Ruifei Ma
Spatial 3D-LLM: Exploring Spatial Awareness in 3D Vision-Language Models
Jul 22, 2025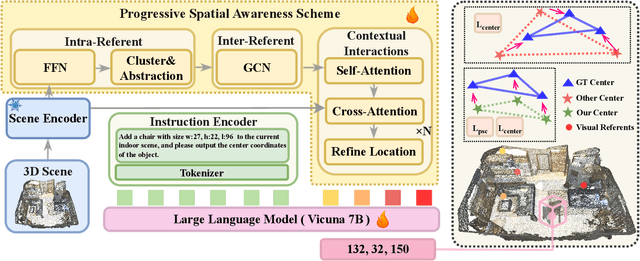
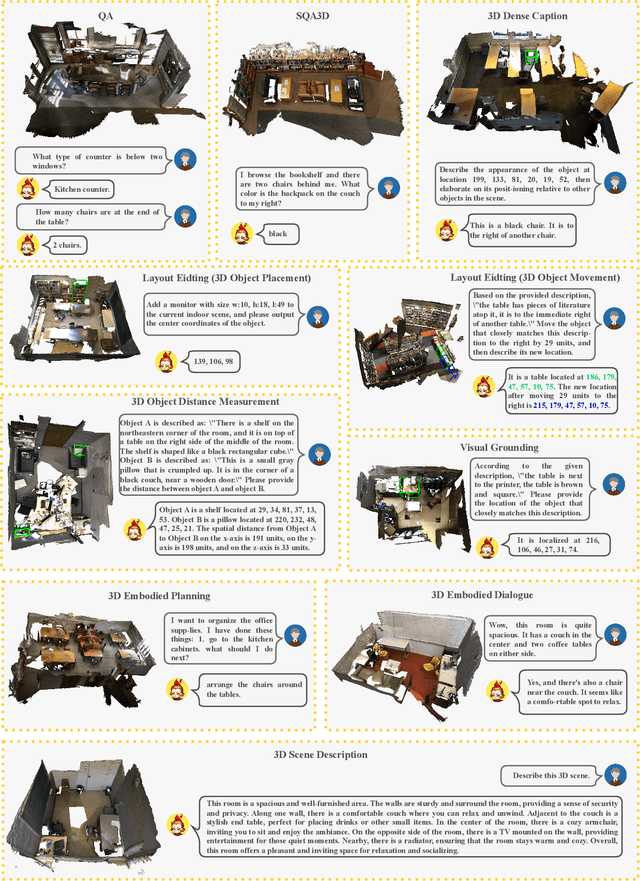
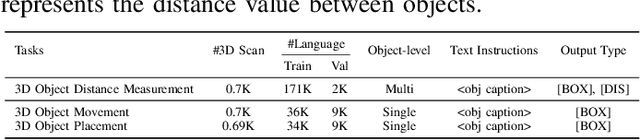
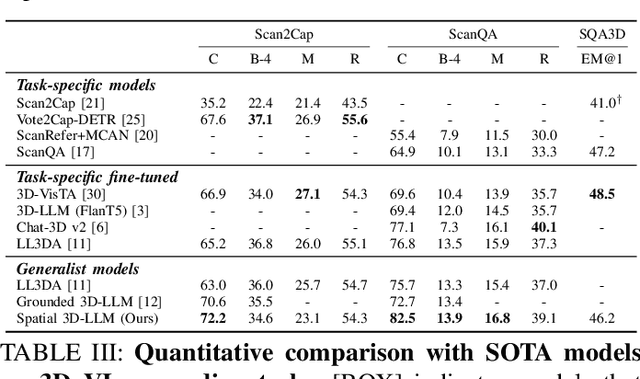
Abstract:New era has unlocked exciting possibilities for extending Large Language Models (LLMs) to tackle 3D vision-language tasks. However, most existing 3D multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) rely on compressing holistic 3D scene information or segmenting independent objects to perform these tasks, which limits their spatial awareness due to insufficient representation of the richness inherent in 3D scenes. To overcome these limitations, we propose Spatial 3D-LLM, a 3D MLLM specifically designed to enhance spatial awareness for 3D vision-language tasks by enriching the spatial embeddings of 3D scenes. Spatial 3D-LLM integrates an LLM backbone with a progressive spatial awareness scheme that progressively captures spatial information as the perception field expands, generating location-enriched 3D scene embeddings to serve as visual prompts. Furthermore, we introduce two novel tasks: 3D object distance measurement and 3D layout editing, and construct a 3D instruction dataset, MODEL, to evaluate the model's spatial awareness capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that Spatial 3D-LLM achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of 3D vision-language tasks, revealing the improvements stemmed from our progressive spatial awareness scheme of mining more profound spatial information. Our code is available at https://github.com/bjshuyuan/Spatial-3D-LLM.
MMGDreamer: Mixed-Modality Graph for Geometry-Controllable 3D Indoor Scene Generation
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Controllable 3D scene generation has extensive applications in virtual reality and interior design, where the generated scenes should exhibit high levels of realism and controllability in terms of geometry. Scene graphs provide a suitable data representation that facilitates these applications. However, current graph-based methods for scene generation are constrained to text-based inputs and exhibit insufficient adaptability to flexible user inputs, hindering the ability to precisely control object geometry. To address this issue, we propose MMGDreamer, a dual-branch diffusion model for scene generation that incorporates a novel Mixed-Modality Graph, visual enhancement module, and relation predictor. The mixed-modality graph allows object nodes to integrate textual and visual modalities, with optional relationships between nodes. It enhances adaptability to flexible user inputs and enables meticulous control over the geometry of objects in the generated scenes. The visual enhancement module enriches the visual fidelity of text-only nodes by constructing visual representations using text embeddings. Furthermore, our relation predictor leverages node representations to infer absent relationships between nodes, resulting in more coherent scene layouts. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that MMGDreamer exhibits superior control of object geometry, achieving state-of-the-art scene generation performance. Project page: https://yangzhifeio.github.io/project/MMGDreamer.
Non-destructive Degradation Pattern Decoupling for Ultra-early Battery Prototype Verification Using Physics-informed Machine Learning
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:Manufacturing complexities and uncertainties have impeded the transition from material prototypes to commercial batteries, making prototype verification critical to quality assessment. A fundamental challenge involves deciphering intertwined chemical processes to characterize degradation patterns and their quantitative relationship with battery performance. Here we show that a physics-informed machine learning approach can quantify and visualize temporally resolved losses concerning thermodynamics and kinetics only using electric signals. Our method enables non-destructive degradation pattern characterization, expediting temperature-adaptable predictions of entire lifetime trajectories, rather than end-of-life points. The verification speed is 25 times faster yet maintaining 95.1% accuracy across temperatures. Such advances facilitate more sustainable management of defective prototypes before massive production, establishing a 19.76 billion USD scrap material recycling market by 2060 in China. By incorporating stepwise charge acceptance as a measure of the initial manufacturing variability of normally identical batteries, we can immediately identify long-term degradation variations. We attribute the predictive power to interpreting machine learning insights using material-agnostic featurization taxonomy for degradation pattern decoupling. Our findings offer new possibilities for dynamic system analysis, such as battery prototype degradation, demonstrating that complex pattern evolutions can be accurately predicted in a non-destructive and data-driven fashion by integrating physics-informed machine learning.
3DMIT: 3D Multi-modal Instruction Tuning for Scene Understanding
Jan 16, 2024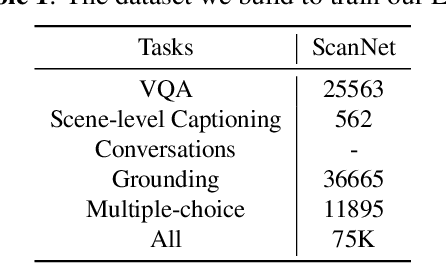
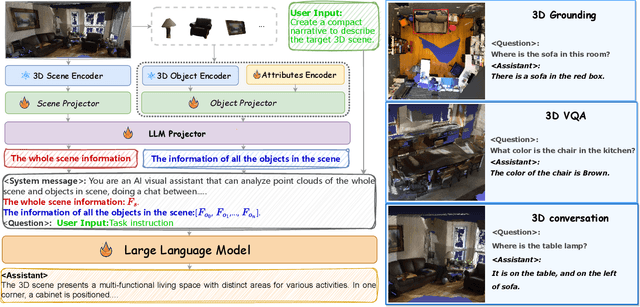
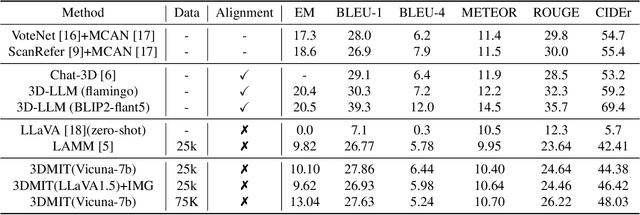
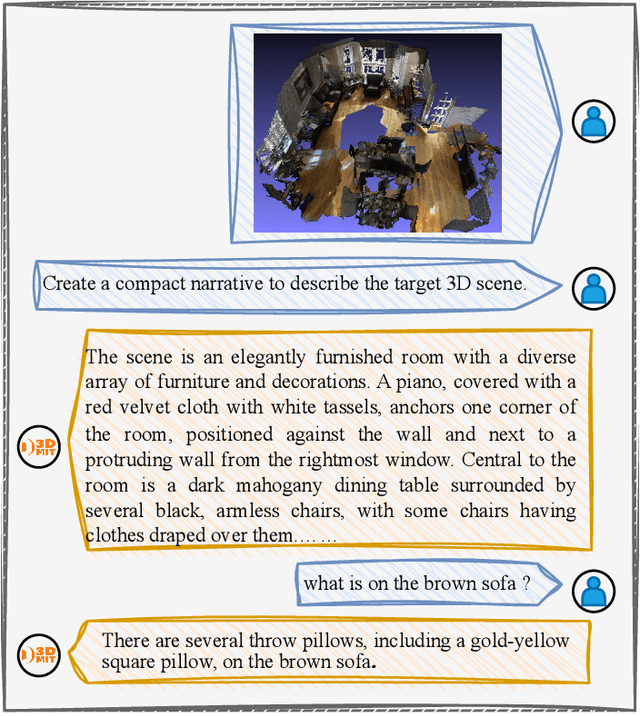
Abstract:The remarkable potential of multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) in comprehending both vision and language information has been widely acknowledged. However, the scarcity of 3D scenes-language pairs in comparison to their 2D counterparts, coupled with the inadequacy of existing approaches in understanding of 3D scenes by LLMs, poses a significant challenge. In response, we collect and construct an extensive dataset comprising 75K instruction-response pairs tailored for 3D scenes. This dataset addresses tasks related to 3D VQA, 3D grounding, and 3D conversation. To further enhance the integration of 3D spatial information into LLMs, we introduce a novel and efficient prompt tuning paradigm, 3DMIT. This paradigm eliminates the alignment stage between 3D scenes and language and extends the instruction prompt with the 3D modality information including the entire scene and segmented objects. We evaluate the effectiveness of our method across diverse tasks in the 3D scene domain and find that our approach serves as a strategic means to enrich LLMs' comprehension of the 3D world. Our code is available at https://github.com/staymylove/3DMIT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge