Xiaoxi Mao
DecBERT: Enhancing the Language Understanding of BERT with Causal Attention Masks
Apr 19, 2022



Abstract:Since 2017, the Transformer-based models play critical roles in various downstream Natural Language Processing tasks. However, a common limitation of the attention mechanism utilized in Transformer Encoder is that it cannot automatically capture the information of word order, so explicit position embeddings are generally required to be fed into the target model. In contrast, Transformer Decoder with the causal attention masks is naturally sensitive to the word order. In this work, we focus on improving the position encoding ability of BERT with the causal attention masks. Furthermore, we propose a new pre-trained language model DecBERT and evaluate it on the GLUE benchmark. Experimental results show that (1) the causal attention mask is effective for BERT on the language understanding tasks; (2) our DecBERT model without position embeddings achieve comparable performance on the GLUE benchmark; and (3) our modification accelerates the pre-training process and DecBERT w/ PE achieves better overall performance than the baseline systems when pre-training with the same amount of computational resources.
Dialog Intent Induction via Density-based Deep Clustering Ensemble
Jan 18, 2022



Abstract:Existing task-oriented chatbots heavily rely on spoken language understanding (SLU) systems to determine a user's utterance's intent and other key information for fulfilling specific tasks. In real-life applications, it is crucial to occasionally induce novel dialog intents from the conversation logs to improve the user experience. In this paper, we propose the Density-based Deep Clustering Ensemble (DDCE) method for dialog intent induction. Compared to existing K-means based methods, our proposed method is more effective in dealing with real-life scenarios where a large number of outliers exist. To maximize data utilization, we jointly optimize texts' representations and the hyperparameters of the clustering algorithm. In addition, we design an outlier-aware clustering ensemble framework to handle the overfitting issue. Experimental results over seven datasets show that our proposed method significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art baselines.
Youling: an AI-Assisted Lyrics Creation System
Jan 18, 2022



Abstract:Recently, a variety of neural models have been proposed for lyrics generation. However, most previous work completes the generation process in a single pass with little human intervention. We believe that lyrics creation is a creative process with human intelligence centered. AI should play a role as an assistant in the lyrics creation process, where human interactions are crucial for high-quality creation. This paper demonstrates \textit{Youling}, an AI-assisted lyrics creation system, designed to collaborate with music creators. In the lyrics generation process, \textit{Youling} supports traditional one pass full-text generation mode as well as an interactive generation mode, which allows users to select the satisfactory sentences from generated candidates conditioned on preceding context. The system also provides a revision module which enables users to revise undesired sentences or words of lyrics repeatedly. Besides, \textit{Youling} allows users to use multifaceted attributes to control the content and format of generated lyrics. The demo video of the system is available at https://youtu.be/DFeNpHk0pm4.
Taming Repetition in Dialogue Generation
Dec 16, 2021



Abstract:The wave of pre-training language models has been continuously improving the quality of the machine-generated conversations, however, some of the generated responses still suffer from excessive repetition, sometimes repeating words from utterance, sometimes repeating words within self-generated responses, or both. Inappropriate repetition of words can significantly degrade the quality of the generated texts. Penalized sampling is one popular solution, reducing the sampling probability of existing words during inference, however, it is highly vulnerable to the inappropriate setting of the static weight. Setting it too high can yield strange and unrealistic sentences while setting it too low makes the task of suppressing repetition trivial. To remedy the shortcomings of the above methods, we design a context-aware classifier to explicitly decide when to allow repetition and when to employ penalized sampling. Such a classifier can be easily integrated with existing decoding methods, reducing repetitions where appropriate while preserving the diversity of the text. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can generate higher quality and more authentic dialogues.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Adapter
Nov 01, 2021



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) with pre-trained language models (PrLM) has achieved promising results since these pre-trained models embed generic knowledge learned from various domains. However, fine-tuning all the parameters of the PrLM on a small domain-specific corpus distort the learned generic knowledge, and it is also expensive to deployment a whole fine-tuned PrLM for each domain. This paper explores an adapter-based fine-tuning approach for unsupervised domain adaptation. Specifically, several trainable adapter modules are inserted in a PrLM, and the embedded generic knowledge is preserved by fixing the parameters of the original PrLM at fine-tuning. A domain-fusion scheme is introduced to train these adapters using a mix-domain corpus to better capture transferable features. Elaborated experiments on two benchmark datasets are carried out, and the results demonstrate that our approach is effective with different tasks, dataset sizes, and domain similarities.
Transferable Persona-Grounded Dialogues via Grounded Minimal Edits
Sep 16, 2021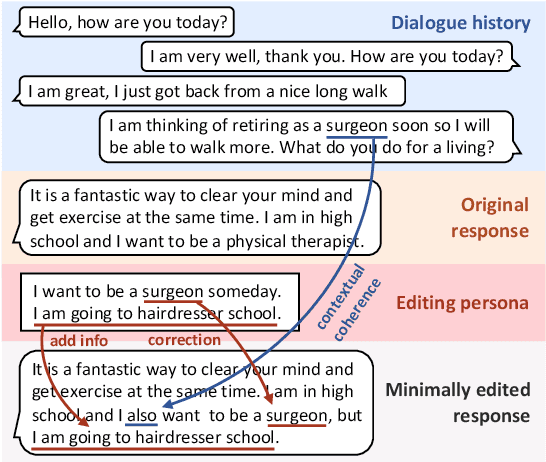

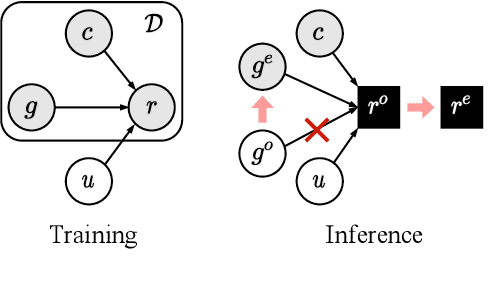

Abstract:Grounded dialogue models generate responses that are grounded on certain concepts. Limited by the distribution of grounded dialogue data, models trained on such data face the transferability challenges in terms of the data distribution and the type of grounded concepts. To address the challenges, we propose the grounded minimal editing framework, which minimally edits existing responses to be grounded on the given concept. Focusing on personas, we propose Grounded Minimal Editor (GME), which learns to edit by disentangling and recombining persona-related and persona-agnostic parts of the response. To evaluate persona-grounded minimal editing, we present the PersonaMinEdit dataset, and experimental results show that GME outperforms competitive baselines by a large margin. To evaluate the transferability, we experiment on the test set of BlendedSkillTalk and show that GME can edit dialogue models' responses to largely improve their persona consistency while preserving the use of knowledge and empathy.
LOT: A Benchmark for Evaluating Chinese Long Text Understanding and Generation
Aug 30, 2021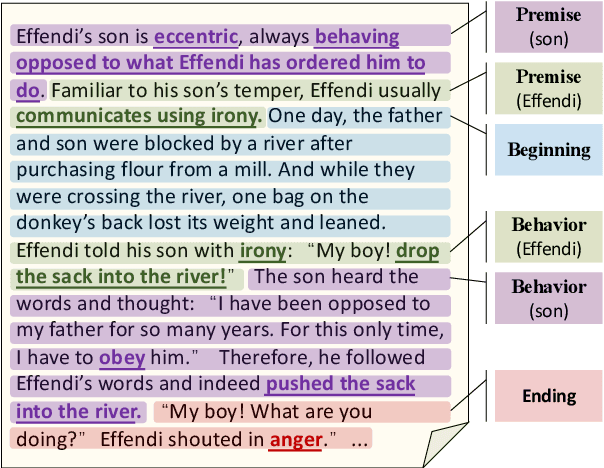
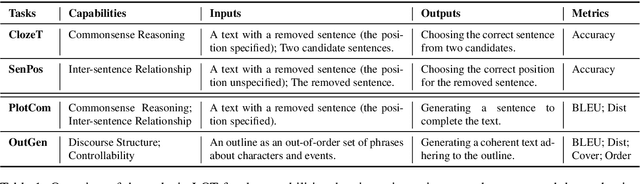
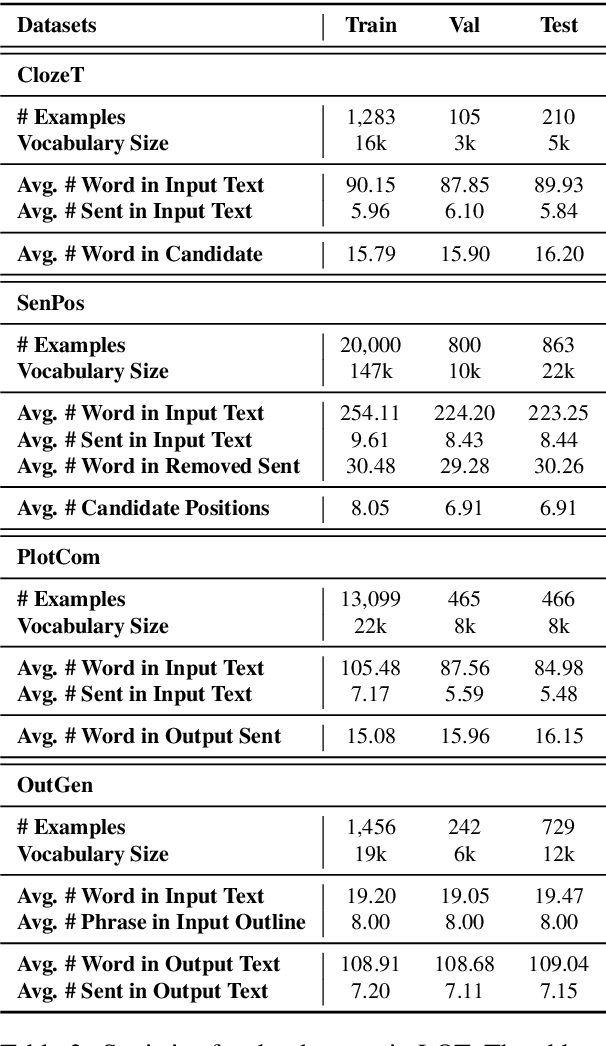
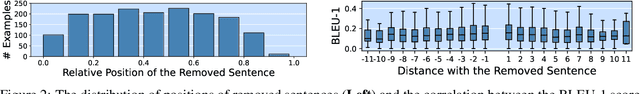
Abstract:Standard multi-task benchmarks are essential for driving the progress of general pretraining models to generalize to various downstream tasks. However, existing benchmarks such as GLUE and GLGE tend to focus on short text understanding and generation tasks, without considering long text modeling, which requires many distinct capabilities such as modeling long-range commonsense and discourse relations, as well as the coherence and controllability of generation. The lack of standardized benchmarks makes it difficult to fully evaluate these capabilities of a model and fairly compare different models, especially Chinese pretraining models. Therefore, we propose LOT, a benchmark including two understanding and two generation tasks for Chinese long text modeling evaluation. We construct the datasets for the tasks based on various kinds of human-written Chinese stories. Besides, we release an encoder-decoder Chinese long text pretraining model named LongLM with up to 1 billion parameters. We pretrain LongLM on 120G Chinese novels with two generative tasks including text infilling and conditional continuation. Extensive experiments on LOT demonstrate that LongLM matches the performance of similar-sized pretraining models on the understanding tasks and outperforms strong baselines substantially on the generation tasks.
Long Text Generation by Modeling Sentence-Level and Discourse-Level Coherence
May 19, 2021



Abstract:Generating long and coherent text is an important but challenging task, particularly for open-ended language generation tasks such as story generation. Despite the success in modeling intra-sentence coherence, existing generation models (e.g., BART) still struggle to maintain a coherent event sequence throughout the generated text. We conjecture that this is because of the difficulty for the decoder to capture the high-level semantics and discourse structures in the context beyond token-level co-occurrence. In this paper, we propose a long text generation model, which can represent the prefix sentences at sentence level and discourse level in the decoding process. To this end, we propose two pretraining objectives to learn the representations by predicting inter-sentence semantic similarity and distinguishing between normal and shuffled sentence orders. Extensive experiments show that our model can generate more coherent texts than state-of-the-art baselines.
OpenMEVA: A Benchmark for Evaluating Open-ended Story Generation Metrics
May 19, 2021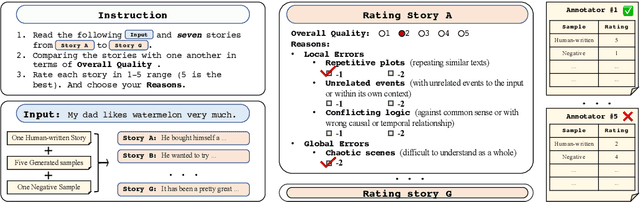
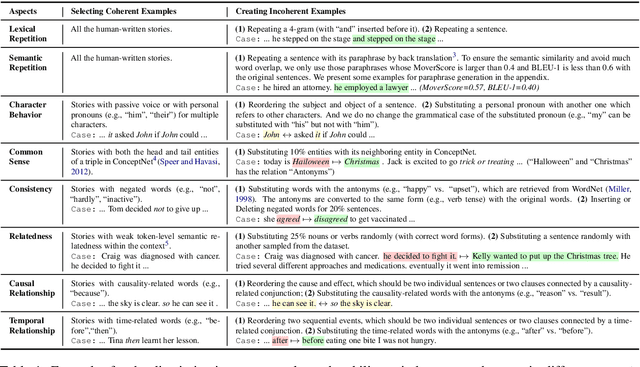
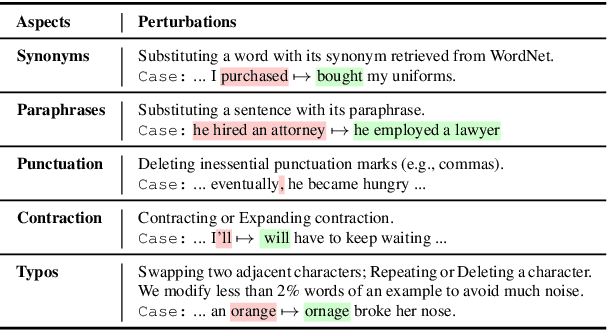
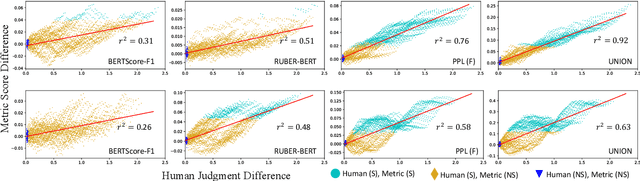
Abstract:Automatic metrics are essential for developing natural language generation (NLG) models, particularly for open-ended language generation tasks such as story generation. However, existing automatic metrics are observed to correlate poorly with human evaluation. The lack of standardized benchmark datasets makes it difficult to fully evaluate the capabilities of a metric and fairly compare different metrics. Therefore, we propose OpenMEVA, a benchmark for evaluating open-ended story generation metrics. OpenMEVA provides a comprehensive test suite to assess the capabilities of metrics, including (a) the correlation with human judgments, (b) the generalization to different model outputs and datasets, (c) the ability to judge story coherence, and (d) the robustness to perturbations. To this end, OpenMEVA includes both manually annotated stories and auto-constructed test examples. We evaluate existing metrics on OpenMEVA and observe that they have poor correlation with human judgments, fail to recognize discourse-level incoherence, and lack inferential knowledge (e.g., causal order between events), the generalization ability and robustness. Our study presents insights for developing NLG models and metrics in further research.
Easy and Efficient Transformer : Scalable Inference Solution For large NLP mode
Apr 26, 2021



Abstract:The ultra-large-scale pre-training model can effectively improve the effect of a variety of tasks, and it also brings a heavy computational burden to inference. This paper introduces a series of ultra-large-scale pre-training model optimization methods that combine algorithm characteristics and GPU processor hardware characteristics, and on this basis, propose an inference engine -- Easy and Efficient Transformer (EET), Which has a significant performance improvement over the existing schemes. We firstly introduce a pre-padding decoding mechanism that improves token parallelism for generation tasks. Then we design high optimized kernels to remove sequence masks and achieve cost-free calculation for padding tokens, as well as support long sequence and long embedding sizes. Thirdly a user-friendly inference system with an easy service pipeline was introduced which greatly reduces the difficulty of engineering deployment with high throughput. Compared to Faster Transformer's implementation for GPT-2 on A100, EET achieves a 1.5-15x state-of-art speedup varying with context length.EET is available https://github.com/NetEase-FuXi/EET.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge