Gao Huang
TwinRL-VLA: Digital Twin-Driven Reinforcement Learning for Real-World Robotic Manipulation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Despite strong generalization capabilities, Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models remain constrained by the high cost of expert demonstrations and insufficient real-world interaction. While online reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promise in improving general foundation models, applying RL to VLA manipulation in real-world settings is still hindered by low exploration efficiency and a restricted exploration space. Through systematic real-world experiments, we observe that the effective exploration space of online RL is closely tied to the data distribution of supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Motivated by this observation, we propose TwinRL, a digital twin-real-world collaborative RL framework designed to scale and guide exploration for VLA models. First, a high-fidelity digital twin is efficiently reconstructed from smartphone-captured scenes, enabling realistic bidirectional transfer between real and simulated environments. During the SFT warm-up stage, we introduce an exploration space expansion strategy using digital twins to broaden the support of the data trajectory distribution. Building on this enhanced initialization, we propose a sim-to-real guided exploration strategy to further accelerate online RL. Specifically, TwinRL performs efficient and parallel online RL in the digital twin prior to deployment, effectively bridging the gap between offline and online training stages. Subsequently, we exploit efficient digital twin sampling to identify failure-prone yet informative configurations, which are used to guide targeted human-in-the-loop rollouts on the real robot. In our experiments, TwinRL approaches 100% success in both in-distribution regions covered by real-world demonstrations and out-of-distribution regions, delivering at least a 30% speedup over prior real-world RL methods and requiring only about 20 minutes on average across four tasks.
SiameseNorm: Breaking the Barrier to Reconciling Pre/Post-Norm
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Modern Transformers predominantly adopt the Pre-Norm paradigm for its optimization stability, foregoing the superior potential of the unstable Post-Norm architecture. Prior attempts to combine their strengths typically lead to a stability-performance trade-off. We attribute this phenomenon to a structural incompatibility within a single-stream design: Any application of the Post-Norm operation inevitably obstructs the clean identity gradient preserved by Pre-Norm. To fundamentally reconcile these paradigms, we propose SiameseNorm, a two-stream architecture that couples Pre-Norm-like and Post-Norm-like streams with shared parameters. This design decouples the optimization dynamics of the two streams, retaining the distinct characteristics of both Pre-Norm and Post-Norm by enabling all residual blocks to receive combined gradients inherited from both paradigms, where one stream secures stability while the other enhances expressivity. Extensive pre-training experiments on 1.3B-parameter models demonstrate that SiameseNorm exhibits exceptional optimization robustness and consistently outperforms strong baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/Qwen-Applications/SiameseNorm.
Thickening-to-Thinning: Reward Shaping via Human-Inspired Learning Dynamics for LLM Reasoning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has emerged as a promising paradigm for enhancing reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, it frequently encounters challenges such as entropy collapse, excessive verbosity, and insufficient exploration for hard problems. Crucially, existing reward schemes fail to distinguish between the need for extensive search during problem-solving and the efficiency required for mastered knowledge. In this work, we introduce T2T(Thickening-to-Thinning), a dynamic reward framework inspired by human learning processes. Specifically, it implements a dual-phase mechanism: (1) On incorrect attempts, T2T incentivizes "thickening" (longer trajectories) to broaden the search space and explore novel solution paths; (2) Upon achieving correctness, it shifts to "thinning", imposing length penalties to discourage redundancy, thereby fostering model confidence and crystallizing reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments on mathematical benchmarks (MATH-500, AIME, AMC) across Qwen-series and Deepseek models demonstrate that T2T significantly outperforms standard GRPO and recent baselines, achieving superior performance.
The Flexibility Trap: Why Arbitrary Order Limits Reasoning Potential in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) break the rigid left-to-right constraint of traditional LLMs, enabling token generation in arbitrary orders. Intuitively, this flexibility implies a solution space that strictly supersets the fixed autoregressive trajectory, theoretically unlocking superior reasoning potential for general tasks like mathematics and coding. Consequently, numerous works have leveraged reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit the reasoning capability of dLLMs. In this paper, we reveal a counter-intuitive reality: arbitrary order generation, in its current form, narrows rather than expands the reasoning boundary of dLLMs. We find that dLLMs tend to exploit this order flexibility to bypass high-uncertainty tokens that are crucial for exploration, leading to a premature collapse of the solution space. This observation challenges the premise of existing RL approaches for dLLMs, where considerable complexities, such as handling combinatorial trajectories and intractable likelihoods, are often devoted to preserving this flexibility. We demonstrate that effective reasoning is better elicited by intentionally forgoing arbitrary order and applying standard Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) instead. Our approach, JustGRPO, is minimalist yet surprisingly effective (e.g., 89.1% accuracy on GSM8K) while fully retaining the parallel decoding ability of dLLMs. Project page: https://nzl-thu.github.io/the-flexibility-trap
Collaborative Low-Rank Adaptation for Pre-Trained Vision Transformers
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has achieved remarkable success in fine-tuning pre-trained vision transformers for various downstream tasks. Existing studies mainly focus on exploring more parameter-efficient strategies or more effective representation learning schemes. However, these methods either sacrifice fine-tuning performance or introduce excessive trainable parameters, failing to strike a balance between learning performance and parameter efficiency. To address this problem, we propose a novel tuning method named collaborative low-rank adaptation (CLoRA) in this paper. CLoRA consists of base-space sharing and sample-agnostic diversity enhancement (SADE) components. To maintain parameter efficiency while expanding the learning capacity of low-rank modules (LRMs), base-space sharing allows all LRMs to share a set of down/up-projection spaces. In CLoRA, the low-rank matrices obtained from the shared spaces collaboratively construct each LRM. Since the representations extracted by these matrices may contain redundant information, SADE is employed to regularize the similarities among them to encourage diverse representations in the training process. We conduct extensive experiments on widely used image and point cloud datasets to evaluate the performance of CLoRA. Experimental results demonstrate that CLoRA strikes a better balance between learning performance and parameter efficiency, while requiring the fewest GFLOPs for point cloud analysis, compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
SenseNova-MARS: Empowering Multimodal Agentic Reasoning and Search via Reinforcement Learning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) can solve complex tasks through agentic reasoning, their capabilities remain largely constrained to text-oriented chain-of-thought or isolated tool invocation. They fail to exhibit the human-like proficiency required to seamlessly interleave dynamic tool manipulation with continuous reasoning, particularly in knowledge-intensive and visually complex scenarios that demand coordinated external tools such as search and image cropping. In this work, we introduce SenseNova-MARS, a novel Multimodal Agentic Reasoning and Search framework that empowers VLMs with interleaved visual reasoning and tool-use capabilities via reinforcement learning (RL). Specifically, SenseNova-MARS dynamically integrates the image search, text search, and image crop tools to tackle fine-grained and knowledge-intensive visual understanding challenges. In the RL stage, we propose the Batch-Normalized Group Sequence Policy Optimization (BN-GSPO) algorithm to improve the training stability and advance the model's ability to invoke tools and reason effectively. To comprehensively evaluate the agentic VLMs on complex visual tasks, we introduce the HR-MMSearch benchmark, the first search-oriented benchmark composed of high-resolution images with knowledge-intensive and search-driven questions. Experiments demonstrate that SenseNova-MARS achieves state-of-the-art performance on open-source search and fine-grained image understanding benchmarks. Specifically, on search-oriented benchmarks, SenseNova-MARS-8B scores 67.84 on MMSearch and 41.64 on HR-MMSearch, surpassing proprietary models such as Gemini-3-Flash and GPT-5. SenseNova-MARS represents a promising step toward agentic VLMs by providing effective and robust tool-use capabilities. To facilitate further research in this field, we will release all code, models, and datasets.
Vision Transformers are Circulant Attention Learners
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:The self-attention mechanism has been a key factor in the advancement of vision Transformers. However, its quadratic complexity imposes a heavy computational burden in high-resolution scenarios, restricting the practical application. Previous methods attempt to mitigate this issue by introducing handcrafted patterns such as locality or sparsity, which inevitably compromise model capacity. In this paper, we present a novel attention paradigm termed \textbf{Circulant Attention} by exploiting the inherent efficient pattern of self-attention. Specifically, we first identify that the self-attention matrix in vision Transformers often approximates the Block Circulant matrix with Circulant Blocks (BCCB), a kind of structured matrix whose multiplication with other matrices can be performed in $\mathcal{O}(N\log N)$ time. Leveraging this interesting pattern, we explicitly model the attention map as its nearest BCCB matrix and propose an efficient computation algorithm for fast calculation. The resulting approach closely mirrors vanilla self-attention, differing only in its use of BCCB matrices. Since our design is inspired by the inherent efficient paradigm, it not only delivers $\mathcal{O}(N\log N)$ computation complexity, but also largely maintains the capacity of standard self-attention. Extensive experiments on diverse visual tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, establishing circulant attention as a promising alternative to self-attention for vision Transformer architectures. Code is available at https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/Circulant-Attention.
Co-GRPO: Co-Optimized Group Relative Policy Optimization for Masked Diffusion Model
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Recently, Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs) have shown promising potential across vision, language, and cross-modal generation. However, a notable discrepancy exists between their training and inference procedures. In particular, MDM inference is a multi-step, iterative process governed not only by the model itself but also by various schedules that dictate the token-decoding trajectory (e.g., how many tokens to decode at each step). In contrast, MDMs are typically trained using a simplified, single-step BERT-style objective that masks a subset of tokens and predicts all of them simultaneously. This step-level simplification fundamentally disconnects the training paradigm from the trajectory-level nature of inference, leaving the inference schedules never optimized during training. In this paper, we introduce Co-GRPO, which reformulates MDM generation as a unified Markov Decision Process (MDP) that jointly incorporates both the model and the inference schedule. By applying Group Relative Policy Optimization at the trajectory level, Co-GRPO cooperatively optimizes model parameters and schedule parameters under a shared reward, without requiring costly backpropagation through the multi-step generation process. This holistic optimization aligns training with inference more thoroughly and substantially improves generation quality. Empirical results across four benchmarks-ImageReward, HPS, GenEval, and DPG-Bench-demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. For more details, please refer to our project page: https://co-grpo.github.io/ .
Few-Step Distillation for Text-to-Image Generation: A Practical Guide
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Diffusion distillation has dramatically accelerated class-conditional image synthesis, but its applicability to open-ended text-to-image (T2I) generation is still unclear. We present the first systematic study that adapts and compares state-of-the-art distillation techniques on a strong T2I teacher model, FLUX.1-lite. By casting existing methods into a unified framework, we identify the key obstacles that arise when moving from discrete class labels to free-form language prompts. Beyond a thorough methodological analysis, we offer practical guidelines on input scaling, network architecture, and hyperparameters, accompanied by an open-source implementation and pretrained student models. Our findings establish a solid foundation for deploying fast, high-fidelity, and resource-efficient diffusion generators in real-world T2I applications. Code is available on github.com/alibaba-damo-academy/T2I-Distill.
UltraDP: Generalizable Carotid Ultrasound Scanning with Force-Aware Diffusion Policy
Nov 19, 2025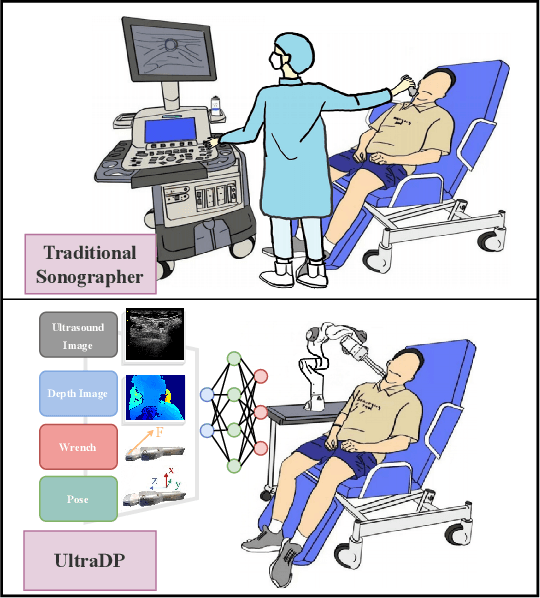
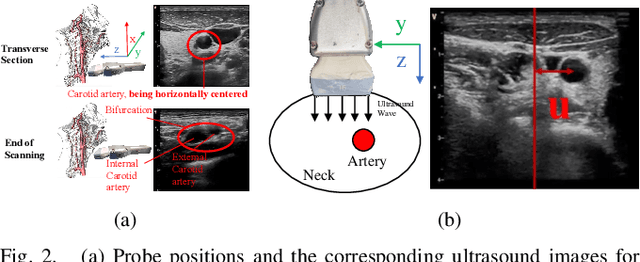
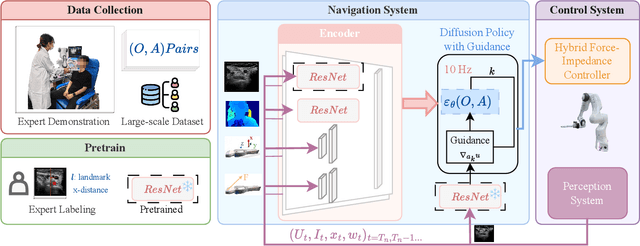
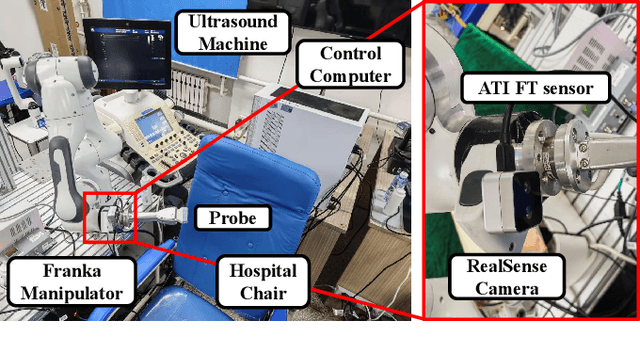
Abstract:Ultrasound scanning is a critical imaging technique for real-time, non-invasive diagnostics. However, variations in patient anatomy and complex human-in-the-loop interactions pose significant challenges for autonomous robotic scanning. Existing ultrasound scanning robots are commonly limited to relatively low generalization and inefficient data utilization. To overcome these limitations, we present UltraDP, a Diffusion-Policy-based method that receives multi-sensory inputs (ultrasound images, wrist camera images, contact wrench, and probe pose) and generates actions that are fit for multi-modal action distributions in autonomous ultrasound scanning of carotid artery. We propose a specialized guidance module to enable the policy to output actions that center the artery in ultrasound images. To ensure stable contact and safe interaction between the robot and the human subject, a hybrid force-impedance controller is utilized to drive the robot to track such trajectories. Also, we have built a large-scale training dataset for carotid scanning comprising 210 scans with 460k sample pairs from 21 volunteers of both genders. By exploring our guidance module and DP's strong generalization ability, UltraDP achieves a 95% success rate in transverse scanning on previously unseen subjects, demonstrating its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge