Chenhao Lin
Pay Less Attention to Function Words for Free Robustness of Vision-Language Models
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:To address the trade-off between robustness and performance for robust VLM, we observe that function words could incur vulnerability of VLMs against cross-modal adversarial attacks, and propose Function-word De-Attention (FDA) accordingly to mitigate the impact of function words. Similar to differential amplifiers, our FDA calculates the original and the function-word cross-attention within attention heads, and differentially subtracts the latter from the former for more aligned and robust VLMs. Comprehensive experiments include 2 SOTA baselines under 6 different attacks on 2 downstream tasks, 3 datasets, and 3 models. Overall, our FDA yields an average 18/13/53% ASR drop with only 0.2/0.3/0.6% performance drops on the 3 tested models on retrieval, and a 90% ASR drop with a 0.3% performance gain on visual grounding. We demonstrate the scalability, generalization, and zero-shot performance of FDA experimentally, as well as in-depth ablation studies and analysis. Code will be made publicly at https://github.com/michaeltian108/FDA.
Multi-modal Deepfake Detection and Localization with FPN-Transformer
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models has enabled the creation of highly realistic deepfake content, posing significant threats to digital trust across audio-visual domains. While unimodal detection methods have shown progress in identifying synthetic media, their inability to leverage cross-modal correlations and precisely localize forged segments limits their practicality against sophisticated, fine-grained manipulations. To address this, we introduce a multi-modal deepfake detection and localization framework based on a Feature Pyramid-Transformer (FPN-Transformer), addressing critical gaps in cross-modal generalization and temporal boundary regression. The proposed approach utilizes pre-trained self-supervised models (WavLM for audio, CLIP for video) to extract hierarchical temporal features. A multi-scale feature pyramid is constructed through R-TLM blocks with localized attention mechanisms, enabling joint analysis of cross-context temporal dependencies. The dual-branch prediction head simultaneously predicts forgery probabilities and refines temporal offsets of manipulated segments, achieving frame-level localization precision. We evaluate our approach on the test set of the IJCAI'25 DDL-AV benchmark, showing a good performance with a final score of 0.7535 for cross-modal deepfake detection and localization in challenging environments. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of our approach and provide a novel way for generalized deepfake detection. Our code is available at https://github.com/Zig-HS/MM-DDL
JADES: A Universal Framework for Jailbreak Assessment via Decompositional Scoring
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Accurately determining whether a jailbreak attempt has succeeded is a fundamental yet unresolved challenge. Existing evaluation methods rely on misaligned proxy indicators or naive holistic judgments. They frequently misinterpret model responses, leading to inconsistent and subjective assessments that misalign with human perception. To address this gap, we introduce JADES (Jailbreak Assessment via Decompositional Scoring), a universal jailbreak evaluation framework. Its key mechanism is to automatically decompose an input harmful question into a set of weighted sub-questions, score each sub-answer, and weight-aggregate the sub-scores into a final decision. JADES also incorporates an optional fact-checking module to strengthen the detection of hallucinations in jailbreak responses. We validate JADES on JailbreakQR, a newly introduced benchmark proposed in this work, consisting of 400 pairs of jailbreak prompts and responses, each meticulously annotated by humans. In a binary setting (success/failure), JADES achieves 98.5% agreement with human evaluators, outperforming strong baselines by over 9%. Re-evaluating five popular attacks on four LLMs reveals substantial overestimation (e.g., LAA's attack success rate on GPT-3.5-Turbo drops from 93% to 69%). Our results show that JADES could deliver accurate, consistent, and interpretable evaluations, providing a reliable basis for measuring future jailbreak attacks.
Adversarial Video Promotion Against Text-to-Video Retrieval
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Thanks to the development of cross-modal models, text-to-video retrieval (T2VR) is advancing rapidly, but its robustness remains largely unexamined. Existing attacks against T2VR are designed to push videos away from queries, i.e., suppressing the ranks of videos, while the attacks that pull videos towards selected queries, i.e., promoting the ranks of videos, remain largely unexplored. These attacks can be more impactful as attackers may gain more views/clicks for financial benefits and widespread (mis)information. To this end, we pioneer the first attack against T2VR to promote videos adversarially, dubbed the Video Promotion attack (ViPro). We further propose Modal Refinement (MoRe) to capture the finer-grained, intricate interaction between visual and textual modalities to enhance black-box transferability. Comprehensive experiments cover 2 existing baselines, 3 leading T2VR models, 3 prevailing datasets with over 10k videos, evaluated under 3 scenarios. All experiments are conducted in a multi-target setting to reflect realistic scenarios where attackers seek to promote the video regarding multiple queries simultaneously. We also evaluated our attacks for defences and imperceptibility. Overall, ViPro surpasses other baselines by over $30/10/4\%$ for white/grey/black-box settings on average. Our work highlights an overlooked vulnerability, provides a qualitative analysis on the upper/lower bound of our attacks, and offers insights into potential counterplays. Code will be publicly available at https://github.com/michaeltian108/ViPro.
D3: Training-Free AI-Generated Video Detection Using Second-Order Features
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:The evolution of video generation techniques, such as Sora, has made it increasingly easy to produce high-fidelity AI-generated videos, raising public concern over the dissemination of synthetic content. However, existing detection methodologies remain limited by their insufficient exploration of temporal artifacts in synthetic videos. To bridge this gap, we establish a theoretical framework through second-order dynamical analysis under Newtonian mechanics, subsequently extending the Second-order Central Difference features tailored for temporal artifact detection. Building on this theoretical foundation, we reveal a fundamental divergence in second-order feature distributions between real and AI-generated videos. Concretely, we propose Detection by Difference of Differences (D3), a novel training-free detection method that leverages the above second-order temporal discrepancies. We validate the superiority of our D3 on 4 open-source datasets (Gen-Video, VideoPhy, EvalCrafter, VidProM), 40 subsets in total. For example, on GenVideo, D3 outperforms the previous best method by 10.39% (absolute) mean Average Precision. Additional experiments on time cost and post-processing operations demonstrate D3's exceptional computational efficiency and strong robust performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/Zig-HS/D3.
Revisiting Adversarial Patch Defenses on Object Detectors: Unified Evaluation, Large-Scale Dataset, and New Insights
Aug 01, 2025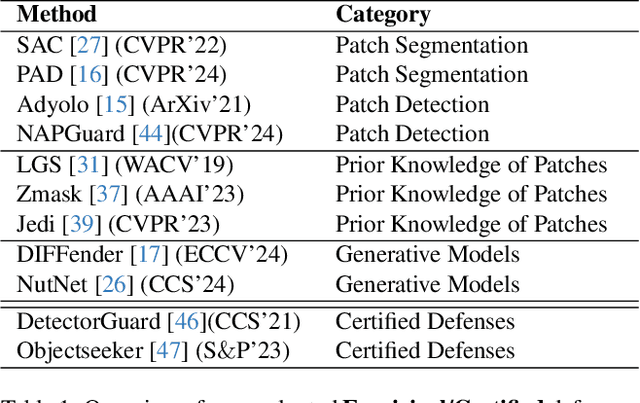

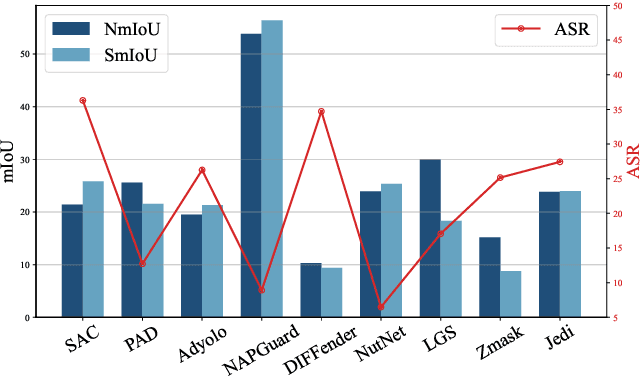
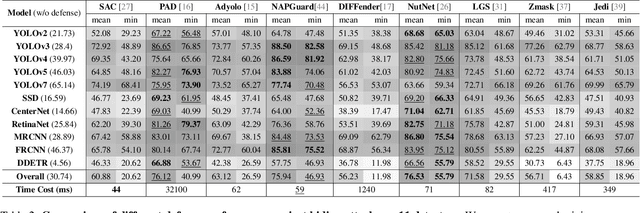
Abstract:Developing reliable defenses against patch attacks on object detectors has attracted increasing interest. However, we identify that existing defense evaluations lack a unified and comprehensive framework, resulting in inconsistent and incomplete assessments of current methods. To address this issue, we revisit 11 representative defenses and present the first patch defense benchmark, involving 2 attack goals, 13 patch attacks, 11 object detectors, and 4 diverse metrics. This leads to the large-scale adversarial patch dataset with 94 types of patches and 94,000 images. Our comprehensive analyses reveal new insights: (1) The difficulty in defending against naturalistic patches lies in the data distribution, rather than the commonly believed high frequencies. Our new dataset with diverse patch distributions can be used to improve existing defenses by 15.09% AP@0.5. (2) The average precision of the attacked object, rather than the commonly pursued patch detection accuracy, shows high consistency with defense performance. (3) Adaptive attacks can substantially bypass existing defenses, and defenses with complex/stochastic models or universal patch properties are relatively robust. We hope that our analyses will serve as guidance on properly evaluating patch attacks/defenses and advancing their design. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Gandolfczjh/APDE, where we will keep integrating new attacks/defenses.
Concept Unlearning by Modeling Key Steps of Diffusion Process
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models (T2I DMs), represented by Stable Diffusion, which generate highly realistic images based on textual input, have been widely used. However, their misuse poses serious security risks. While existing concept unlearning methods aim to mitigate these risks, they struggle to balance unlearning effectiveness with generative retainability.To overcome this limitation, we innovatively propose the Key Step Concept Unlearning (KSCU) method, which ingeniously capitalizes on the unique stepwise sampling characteristic inherent in diffusion models during the image generation process. Unlike conventional approaches that treat all denoising steps equally, KSCU strategically focuses on pivotal steps with the most influence over the final outcome by dividing key steps for different concept unlearning tasks and fine-tuning the model only at those steps. This targeted approach reduces the number of parameter updates needed for effective unlearning, while maximizing the retention of the model's generative capabilities.Through extensive benchmark experiments, we demonstrate that KSCU effectively prevents T2I DMs from generating undesirable images while better retaining the model's generative capabilities.Our code will be released.
Seeing It or Not? Interpretable Vision-aware Latent Steering to Mitigate Object Hallucinations
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable success but continue to struggle with object hallucination (OH), generating outputs inconsistent with visual inputs. While previous work has proposed methods to reduce OH, the visual decision-making mechanisms that lead to hallucinations remain poorly understood. In this paper, we propose VaLSe, a Vision-aware Latent Steering framework that adopts an interpretation-then-mitigation strategy to address OH in LVLMs. By tackling dual challenges of modeling complex vision-language interactions and eliminating spurious activation artifacts, VaLSe can generate visual contribution maps that trace how specific visual inputs influence individual output tokens. These maps reveal the model's vision-aware focus regions, which are then used to perform latent space steering, realigning internal representations toward semantically relevant content and reducing hallucinated outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VaLSe is a powerful interpretability tool and an effective method for enhancing model robustness against OH across multiple benchmarks. Furthermore, our analysis uncovers limitations in existing OH evaluation metrics, underscoring the need for more nuanced, interpretable, and visually grounded OH benchmarks in future work. Code is available at: https://github.com/Ziwei-Zheng/VaLSe.
Use as Many Surrogates as You Want: Selective Ensemble Attack to Unleash Transferability without Sacrificing Resource Efficiency
May 19, 2025Abstract:In surrogate ensemble attacks, using more surrogate models yields higher transferability but lower resource efficiency. This practical trade-off between transferability and efficiency has largely limited existing attacks despite many pre-trained models are easily accessible online. In this paper, we argue that such a trade-off is caused by an unnecessary common assumption, i.e., all models should be identical across iterations. By lifting this assumption, we can use as many surrogates as we want to unleash transferability without sacrificing efficiency. Concretely, we propose Selective Ensemble Attack (SEA), which dynamically selects diverse models (from easily accessible pre-trained models) across iterations based on our new interpretation of decoupling within-iteration and cross-iteration model diversity.In this way, the number of within-iteration models is fixed for maintaining efficiency, while only cross-iteration model diversity is increased for higher transferability. Experiments on ImageNet demonstrate the superiority of SEA in various scenarios. For example, when dynamically selecting 4 from 20 accessible models, SEA yields 8.5% higher transferability than existing attacks under the same efficiency. The superiority of SEA also generalizes to real-world systems, such as commercial vision APIs and large vision-language models. Overall, SEA opens up the possibility of adaptively balancing transferability and efficiency according to specific resource requirements.
HCMA: Hierarchical Cross-model Alignment for Grounded Text-to-Image Generation
May 15, 2025
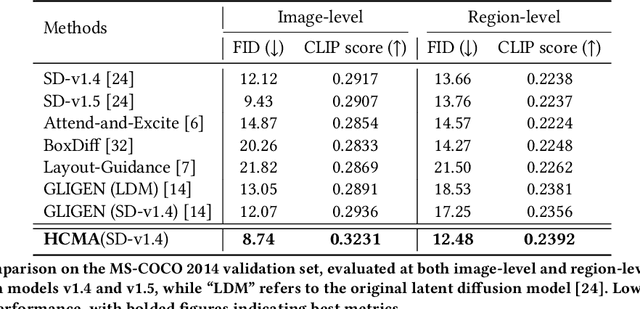
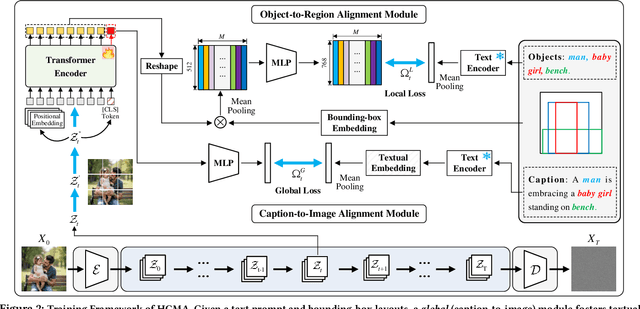
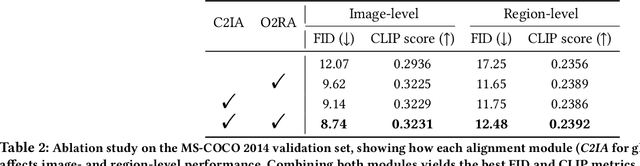
Abstract:Text-to-image synthesis has progressed to the point where models can generate visually compelling images from natural language prompts. Yet, existing methods often fail to reconcile high-level semantic fidelity with explicit spatial control, particularly in scenes involving multiple objects, nuanced relations, or complex layouts. To bridge this gap, we propose a Hierarchical Cross-Modal Alignment (HCMA) framework for grounded text-to-image generation. HCMA integrates two alignment modules into each diffusion sampling step: a global module that continuously aligns latent representations with textual descriptions to ensure scene-level coherence, and a local module that employs bounding-box layouts to anchor objects at specified locations, enabling fine-grained spatial control. Extensive experiments on the MS-COCO 2014 validation set show that HCMA surpasses state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a 0.69 improvement in Frechet Inception Distance (FID) and a 0.0295 gain in CLIP Score. These results demonstrate HCMA's effectiveness in faithfully capturing intricate textual semantics while adhering to user-defined spatial constraints, offering a robust solution for semantically grounded image generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/hwang-cs-ime/HCMA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge