Mengtian Zhang
Non-destructive Degradation Pattern Decoupling for Ultra-early Battery Prototype Verification Using Physics-informed Machine Learning
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:Manufacturing complexities and uncertainties have impeded the transition from material prototypes to commercial batteries, making prototype verification critical to quality assessment. A fundamental challenge involves deciphering intertwined chemical processes to characterize degradation patterns and their quantitative relationship with battery performance. Here we show that a physics-informed machine learning approach can quantify and visualize temporally resolved losses concerning thermodynamics and kinetics only using electric signals. Our method enables non-destructive degradation pattern characterization, expediting temperature-adaptable predictions of entire lifetime trajectories, rather than end-of-life points. The verification speed is 25 times faster yet maintaining 95.1% accuracy across temperatures. Such advances facilitate more sustainable management of defective prototypes before massive production, establishing a 19.76 billion USD scrap material recycling market by 2060 in China. By incorporating stepwise charge acceptance as a measure of the initial manufacturing variability of normally identical batteries, we can immediately identify long-term degradation variations. We attribute the predictive power to interpreting machine learning insights using material-agnostic featurization taxonomy for degradation pattern decoupling. Our findings offer new possibilities for dynamic system analysis, such as battery prototype degradation, demonstrating that complex pattern evolutions can be accurately predicted in a non-destructive and data-driven fashion by integrating physics-informed machine learning.
Networked Time Series Prediction with Incomplete Data
Oct 05, 2021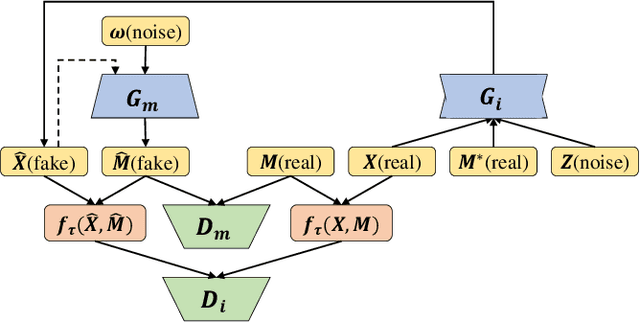
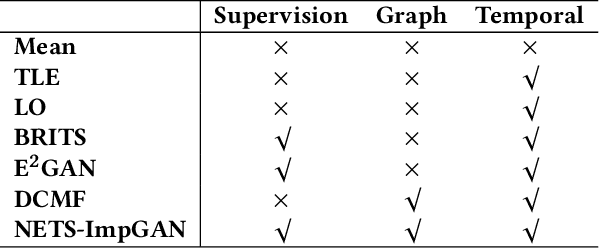
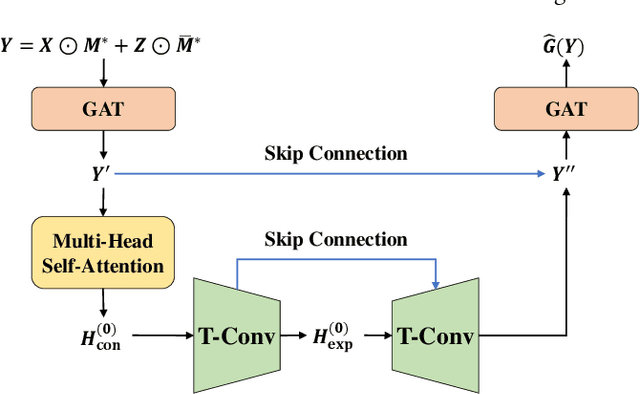
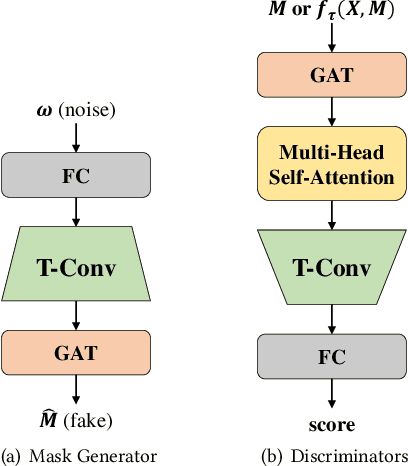
Abstract:A networked time series (NETS) is a family of time series on a given graph, one for each node. It has found a wide range of applications from intelligent transportation, environment monitoring to mobile network management. An important task in such applications is to predict the future values of a NETS based on its historical values and the underlying graph. Most existing methods require complete data for training. However, in real-world scenarios, it is not uncommon to have missing data due to sensor malfunction, incomplete sensing coverage, etc. In this paper, we study the problem of NETS prediction with incomplete data. We propose NETS-ImpGAN, a novel deep learning framework that can be trained on incomplete data with missing values in both history and future. Furthermore, we propose novel Graph Temporal Attention Networks by incorporating the attention mechanism to capture both inter-time series correlations and temporal correlations. We conduct extensive experiments on three real-world datasets under different missing patterns and missing rates. The experimental results show that NETS-ImpGAN outperforms existing methods except when data exhibit very low variance, in which case NETS-ImpGAN still achieves competitive performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge