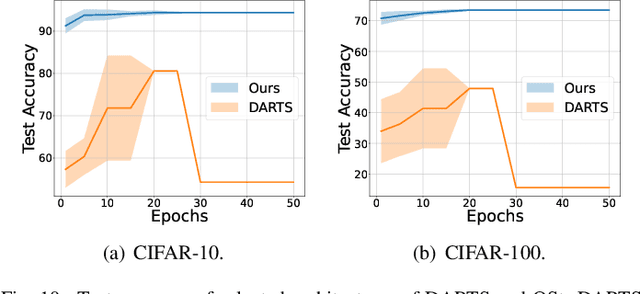
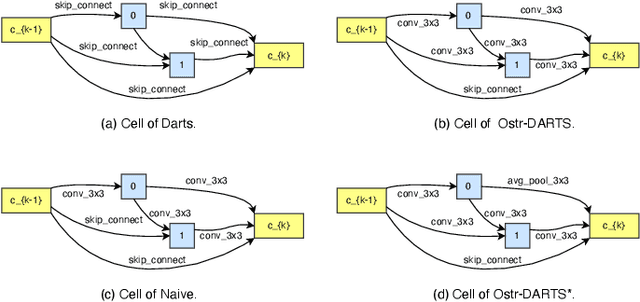
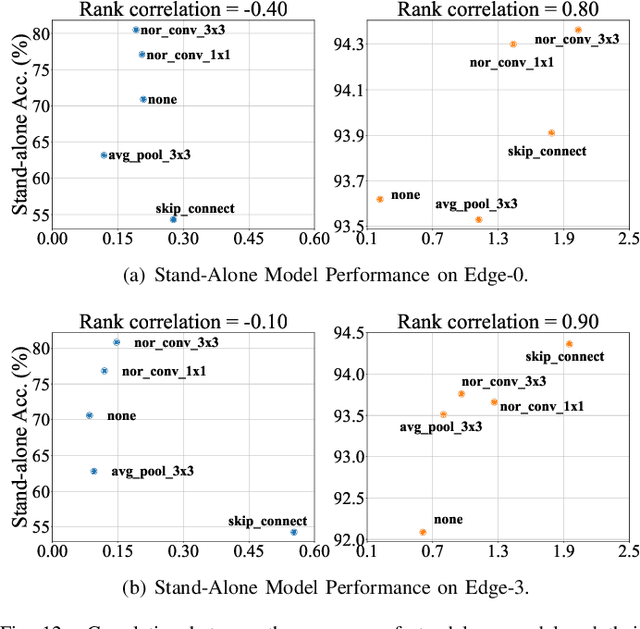
Abstract:Differentiable architecture search (DARTS) has emerged as a promising technique for effective neural architecture search, and it mainly contains two steps to find the high-performance architecture: First, the DARTS supernet that consists of mixed operations will be optimized via gradient descent. Second, the final architecture will be built by the selected operations that contribute the most to the supernet. Although DARTS improves the efficiency of NAS, it suffers from the well-known degeneration issue which can lead to deteriorating architectures. Existing works mainly attribute the degeneration issue to the failure of its supernet optimization, while little attention has been paid to the selection method. In this paper, we cease to apply the widely-used magnitude-based selection method and propose a novel criterion based on operation strength that estimates the importance of an operation by its effect on the final loss. We show that the degeneration issue can be effectively addressed by using the proposed criterion without any modification of supernet optimization, indicating that the magnitude-based selection method can be a critical reason for the instability of DARTS. The experiments on NAS-Bench-201 and DARTS search spaces show the effectiveness of our method.
On Learnable Parameters of Optimal and Suboptimal Deep Learning Models
Aug 21, 2024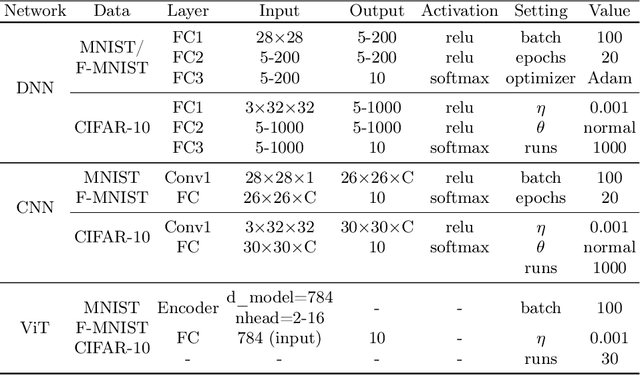
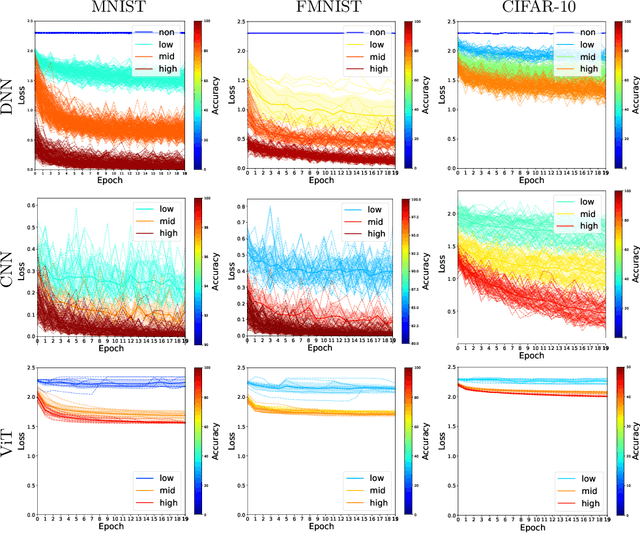
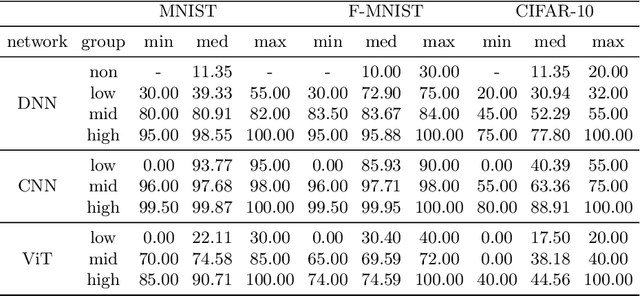
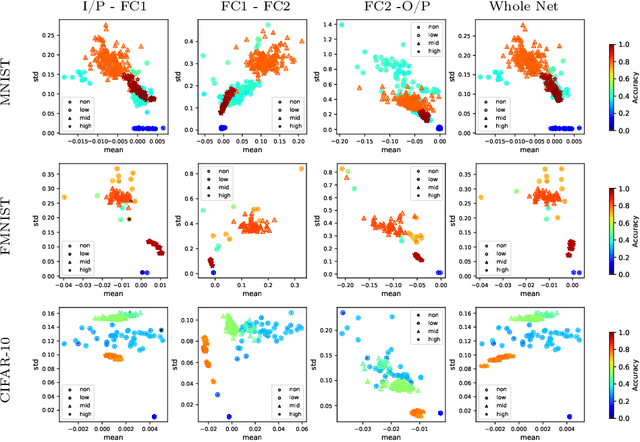
Abstract:We scrutinize the structural and operational aspects of deep learning models, particularly focusing on the nuances of learnable parameters (weight) statistics, distribution, node interaction, and visualization. By establishing correlations between variance in weight patterns and overall network performance, we investigate the varying (optimal and suboptimal) performances of various deep-learning models. Our empirical analysis extends across widely recognized datasets such as MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and CIFAR-10, and various deep learning models such as deep neural networks (DNNs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and vision transformer (ViT), enabling us to pinpoint characteristics of learnable parameters that correlate with successful networks. Through extensive experiments on the diverse architectures of deep learning models, we shed light on the critical factors that influence the functionality and efficiency of DNNs. Our findings reveal that successful networks, irrespective of datasets or models, are invariably similar to other successful networks in their converged weights statistics and distribution, while poor-performing networks vary in their weights. In addition, our research shows that the learnable parameters of widely varied deep learning models such as DNN, CNN, and ViT exhibit similar learning characteristics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge