Guangyao Zhai
Foundation Visual Encoders Are Secretly Few-Shot Anomaly Detectors
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Few-shot anomaly detection streamlines and simplifies industrial safety inspection. However, limited samples make accurate differentiation between normal and abnormal features challenging, and even more so under category-agnostic conditions. Large-scale pre-training of foundation visual encoders has advanced many fields, as the enormous quantity of data helps to learn the general distribution of normal images. We observe that the anomaly amount in an image directly correlates with the difference in the learnt embeddings and utilize this to design a few-shot anomaly detector termed FoundAD. This is done by learning a nonlinear projection operator onto the natural image manifold. The simple operator acts as an effective tool for anomaly detection to characterize and identify out-of-distribution regions in an image. Extensive experiments show that our approach supports multi-class detection and achieves competitive performance while using substantially fewer parameters than prior methods. Backed up by evaluations with multiple foundation encoders, including fresh DINOv3, we believe this idea broadens the perspective on foundation features and advances the field of few-shot anomaly detection.
Video Perception Models for 3D Scene Synthesis
Jun 25, 2025



Abstract:Traditionally, 3D scene synthesis requires expert knowledge and significant manual effort. Automating this process could greatly benefit fields such as architectural design, robotics simulation, virtual reality, and gaming. Recent approaches to 3D scene synthesis often rely on the commonsense reasoning of large language models (LLMs) or strong visual priors of modern image generation models. However, current LLMs demonstrate limited 3D spatial reasoning ability, which restricts their ability to generate realistic and coherent 3D scenes. Meanwhile, image generation-based methods often suffer from constraints in viewpoint selection and multi-view inconsistencies. In this work, we present Video Perception models for 3D Scene synthesis (VIPScene), a novel framework that exploits the encoded commonsense knowledge of the 3D physical world in video generation models to ensure coherent scene layouts and consistent object placements across views. VIPScene accepts both text and image prompts and seamlessly integrates video generation, feedforward 3D reconstruction, and open-vocabulary perception models to semantically and geometrically analyze each object in a scene. This enables flexible scene synthesis with high realism and structural consistency. For more precise analysis, we further introduce First-Person View Score (FPVScore) for coherence and plausibility evaluation, utilizing continuous first-person perspective to capitalize on the reasoning ability of multimodal large language models. Extensive experiments show that VIPScene significantly outperforms existing methods and generalizes well across diverse scenarios. The code will be released.
FA-BARF: Frequency Adapted Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields
Mar 15, 2025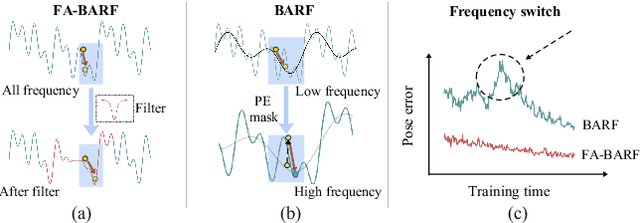
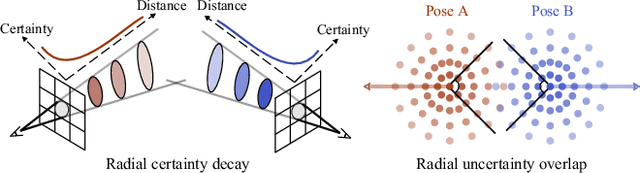
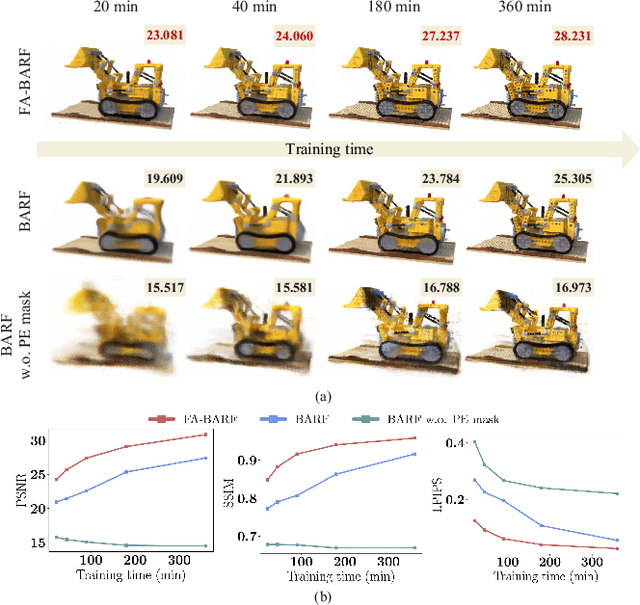
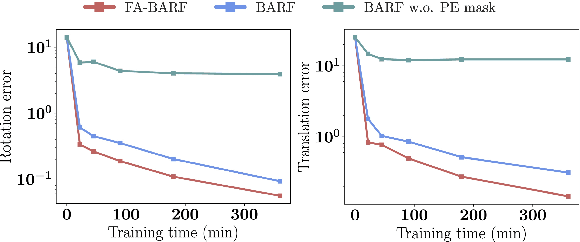
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have exhibited highly effective performance for photorealistic novel view synthesis recently. However, the key limitation it meets is the reliance on a hand-crafted frequency annealing strategy to recover 3D scenes with imperfect camera poses. The strategy exploits a temporal low-pass filter to guarantee convergence while decelerating the joint optimization of implicit scene reconstruction and camera registration. In this work, we introduce the Frequency Adapted Bundle Adjusting Radiance Field (FA-BARF), substituting the temporal low-pass filter for a frequency-adapted spatial low-pass filter to address the decelerating problem. We establish a theoretical framework to interpret the relationship between position encoding of NeRF and camera registration and show that our frequency-adapted filter can mitigate frequency fluctuation caused by the temporal filter. Furthermore, we show that applying a spatial low-pass filter in NeRF can optimize camera poses productively through radial uncertainty overlaps among various views. Extensive experiments show that FA-BARF can accelerate the joint optimization process under little perturbations in object-centric scenes and recover real-world scenes with unknown camera poses. This implies wider possibilities for NeRF applied in dense 3D mapping and reconstruction under real-time requirements. The code will be released upon paper acceptance.
Every FLOP Counts: Scaling a 300B Mixture-of-Experts LING LLM without Premium GPUs
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:In this technical report, we tackle the challenges of training large-scale Mixture of Experts (MoE) models, focusing on overcoming cost inefficiency and resource limitations prevalent in such systems. To address these issues, we present two differently sized MoE large language models (LLMs), namely Ling-Lite and Ling-Plus (referred to as "Bailing" in Chinese, spelled B\v{a}il\'ing in Pinyin). Ling-Lite contains 16.8 billion parameters with 2.75 billion activated parameters, while Ling-Plus boasts 290 billion parameters with 28.8 billion activated parameters. Both models exhibit comparable performance to leading industry benchmarks. This report offers actionable insights to improve the efficiency and accessibility of AI development in resource-constrained settings, promoting more scalable and sustainable technologies. Specifically, to reduce training costs for large-scale MoE models, we propose innovative methods for (1) optimization of model architecture and training processes, (2) refinement of training anomaly handling, and (3) enhancement of model evaluation efficiency. Additionally, leveraging high-quality data generated from knowledge graphs, our models demonstrate superior capabilities in tool use compared to other models. Ultimately, our experimental findings demonstrate that a 300B MoE LLM can be effectively trained on lower-performance devices while achieving comparable performance to models of a similar scale, including dense and MoE models. Compared to high-performance devices, utilizing a lower-specification hardware system during the pre-training phase demonstrates significant cost savings, reducing computing costs by approximately 20%. The models can be accessed at https://huggingface.co/inclusionAI.
MMGDreamer: Mixed-Modality Graph for Geometry-Controllable 3D Indoor Scene Generation
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Controllable 3D scene generation has extensive applications in virtual reality and interior design, where the generated scenes should exhibit high levels of realism and controllability in terms of geometry. Scene graphs provide a suitable data representation that facilitates these applications. However, current graph-based methods for scene generation are constrained to text-based inputs and exhibit insufficient adaptability to flexible user inputs, hindering the ability to precisely control object geometry. To address this issue, we propose MMGDreamer, a dual-branch diffusion model for scene generation that incorporates a novel Mixed-Modality Graph, visual enhancement module, and relation predictor. The mixed-modality graph allows object nodes to integrate textual and visual modalities, with optional relationships between nodes. It enhances adaptability to flexible user inputs and enables meticulous control over the geometry of objects in the generated scenes. The visual enhancement module enriches the visual fidelity of text-only nodes by constructing visual representations using text embeddings. Furthermore, our relation predictor leverages node representations to infer absent relationships between nodes, resulting in more coherent scene layouts. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that MMGDreamer exhibits superior control of object geometry, achieving state-of-the-art scene generation performance. Project page: https://yangzhifeio.github.io/project/MMGDreamer.
VideoINSTA: Zero-shot Long Video Understanding via Informative Spatial-Temporal Reasoning with LLMs
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:In the video-language domain, recent works in leveraging zero-shot Large Language Model-based reasoning for video understanding have become competitive challengers to previous end-to-end models. However, long video understanding presents unique challenges due to the complexity of reasoning over extended timespans, even for zero-shot LLM-based approaches. The challenge of information redundancy in long videos prompts the question of what specific information is essential for large language models (LLMs) and how to leverage them for complex spatial-temporal reasoning in long-form video analysis. We propose a framework VideoINSTA, i.e. INformative Spatial-TemporAl Reasoning for zero-shot long-form video understanding. VideoINSTA contributes (1) a zero-shot framework for long video understanding using LLMs; (2) an event-based temporal reasoning and content-based spatial reasoning approach for LLMs to reason over spatial-temporal information in videos; (3) a self-reflective information reasoning scheme balancing temporal factors based on information sufficiency and prediction confidence. Our model significantly improves the state-of-the-art on three long video question-answering benchmarks: EgoSchema, NextQA, and IntentQA, and the open question answering dataset ActivityNetQA. The code is released here: https://github.com/mayhugotong/VideoINSTA.
EchoScene: Indoor Scene Generation via Information Echo over Scene Graph Diffusion
May 02, 2024Abstract:We present EchoScene, an interactive and controllable generative model that generates 3D indoor scenes on scene graphs. EchoScene leverages a dual-branch diffusion model that dynamically adapts to scene graphs. Existing methods struggle to handle scene graphs due to varying numbers of nodes, multiple edge combinations, and manipulator-induced node-edge operations. EchoScene overcomes this by associating each node with a denoising process and enables collaborative information exchange, enhancing controllable and consistent generation aware of global constraints. This is achieved through an information echo scheme in both shape and layout branches. At every denoising step, all processes share their denoising data with an information exchange unit that combines these updates using graph convolution. The scheme ensures that the denoising processes are influenced by a holistic understanding of the scene graph, facilitating the generation of globally coherent scenes. The resulting scenes can be manipulated during inference by editing the input scene graph and sampling the noise in the diffusion model. Extensive experiments validate our approach, which maintains scene controllability and surpasses previous methods in generation fidelity. Moreover, the generated scenes are of high quality and thus directly compatible with off-the-shelf texture generation. Code and trained models are open-sourced.
GeoGaussian: Geometry-aware Gaussian Splatting for Scene Rendering
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:During the Gaussian Splatting optimization process, the scene's geometry can gradually deteriorate if its structure is not deliberately preserved, especially in non-textured regions such as walls, ceilings, and furniture surfaces. This degradation significantly affects the rendering quality of novel views that deviate significantly from the viewpoints in the training data. To mitigate this issue, we propose a novel approach called GeoGaussian. Based on the smoothly connected areas observed from point clouds, this method introduces a novel pipeline to initialize thin Gaussians aligned with the surfaces, where the characteristic can be transferred to new generations through a carefully designed densification strategy. Finally, the pipeline ensures that the scene's geometry and texture are maintained through constrained optimization processes with explicit geometry constraints. Benefiting from the proposed architecture, the generative ability of 3D Gaussians is enhanced, especially in structured regions. Our proposed pipeline achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis and geometric reconstruction, as evaluated qualitatively and quantitatively on public datasets.
SecondPose: SE(3)-Consistent Dual-Stream Feature Fusion for Category-Level Pose Estimation
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation, aiming to predict the 6D pose and 3D size of objects from known categories, typically struggles with large intra-class shape variation. Existing works utilizing mean shapes often fall short of capturing this variation. To address this issue, we present SecondPose, a novel approach integrating object-specific geometric features with semantic category priors from DINOv2. Leveraging the advantage of DINOv2 in providing SE(3)-consistent semantic features, we hierarchically extract two types of SE(3)-invariant geometric features to further encapsulate local-to-global object-specific information. These geometric features are then point-aligned with DINOv2 features to establish a consistent object representation under SE(3) transformations, facilitating the mapping from camera space to the pre-defined canonical space, thus further enhancing pose estimation. Extensive experiments on NOCS-REAL275 demonstrate that SecondPose achieves a 12.4% leap forward over the state-of-the-art. Moreover, on a more complex dataset HouseCat6D which provides photometrically challenging objects, SecondPose still surpasses other competitors by a large margin. The code will be released soon.
ShapeMaker: Self-Supervised Joint Shape Canonicalization, Segmentation, Retrieval and Deformation
Nov 18, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present ShapeMaker, a unified self-supervised learning framework for joint shape canonicalization, segmentation, retrieval and deformation. Given a partially-observed object in an arbitrary pose, we first canonicalize the object by extracting point-wise affine-invariant features, disentangling inherent structure of the object with its pose and size. These learned features are then leveraged to predict semantically consistent part segmentation and corresponding part centers. Next, our lightweight retrieval module aggregates the features within each part as its retrieval token and compare all the tokens with source shapes from a pre-established database to identify the most geometrically similar shape. Finally, we deform the retrieved shape in the deformation module to tightly fit the input object by harnessing part center guided neural cage deformation. The key insight of ShapeMaker is the simultaneous training of the four highly-associated processes: canonicalization, segmentation, retrieval, and deformation, leveraging cross-task consistency losses for mutual supervision. Extensive experiments on synthetic datasets PartNet, ComplementMe, and real-world dataset Scan2CAD demonstrate that ShapeMaker surpasses competitors by a large margin. Codes will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge