Chen Henry Wu
OpenCUA: Open Foundations for Computer-Use Agents
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities as computer-use agents (CUAs) capable of automating diverse computer tasks. As their commercial potential grows, critical details of the most capable CUA systems remain closed. As these agents will increasingly mediate digital interactions and execute consequential decisions on our behalf, the research community needs access to open CUA frameworks to study their capabilities, limitations, and risks. To bridge this gap, we propose OpenCUA, a comprehensive open-source framework for scaling CUA data and foundation models. Our framework consists of: (1) an annotation infrastructure that seamlessly captures human computer-use demonstrations; (2) AgentNet, the first large-scale computer-use task dataset spanning 3 operating systems and 200+ applications and websites; (3) a scalable pipeline that transforms demonstrations into state-action pairs with reflective long Chain-of-Thought reasoning that sustain robust performance gains as data scales. Our end-to-end agent models demonstrate strong performance across CUA benchmarks. In particular, OpenCUA-32B achieves an average success rate of 34.8% on OSWorld-Verified, establishing a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) among open-source models and surpassing OpenAI CUA (GPT-4o). Further analysis confirms that our approach generalizes well across domains and benefits significantly from increased test-time computation. We release our annotation tool, datasets, code, and models to build open foundations for further CUA research.
Roll the dice & look before you leap: Going beyond the creative limits of next-token prediction
Apr 21, 2025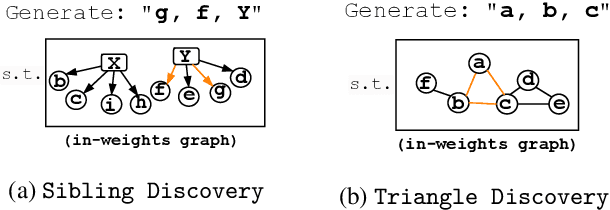
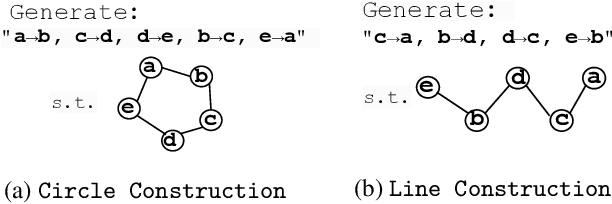
Abstract:We design a suite of minimal algorithmic tasks that are a loose abstraction of open-ended real-world tasks. This allows us to cleanly and controllably quantify the creative limits of the present-day language model. Much like real-world tasks that require a creative, far-sighted leap of thought, our tasks require an implicit, open-ended stochastic planning step that either (a) discovers new connections in an abstract knowledge graph (like in wordplay, drawing analogies, or research) or (b) constructs new patterns (like in designing math problems or new proteins). In these tasks, we empirically and conceptually argue how next-token learning is myopic and memorizes excessively; comparatively, multi-token approaches, namely teacherless training and diffusion models, excel in producing diverse and original output. Secondly, in our tasks, we find that to elicit randomness from the Transformer without hurting coherence, it is better to inject noise right at the input layer (via a method we dub hash-conditioning) rather than defer to temperature sampling from the output layer. Thus, our work offers a principled, minimal test-bed for analyzing open-ended creative skills, and offers new arguments for going beyond next-token learning and softmax-based sampling. We make part of the code available under https://github.com/chenwu98/algorithmic-creativity
Adversarial Attacks on Multimodal Agents
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Vision-enabled language models (VLMs) are now used to build autonomous multimodal agents capable of taking actions in real environments. In this paper, we show that multimodal agents raise new safety risks, even though attacking agents is more challenging than prior attacks due to limited access to and knowledge about the environment. Our attacks use adversarial text strings to guide gradient-based perturbation over one trigger image in the environment: (1) our captioner attack attacks white-box captioners if they are used to process images into captions as additional inputs to the VLM; (2) our CLIP attack attacks a set of CLIP models jointly, which can transfer to proprietary VLMs. To evaluate the attacks, we curated VisualWebArena-Adv, a set of adversarial tasks based on VisualWebArena, an environment for web-based multimodal agent tasks. Within an L-infinity norm of $16/256$ on a single image, the captioner attack can make a captioner-augmented GPT-4V agent execute the adversarial goals with a 75% success rate. When we remove the captioner or use GPT-4V to generate its own captions, the CLIP attack can achieve success rates of 21% and 43%, respectively. Experiments on agents based on other VLMs, such as Gemini-1.5, Claude-3, and GPT-4o, show interesting differences in their robustness. Further analysis reveals several key factors contributing to the attack's success, and we also discuss the implications for defenses as well. Project page: https://chenwu.io/attack-agent Code and data: https://github.com/ChenWu98/agent-attack
Personalized Face Inpainting with Diffusion Models by Parallel Visual Attention
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:Face inpainting is important in various applications, such as photo restoration, image editing, and virtual reality. Despite the significant advances in face generative models, ensuring that a person's unique facial identity is maintained during the inpainting process is still an elusive goal. Current state-of-the-art techniques, exemplified by MyStyle, necessitate resource-intensive fine-tuning and a substantial number of images for each new identity. Furthermore, existing methods often fall short in accommodating user-specified semantic attributes, such as beard or expression. To improve inpainting results, and reduce the computational complexity during inference, this paper proposes the use of Parallel Visual Attention (PVA) in conjunction with diffusion models. Specifically, we insert parallel attention matrices to each cross-attention module in the denoising network, which attends to features extracted from reference images by an identity encoder. We train the added attention modules and identity encoder on CelebAHQ-IDI, a dataset proposed for identity-preserving face inpainting. Experiments demonstrate that PVA attains unparalleled identity resemblance in both face inpainting and face inpainting with language guidance tasks, in comparison to various benchmarks, including MyStyle, Paint by Example, and Custom Diffusion. Our findings reveal that PVA ensures good identity preservation while offering effective language-controllability. Additionally, in contrast to Custom Diffusion, PVA requires just 40 fine-tuning steps for each new identity, which translates to a significant speed increase of over 20 times.
Text2Reward: Automated Dense Reward Function Generation for Reinforcement Learning
Sep 21, 2023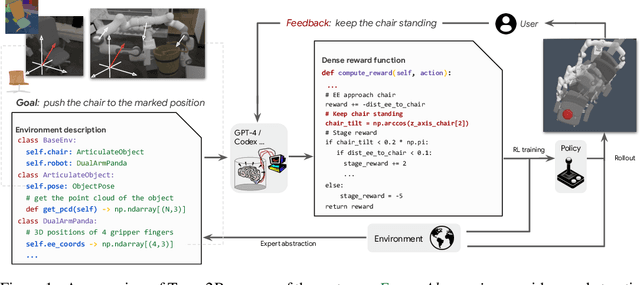
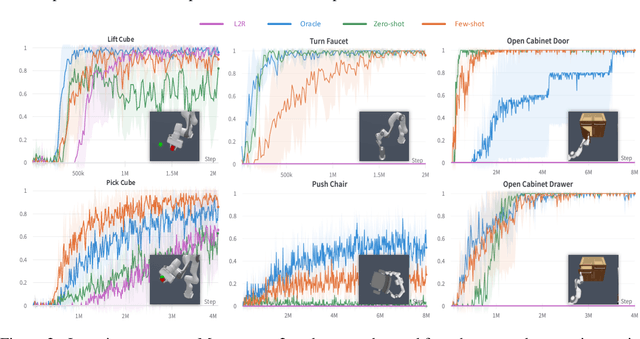
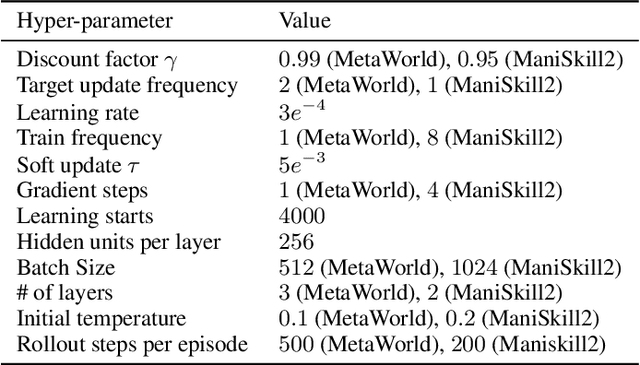
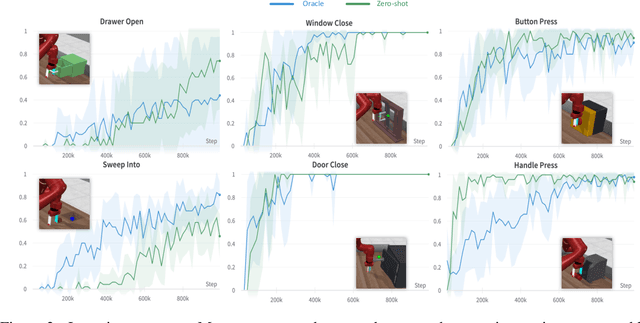
Abstract:Designing reward functions is a longstanding challenge in reinforcement learning (RL); it requires specialized knowledge or domain data, leading to high costs for development. To address this, we introduce Text2Reward, a data-free framework that automates the generation of dense reward functions based on large language models (LLMs). Given a goal described in natural language, Text2Reward generates dense reward functions as an executable program grounded in a compact representation of the environment. Unlike inverse RL and recent work that uses LLMs to write sparse reward codes, Text2Reward produces interpretable, free-form dense reward codes that cover a wide range of tasks, utilize existing packages, and allow iterative refinement with human feedback. We evaluate Text2Reward on two robotic manipulation benchmarks (ManiSkill2, MetaWorld) and two locomotion environments of MuJoCo. On 13 of the 17 manipulation tasks, policies trained with generated reward codes achieve similar or better task success rates and convergence speed than expert-written reward codes. For locomotion tasks, our method learns six novel locomotion behaviors with a success rate exceeding 94%. Furthermore, we show that the policies trained in the simulator with our method can be deployed in the real world. Finally, Text2Reward further improves the policies by refining their reward functions with human feedback. Video results are available at https://text-to-reward.github.io
ITI-GEN: Inclusive Text-to-Image Generation
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:Text-to-image generative models often reflect the biases of the training data, leading to unequal representations of underrepresented groups. This study investigates inclusive text-to-image generative models that generate images based on human-written prompts and ensure the resulting images are uniformly distributed across attributes of interest. Unfortunately, directly expressing the desired attributes in the prompt often leads to sub-optimal results due to linguistic ambiguity or model misrepresentation. Hence, this paper proposes a drastically different approach that adheres to the maxim that "a picture is worth a thousand words". We show that, for some attributes, images can represent concepts more expressively than text. For instance, categories of skin tones are typically hard to specify by text but can be easily represented by example images. Building upon these insights, we propose a novel approach, ITI-GEN, that leverages readily available reference images for Inclusive Text-to-Image GENeration. The key idea is learning a set of prompt embeddings to generate images that can effectively represent all desired attribute categories. More importantly, ITI-GEN requires no model fine-tuning, making it computationally efficient to augment existing text-to-image models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ITI-GEN largely improves over state-of-the-art models to generate inclusive images from a prompt. Project page: https://czhang0528.github.io/iti-gen.
PATMAT: Person Aware Tuning of Mask-Aware Transformer for Face Inpainting
Apr 12, 2023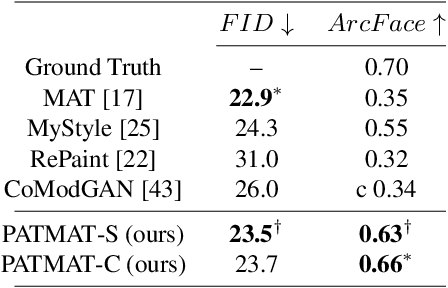
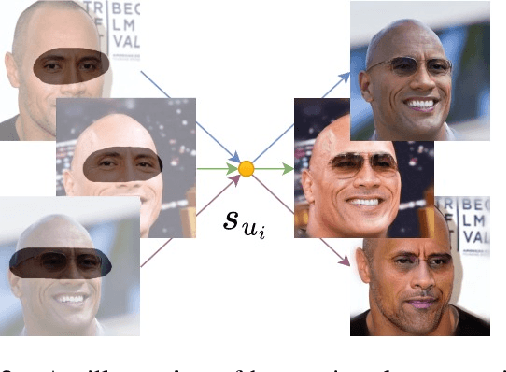

Abstract:Generative models such as StyleGAN2 and Stable Diffusion have achieved state-of-the-art performance in computer vision tasks such as image synthesis, inpainting, and de-noising. However, current generative models for face inpainting often fail to preserve fine facial details and the identity of the person, despite creating aesthetically convincing image structures and textures. In this work, we propose Person Aware Tuning (PAT) of Mask-Aware Transformer (MAT) for face inpainting, which addresses this issue. Our proposed method, PATMAT, effectively preserves identity by incorporating reference images of a subject and fine-tuning a MAT architecture trained on faces. By using ~40 reference images, PATMAT creates anchor points in MAT's style module, and tunes the model using the fixed anchors to adapt the model to a new face identity. Moreover, PATMAT's use of multiple images per anchor during training allows the model to use fewer reference images than competing methods. We demonstrate that PATMAT outperforms state-of-the-art models in terms of image quality, the preservation of person-specific details, and the identity of the subject. Our results suggest that PATMAT can be a promising approach for improving the quality of personalized face inpainting.
Zero-shot Model Diagnosis
Mar 27, 2023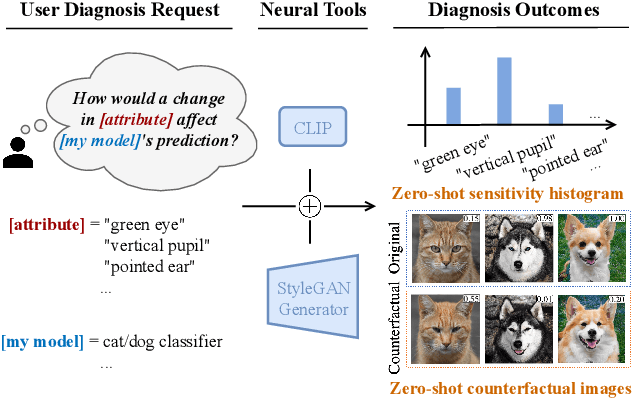
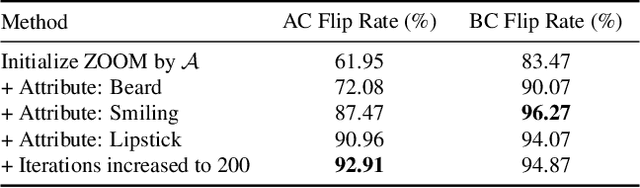
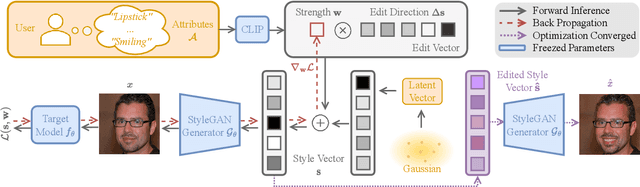
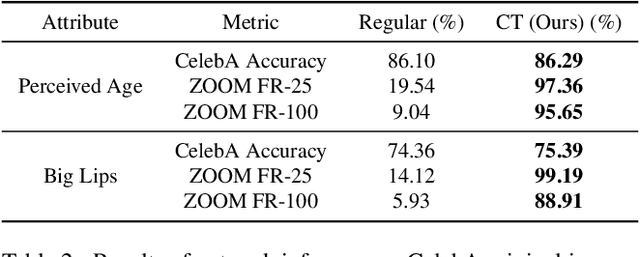
Abstract:When it comes to deploying deep vision models, the behavior of these systems must be explicable to ensure confidence in their reliability and fairness. A common approach to evaluate deep learning models is to build a labeled test set with attributes of interest and assess how well it performs. However, creating a balanced test set (i.e., one that is uniformly sampled over all the important traits) is often time-consuming, expensive, and prone to mistakes. The question we try to address is: can we evaluate the sensitivity of deep learning models to arbitrary visual attributes without an annotated test set? This paper argues the case that Zero-shot Model Diagnosis (ZOOM) is possible without the need for a test set nor labeling. To avoid the need for test sets, our system relies on a generative model and CLIP. The key idea is enabling the user to select a set of prompts (relevant to the problem) and our system will automatically search for semantic counterfactual images (i.e., synthesized images that flip the prediction in the case of a binary classifier) using the generative model. We evaluate several visual tasks (classification, key-point detection, and segmentation) in multiple visual domains to demonstrate the viability of our methodology. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method is capable of producing counterfactual images and offering sensitivity analysis for model diagnosis without the need for a test set.
Semantic Image Attack for Visual Model Diagnosis
Mar 23, 2023



Abstract:In practice, metric analysis on a specific train and test dataset does not guarantee reliable or fair ML models. This is partially due to the fact that obtaining a balanced, diverse, and perfectly labeled dataset is typically expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone. Rather than relying on a carefully designed test set to assess ML models' failures, fairness, or robustness, this paper proposes Semantic Image Attack (SIA), a method based on the adversarial attack that provides semantic adversarial images to allow model diagnosis, interpretability, and robustness. Traditional adversarial training is a popular methodology for robustifying ML models against attacks. However, existing adversarial methods do not combine the two aspects that enable the interpretation and analysis of the model's flaws: semantic traceability and perceptual quality. SIA combines the two features via iterative gradient ascent on a predefined semantic attribute space and the image space. We illustrate the validity of our approach in three scenarios for keypoint detection and classification. (1) Model diagnosis: SIA generates a histogram of attributes that highlights the semantic vulnerability of the ML model (i.e., attributes that make the model fail). (2) Stronger attacks: SIA generates adversarial examples with visually interpretable attributes that lead to higher attack success rates than baseline methods. The adversarial training on SIA improves the transferable robustness across different gradient-based attacks. (3) Robustness to imbalanced datasets: we use SIA to augment the underrepresented classes, which outperforms strong augmentation and re-balancing baselines.
Unifying Diffusion Models' Latent Space, with Applications to CycleDiffusion and Guidance
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved unprecedented performance in generative modeling. The commonly-adopted formulation of the latent code of diffusion models is a sequence of gradually denoised samples, as opposed to the simpler (e.g., Gaussian) latent space of GANs, VAEs, and normalizing flows. This paper provides an alternative, Gaussian formulation of the latent space of various diffusion models, as well as an invertible DPM-Encoder that maps images into the latent space. While our formulation is purely based on the definition of diffusion models, we demonstrate several intriguing consequences. (1) Empirically, we observe that a common latent space emerges from two diffusion models trained independently on related domains. In light of this finding, we propose CycleDiffusion, which uses DPM-Encoder for unpaired image-to-image translation. Furthermore, applying CycleDiffusion to text-to-image diffusion models, we show that large-scale text-to-image diffusion models can be used as zero-shot image-to-image editors. (2) One can guide pre-trained diffusion models and GANs by controlling the latent codes in a unified, plug-and-play formulation based on energy-based models. Using the CLIP model and a face recognition model as guidance, we demonstrate that diffusion models have better coverage of low-density sub-populations and individuals than GANs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge