Ruida Zhang
Open-Vocabulary Functional 3D Scene Graphs for Real-World Indoor Spaces
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:We introduce the task of predicting functional 3D scene graphs for real-world indoor environments from posed RGB-D images. Unlike traditional 3D scene graphs that focus on spatial relationships of objects, functional 3D scene graphs capture objects, interactive elements, and their functional relationships. Due to the lack of training data, we leverage foundation models, including visual language models (VLMs) and large language models (LLMs), to encode functional knowledge. We evaluate our approach on an extended SceneFun3D dataset and a newly collected dataset, FunGraph3D, both annotated with functional 3D scene graphs. Our method significantly outperforms adapted baselines, including Open3DSG and ConceptGraph, demonstrating its effectiveness in modeling complex scene functionalities. We also demonstrate downstream applications such as 3D question answering and robotic manipulation using functional 3D scene graphs. See our project page at https://openfungraph.github.io
GIVEPose: Gradual Intra-class Variation Elimination for RGB-based Category-Level Object Pose Estimation
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in RGBD-based category-level object pose estimation have been limited by their reliance on precise depth information, restricting their broader applicability. In response, RGB-based methods have been developed. Among these methods, geometry-guided pose regression that originated from instance-level tasks has demonstrated strong performance. However, we argue that the NOCS map is an inadequate intermediate representation for geometry-guided pose regression method, as its many-to-one correspondence with category-level pose introduces redundant instance-specific information, resulting in suboptimal results. This paper identifies the intra-class variation problem inherent in pose regression based solely on the NOCS map and proposes the Intra-class Variation-Free Consensus (IVFC) map, a novel coordinate representation generated from the category-level consensus model. By leveraging the complementary strengths of the NOCS map and the IVFC map, we introduce GIVEPose, a framework that implements Gradual Intra-class Variation Elimination for category-level object pose estimation. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that GIVEPose significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art RGB-based approaches, achieving substantial improvements in category-level object pose estimation. Our code is available at https://github.com/ziqin-h/GIVEPose.
FA-BARF: Frequency Adapted Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields
Mar 15, 2025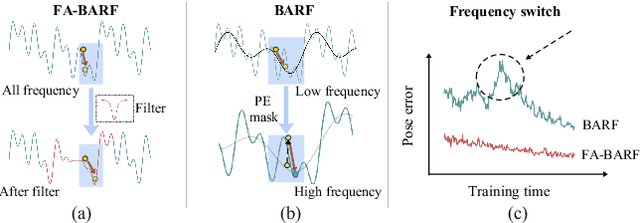
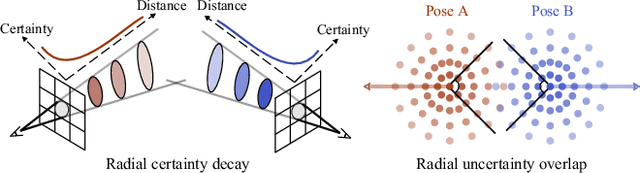
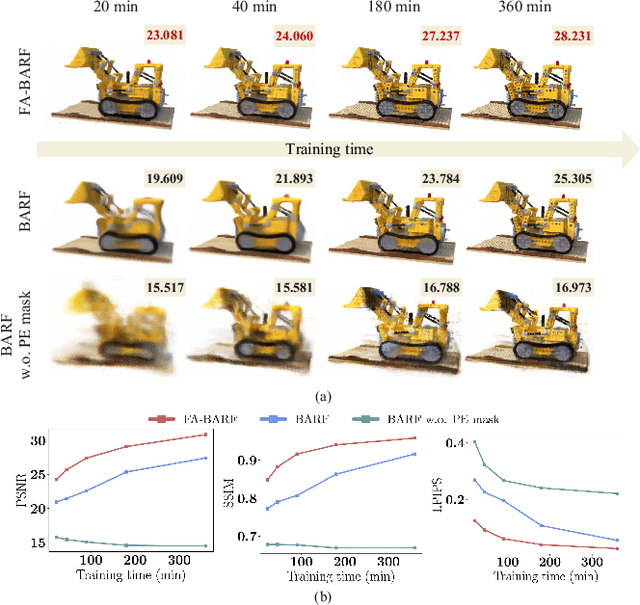
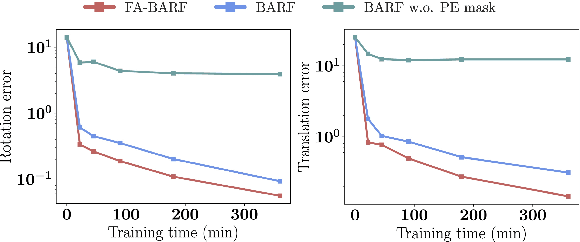
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have exhibited highly effective performance for photorealistic novel view synthesis recently. However, the key limitation it meets is the reliance on a hand-crafted frequency annealing strategy to recover 3D scenes with imperfect camera poses. The strategy exploits a temporal low-pass filter to guarantee convergence while decelerating the joint optimization of implicit scene reconstruction and camera registration. In this work, we introduce the Frequency Adapted Bundle Adjusting Radiance Field (FA-BARF), substituting the temporal low-pass filter for a frequency-adapted spatial low-pass filter to address the decelerating problem. We establish a theoretical framework to interpret the relationship between position encoding of NeRF and camera registration and show that our frequency-adapted filter can mitigate frequency fluctuation caused by the temporal filter. Furthermore, we show that applying a spatial low-pass filter in NeRF can optimize camera poses productively through radial uncertainty overlaps among various views. Extensive experiments show that FA-BARF can accelerate the joint optimization process under little perturbations in object-centric scenes and recover real-world scenes with unknown camera poses. This implies wider possibilities for NeRF applied in dense 3D mapping and reconstruction under real-time requirements. The code will be released upon paper acceptance.
Street Gaussians without 3D Object Tracker
Dec 07, 2024



Abstract:Realistic scene reconstruction in driving scenarios poses significant challenges due to fast-moving objects. Most existing methods rely on labor-intensive manual labeling of object poses to reconstruct dynamic objects in canonical space and move them based on these poses during rendering. While some approaches attempt to use 3D object trackers to replace manual annotations, the limited generalization of 3D trackers -- caused by the scarcity of large-scale 3D datasets -- results in inferior reconstructions in real-world settings. In contrast, 2D foundation models demonstrate strong generalization capabilities. To eliminate the reliance on 3D trackers and enhance robustness across diverse environments, we propose a stable object tracking module by leveraging associations from 2D deep trackers within a 3D object fusion strategy. We address inevitable tracking errors by further introducing a motion learning strategy in an implicit feature space that autonomously corrects trajectory errors and recovers missed detections. Experimental results on Waymo-NOTR datasets show we achieve state-of-the-art performance. Our code will be made publicly available.
UNOPose: Unseen Object Pose Estimation with an Unposed RGB-D Reference Image
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Unseen object pose estimation methods often rely on CAD models or multiple reference views, making the onboarding stage costly. To simplify reference acquisition, we aim to estimate the unseen object's pose through a single unposed RGB-D reference image. While previous works leverage reference images as pose anchors to limit the range of relative pose, our scenario presents significant challenges since the relative transformation could vary across the entire SE(3) space. Moreover, factors like occlusion, sensor noise, and extreme geometry could result in low viewpoint overlap. To address these challenges, we present a novel approach and benchmark, termed UNOPose, for unseen one-reference-based object pose estimation. Building upon a coarse-to-fine paradigm, UNOPose constructs an SE(3)-invariant reference frame to standardize object representation despite pose and size variations. To alleviate small overlap across viewpoints, we recalibrate the weight of each correspondence based on its predicted likelihood of being within the overlapping region. Evaluated on our proposed benchmark based on the BOP Challenge, UNOPose demonstrates superior performance, significantly outperforming traditional and learning-based methods in the one-reference setting and remaining competitive with CAD-model-based methods. The code and dataset will be available.
RaSim: A Range-aware High-fidelity RGB-D Data Simulation Pipeline for Real-world Applications
Apr 05, 2024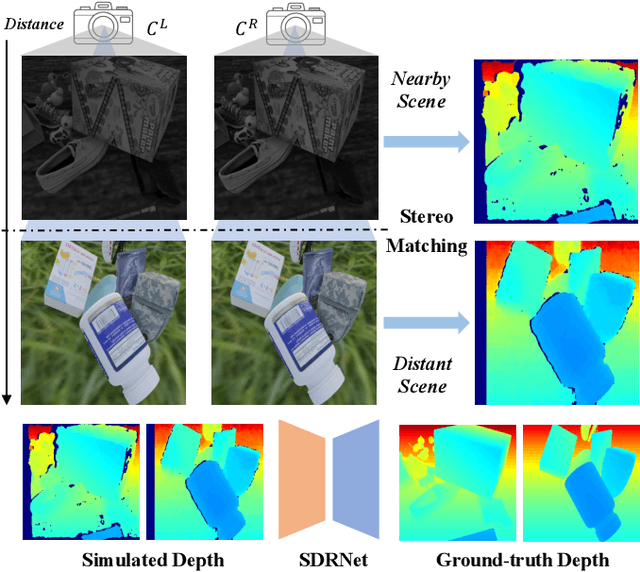
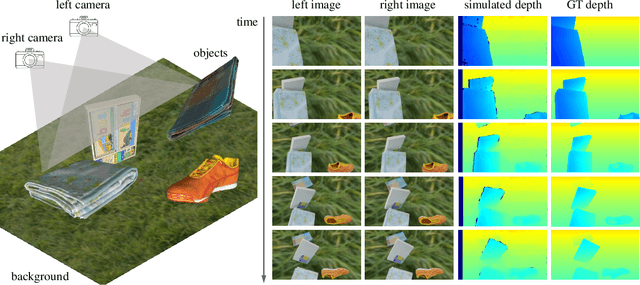
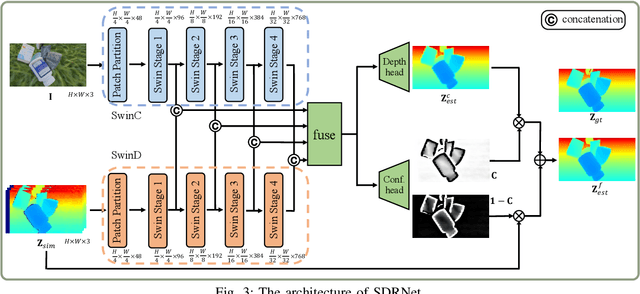
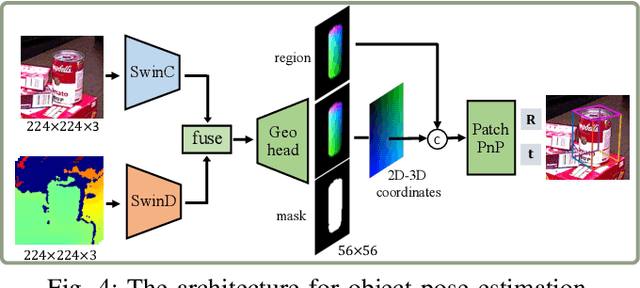
Abstract:In robotic vision, a de-facto paradigm is to learn in simulated environments and then transfer to real-world applications, which poses an essential challenge in bridging the sim-to-real domain gap. While mainstream works tackle this problem in the RGB domain, we focus on depth data synthesis and develop a range-aware RGB-D data simulation pipeline (RaSim). In particular, high-fidelity depth data is generated by imitating the imaging principle of real-world sensors. A range-aware rendering strategy is further introduced to enrich data diversity. Extensive experiments show that models trained with RaSim can be directly applied to real-world scenarios without any finetuning and excel at downstream RGB-D perception tasks.
KP-RED: Exploiting Semantic Keypoints for Joint 3D Shape Retrieval and Deformation
Mar 20, 2024
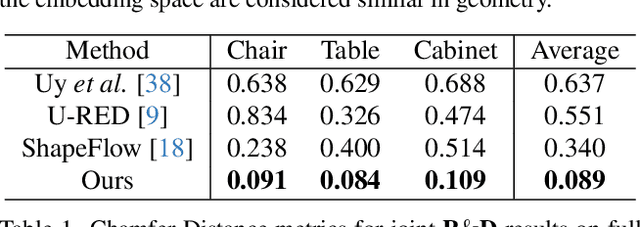


Abstract:In this paper, we present KP-RED, a unified KeyPoint-driven REtrieval and Deformation framework that takes object scans as input and jointly retrieves and deforms the most geometrically similar CAD models from a pre-processed database to tightly match the target. Unlike existing dense matching based methods that typically struggle with noisy partial scans, we propose to leverage category-consistent sparse keypoints to naturally handle both full and partial object scans. Specifically, we first employ a lightweight retrieval module to establish a keypoint-based embedding space, measuring the similarity among objects by dynamically aggregating deformation-aware local-global features around extracted keypoints. Objects that are close in the embedding space are considered similar in geometry. Then we introduce the neural cage-based deformation module that estimates the influence vector of each keypoint upon cage vertices inside its local support region to control the deformation of the retrieved shape. Extensive experiments on the synthetic dataset PartNet and the real-world dataset Scan2CAD demonstrate that KP-RED surpasses existing state-of-the-art approaches by a large margin. Codes and trained models will be released in https://github.com/lolrudy/KP-RED.
SecondPose: SE(3)-Consistent Dual-Stream Feature Fusion for Category-Level Pose Estimation
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation, aiming to predict the 6D pose and 3D size of objects from known categories, typically struggles with large intra-class shape variation. Existing works utilizing mean shapes often fall short of capturing this variation. To address this issue, we present SecondPose, a novel approach integrating object-specific geometric features with semantic category priors from DINOv2. Leveraging the advantage of DINOv2 in providing SE(3)-consistent semantic features, we hierarchically extract two types of SE(3)-invariant geometric features to further encapsulate local-to-global object-specific information. These geometric features are then point-aligned with DINOv2 features to establish a consistent object representation under SE(3) transformations, facilitating the mapping from camera space to the pre-defined canonical space, thus further enhancing pose estimation. Extensive experiments on NOCS-REAL275 demonstrate that SecondPose achieves a 12.4% leap forward over the state-of-the-art. Moreover, on a more complex dataset HouseCat6D which provides photometrically challenging objects, SecondPose still surpasses other competitors by a large margin. The code will be released soon.
ShapeMaker: Self-Supervised Joint Shape Canonicalization, Segmentation, Retrieval and Deformation
Nov 18, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present ShapeMaker, a unified self-supervised learning framework for joint shape canonicalization, segmentation, retrieval and deformation. Given a partially-observed object in an arbitrary pose, we first canonicalize the object by extracting point-wise affine-invariant features, disentangling inherent structure of the object with its pose and size. These learned features are then leveraged to predict semantically consistent part segmentation and corresponding part centers. Next, our lightweight retrieval module aggregates the features within each part as its retrieval token and compare all the tokens with source shapes from a pre-established database to identify the most geometrically similar shape. Finally, we deform the retrieved shape in the deformation module to tightly fit the input object by harnessing part center guided neural cage deformation. The key insight of ShapeMaker is the simultaneous training of the four highly-associated processes: canonicalization, segmentation, retrieval, and deformation, leveraging cross-task consistency losses for mutual supervision. Extensive experiments on synthetic datasets PartNet, ComplementMe, and real-world dataset Scan2CAD demonstrate that ShapeMaker surpasses competitors by a large margin. Codes will be released soon.
MOHO: Learning Single-view Hand-held Object Reconstruction with Multi-view Occlusion-Aware Supervision
Oct 18, 2023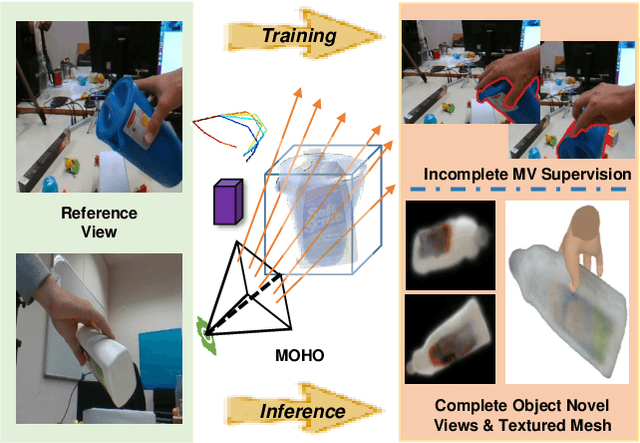
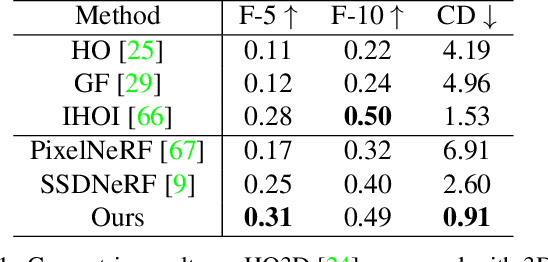
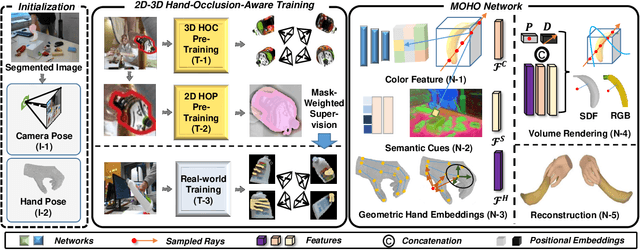
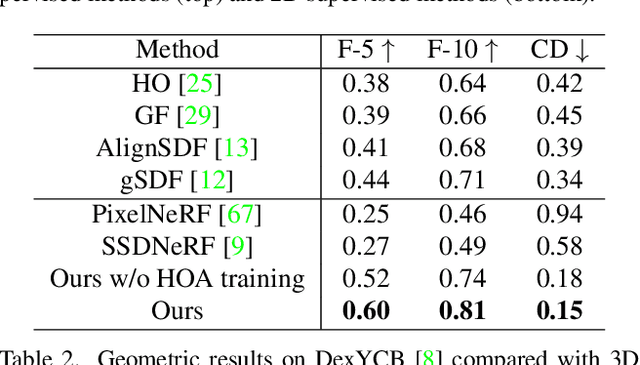
Abstract:Previous works concerning single-view hand-held object reconstruction typically utilize supervision from 3D ground truth models, which are hard to collect in real world. In contrast, abundant videos depicting hand-object interactions can be accessed easily with low cost, although they only give partial object observations with complex occlusion. In this paper, we present MOHO to reconstruct hand-held object from a single image with multi-view supervision from hand-object videos, tackling two predominant challenges including object's self-occlusion and hand-induced occlusion. MOHO inputs semantic features indicating visible object parts and geometric embeddings provided by hand articulations as partial-to-full cues to resist object's self-occlusion, so as to recover full shape of the object. Meanwhile, a novel 2D-3D hand-occlusion-aware training scheme following the synthetic-to-real paradigm is proposed to release hand-induced occlusion. In the synthetic pre-training stage, 2D-3D hand-object correlations are constructed by supervising MOHO with rendered images to complete the hand-concealed regions of the object in both 2D and 3D space. Subsequently, MOHO is finetuned in real world by the mask-weighted volume rendering supervision adopting hand-object correlations obtained during pre-training. Extensive experiments on HO3D and DexYCB datasets demonstrate that 2D-supervised MOHO gains superior results against 3D-supervised methods by a large margin. Codes and key assets will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge