Yamei Chen
Symbolic Graphics Programming with Large Language Models
Sep 05, 2025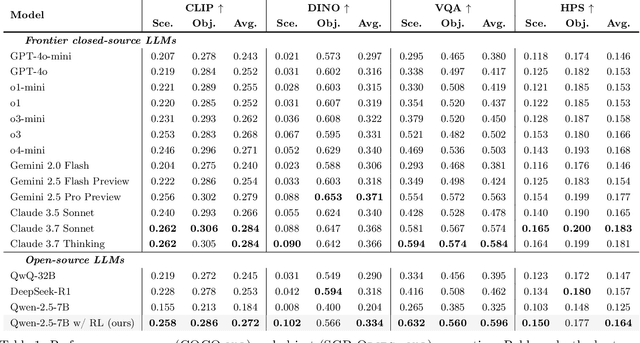
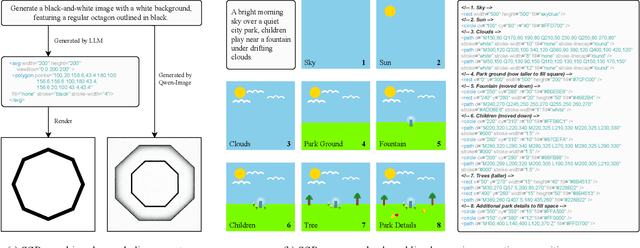
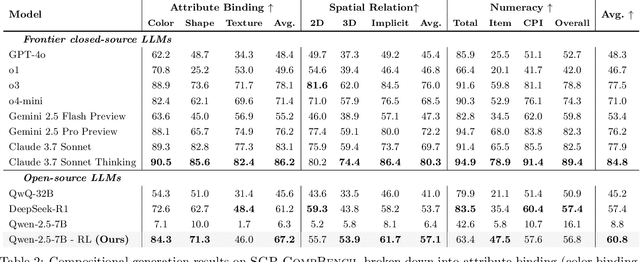
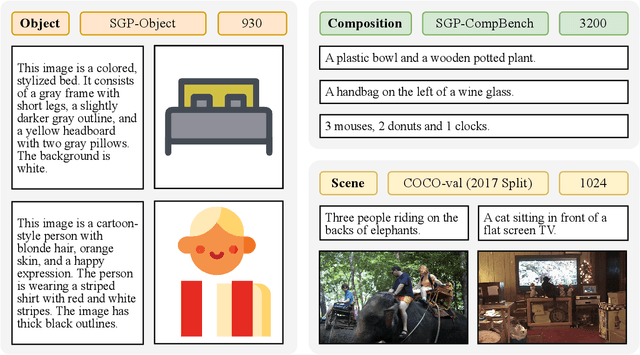
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at program synthesis, yet their ability to produce symbolic graphics programs (SGPs) that render into precise visual content remains underexplored. We study symbolic graphics programming, where the goal is to generate an SGP from a natural-language description. This task also serves as a lens into how LLMs understand the visual world by prompting them to generate images rendered from SGPs. Among various SGPs, our paper sticks to scalable vector graphics (SVGs). We begin by examining the extent to which LLMs can generate SGPs. To this end, we introduce SGP-GenBench, a comprehensive benchmark covering object fidelity, scene fidelity, and compositionality (attribute binding, spatial relations, numeracy). On SGP-GenBench, we discover that frontier proprietary models substantially outperform open-source models, and performance correlates well with general coding capabilities. Motivated by this gap, we aim to improve LLMs' ability to generate SGPs. We propose a reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable rewards approach, where a format-validity gate ensures renderable SVG, and a cross-modal reward aligns text and the rendered image via strong vision encoders (e.g., SigLIP for text-image and DINO for image-image). Applied to Qwen-2.5-7B, our method substantially improves SVG generation quality and semantics, achieving performance on par with frontier systems. We further analyze training dynamics, showing that RL induces (i) finer decomposition of objects into controllable primitives and (ii) contextual details that improve scene coherence. Our results demonstrate that symbolic graphics programming offers a precise and interpretable lens on cross-modal grounding.
SecondPose: SE(3)-Consistent Dual-Stream Feature Fusion for Category-Level Pose Estimation
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation, aiming to predict the 6D pose and 3D size of objects from known categories, typically struggles with large intra-class shape variation. Existing works utilizing mean shapes often fall short of capturing this variation. To address this issue, we present SecondPose, a novel approach integrating object-specific geometric features with semantic category priors from DINOv2. Leveraging the advantage of DINOv2 in providing SE(3)-consistent semantic features, we hierarchically extract two types of SE(3)-invariant geometric features to further encapsulate local-to-global object-specific information. These geometric features are then point-aligned with DINOv2 features to establish a consistent object representation under SE(3) transformations, facilitating the mapping from camera space to the pre-defined canonical space, thus further enhancing pose estimation. Extensive experiments on NOCS-REAL275 demonstrate that SecondPose achieves a 12.4% leap forward over the state-of-the-art. Moreover, on a more complex dataset HouseCat6D which provides photometrically challenging objects, SecondPose still surpasses other competitors by a large margin. The code will be released soon.
LOT: A Benchmark for Evaluating Chinese Long Text Understanding and Generation
Aug 30, 2021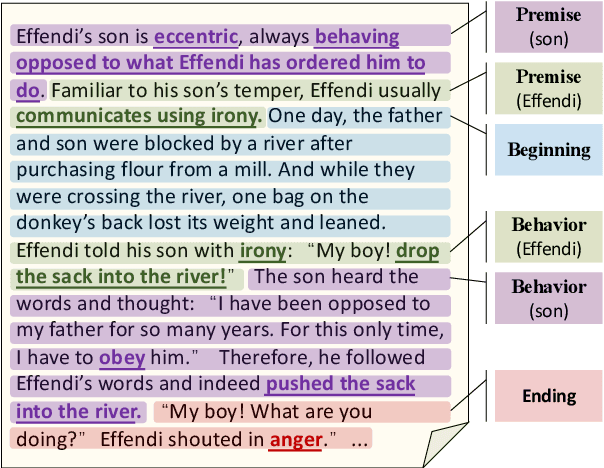
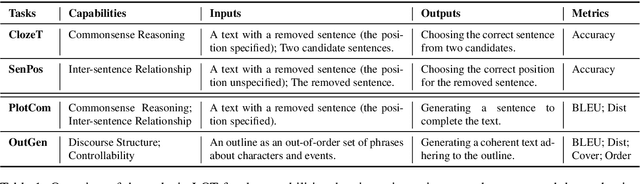
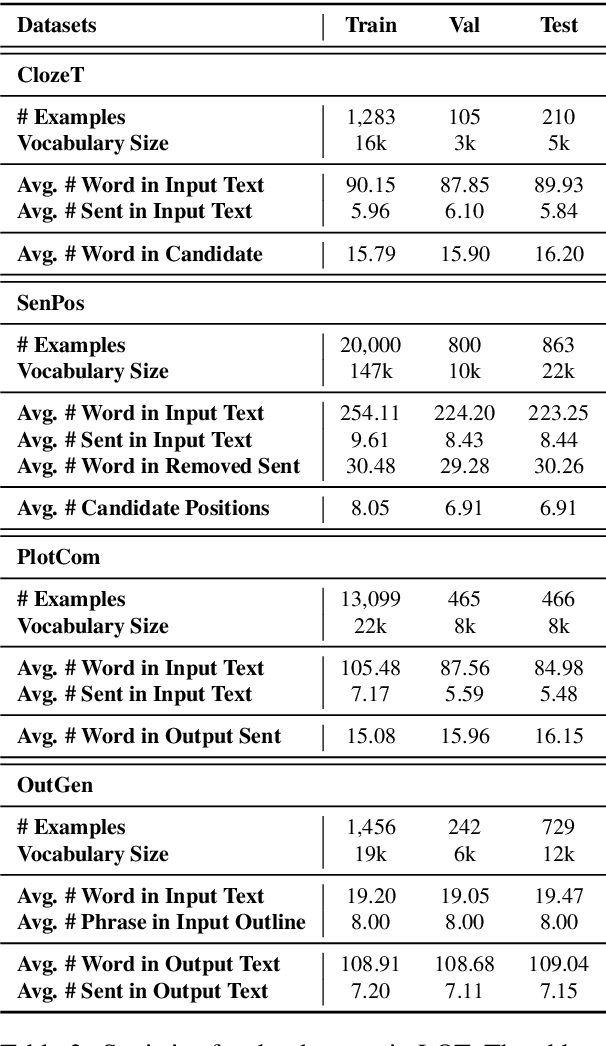
Abstract:Standard multi-task benchmarks are essential for driving the progress of general pretraining models to generalize to various downstream tasks. However, existing benchmarks such as GLUE and GLGE tend to focus on short text understanding and generation tasks, without considering long text modeling, which requires many distinct capabilities such as modeling long-range commonsense and discourse relations, as well as the coherence and controllability of generation. The lack of standardized benchmarks makes it difficult to fully evaluate these capabilities of a model and fairly compare different models, especially Chinese pretraining models. Therefore, we propose LOT, a benchmark including two understanding and two generation tasks for Chinese long text modeling evaluation. We construct the datasets for the tasks based on various kinds of human-written Chinese stories. Besides, we release an encoder-decoder Chinese long text pretraining model named LongLM with up to 1 billion parameters. We pretrain LongLM on 120G Chinese novels with two generative tasks including text infilling and conditional continuation. Extensive experiments on LOT demonstrate that LongLM matches the performance of similar-sized pretraining models on the understanding tasks and outperforms strong baselines substantially on the generation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge